This document discusses developing pricing strategies and programs. It covers understanding pricing, setting prices, adapting prices, and initiating and responding to price changes. Some key points include:
- Pricing must be consistent with a firm's marketing strategy and target markets. Price is determined by costs, demand, competitors, and consumer psychology.
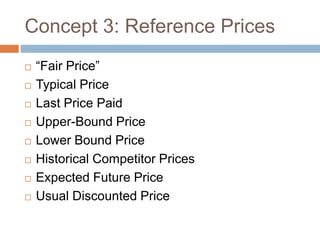
- Technologies like the internet have increased price transparency and consumer power. Consumers actively process various price information and signals.
- Firms estimate costs, demand, and analyze competitors to determine an appropriate pricing method and final price. Methods include markup, target return, and value-based pricing.
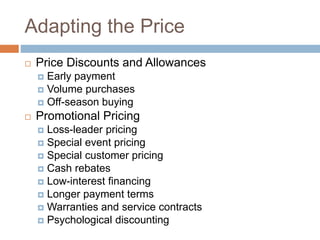
- Prices must be adapted based on location, time of year, product life cycle stage,