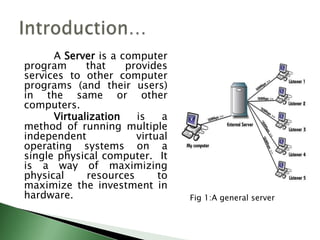
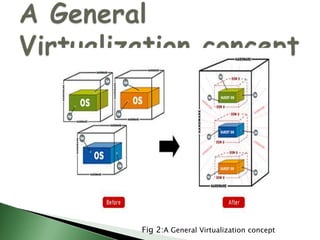
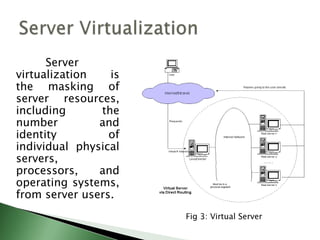
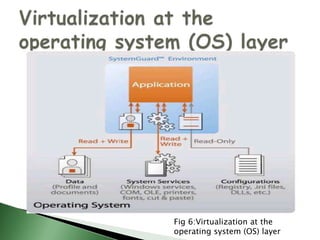
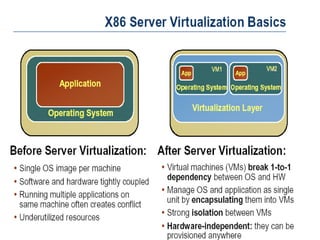
Server virtualization allows multiple virtual servers to run on a single physical server by dividing the physical resources of the server. There are three main approaches to server virtualization: virtual machine models use a hypervisor to run virtual machines; paravirtual machine models modify the guest OS code; and operating system-level virtualization exports OS functionality without a hypervisor. Server virtualization provides benefits like reduced costs, improved resource utilization, increased availability, and easier disaster recovery. The future of virtualization involves the continued evolution of operating systems to support new forms of multitenancy.