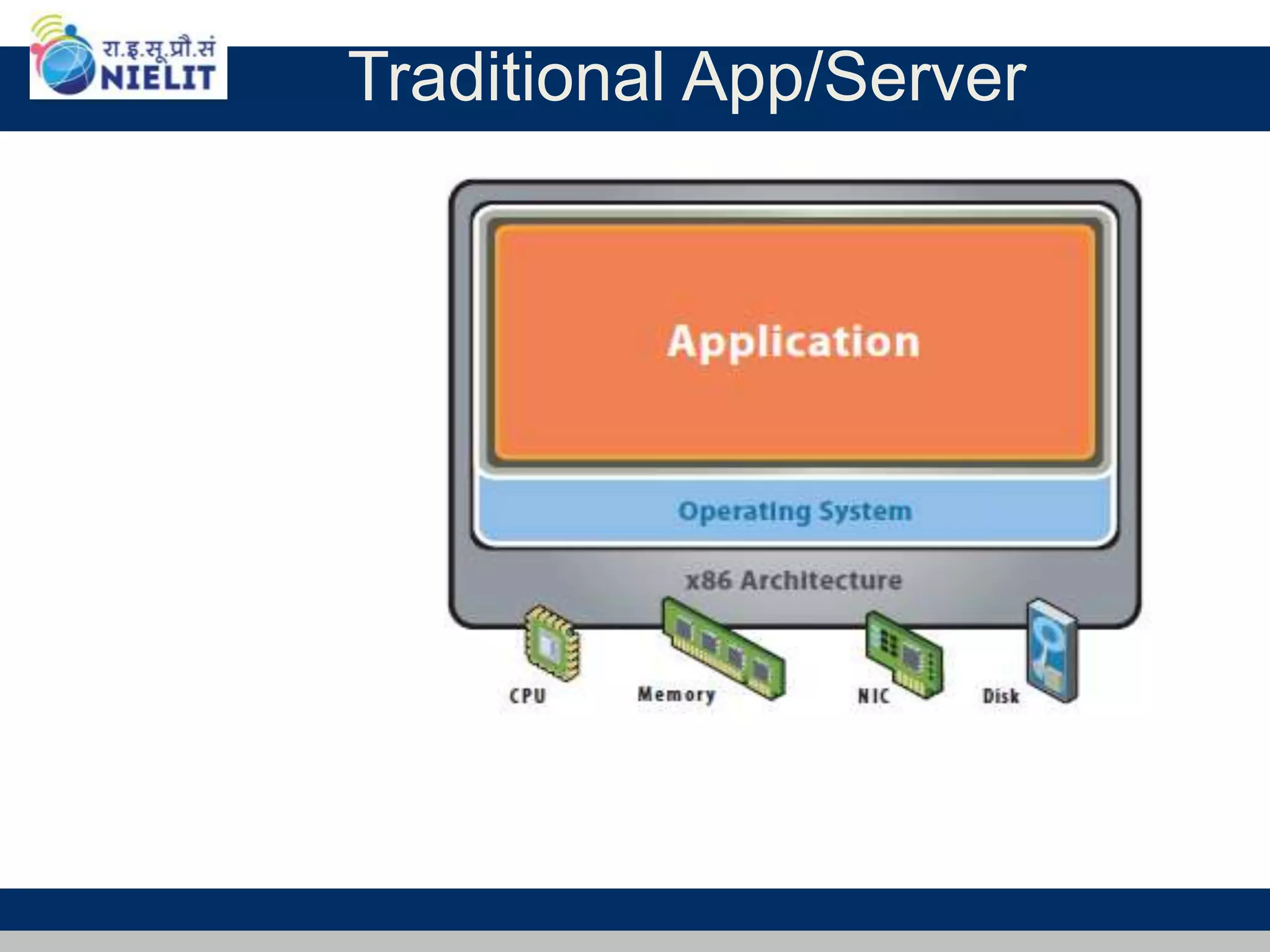
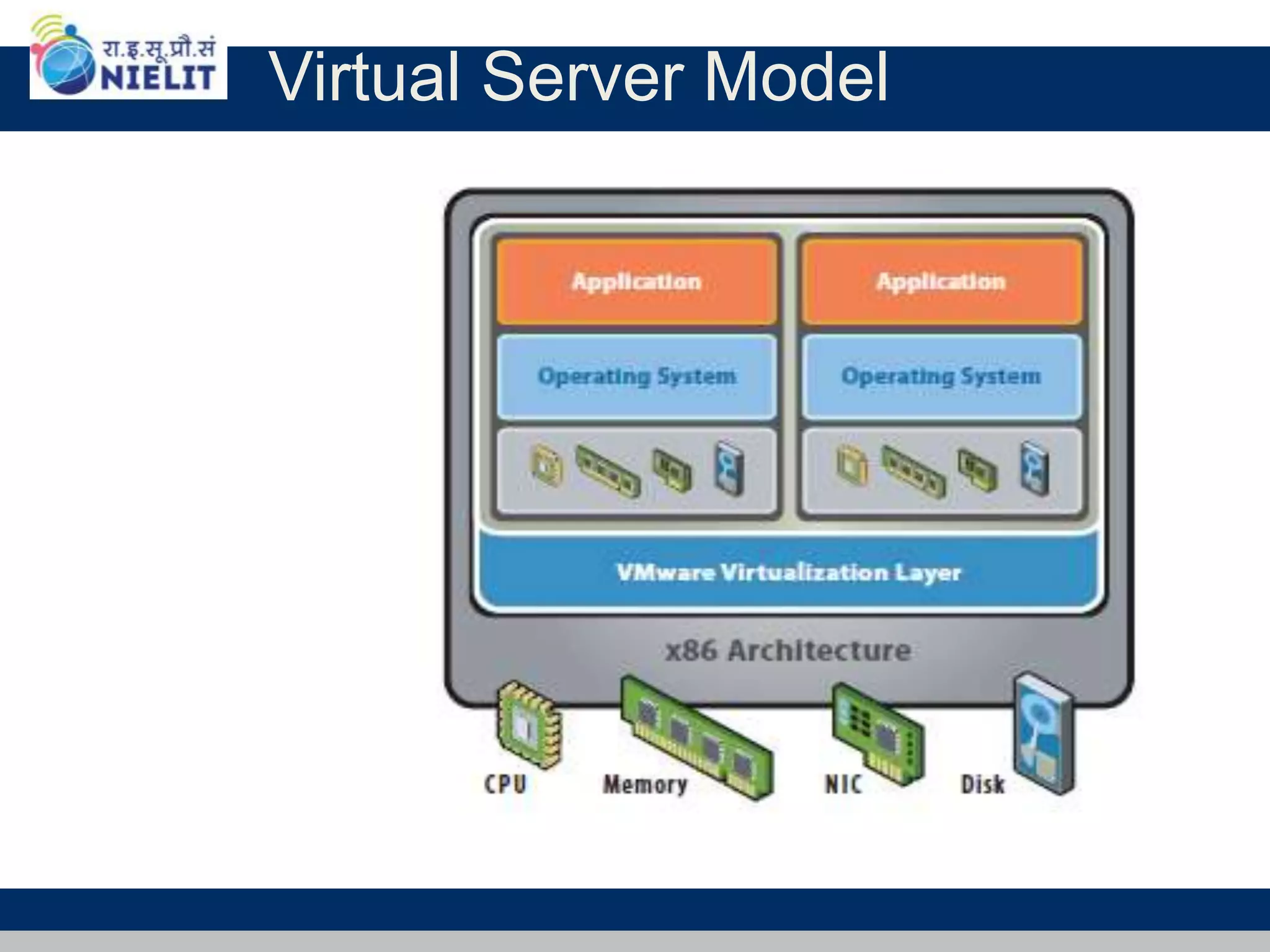
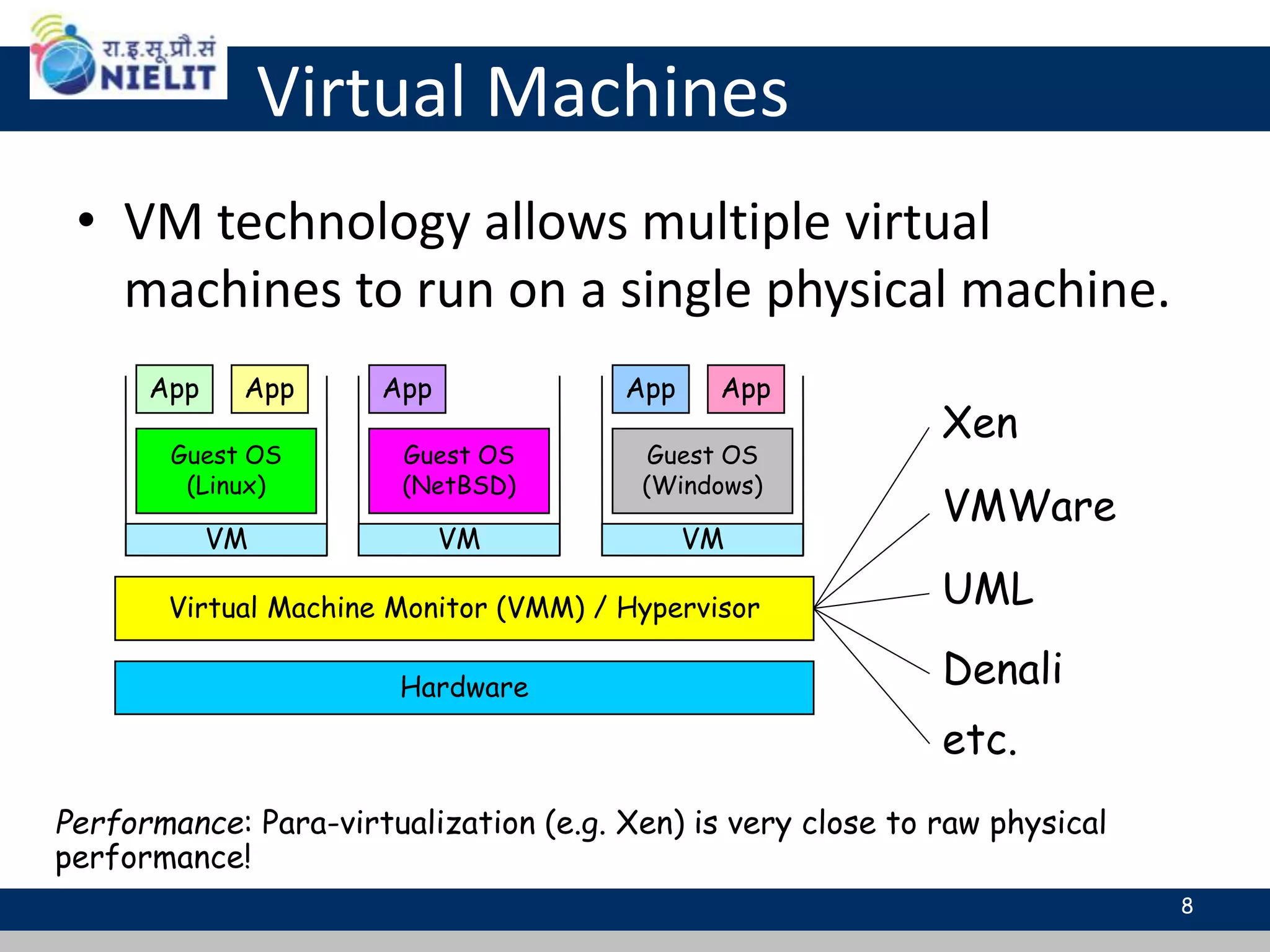
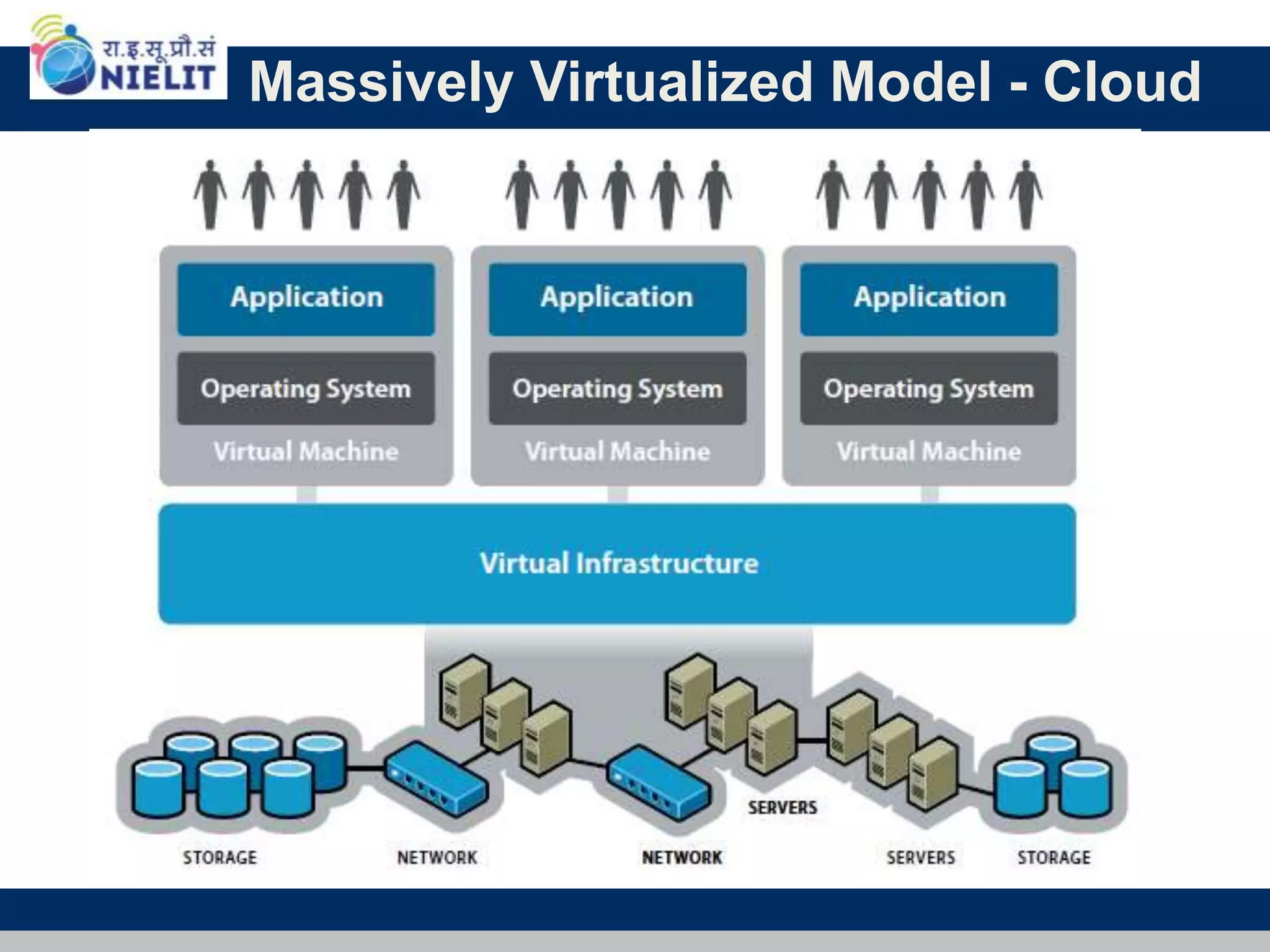
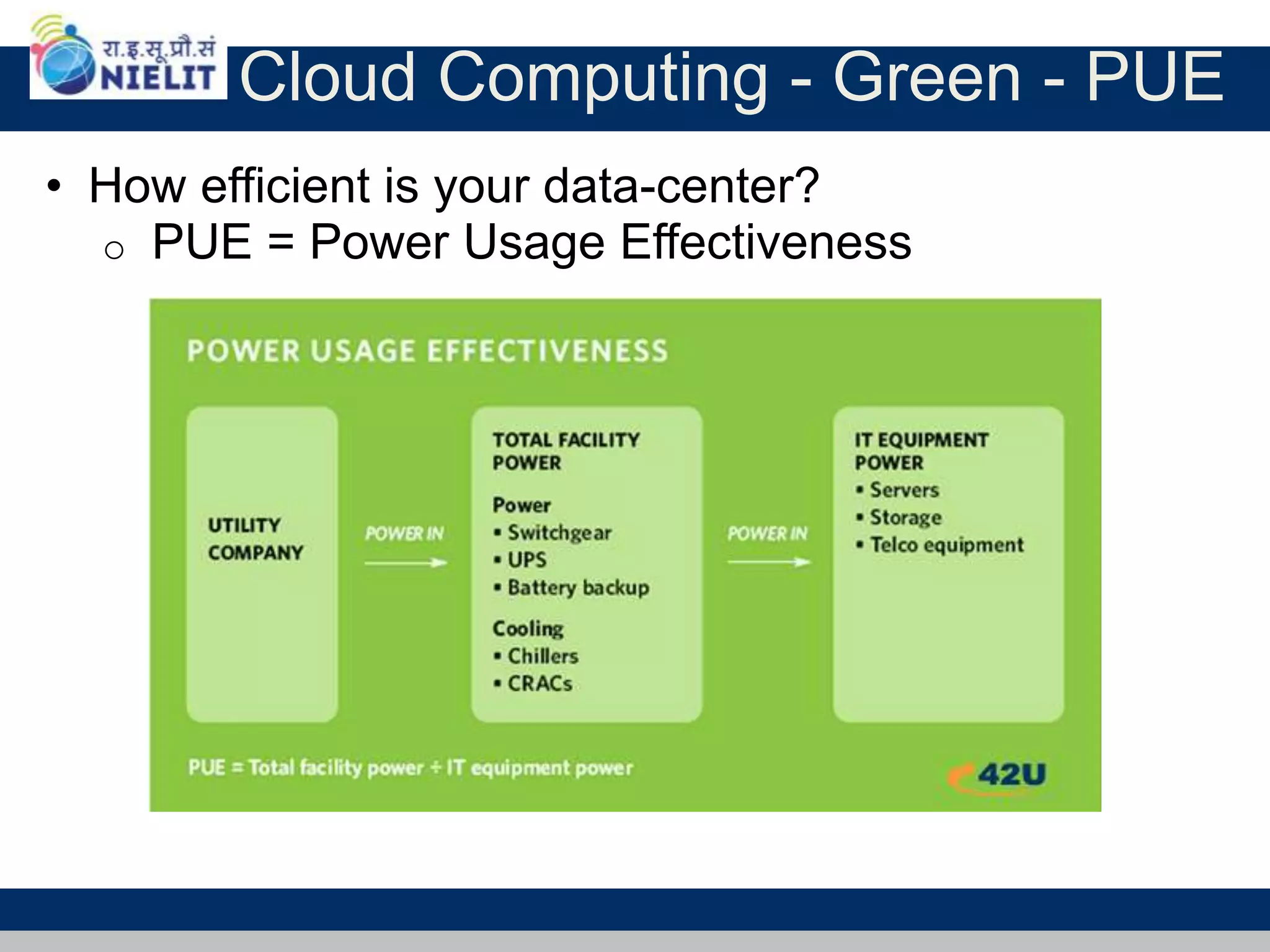
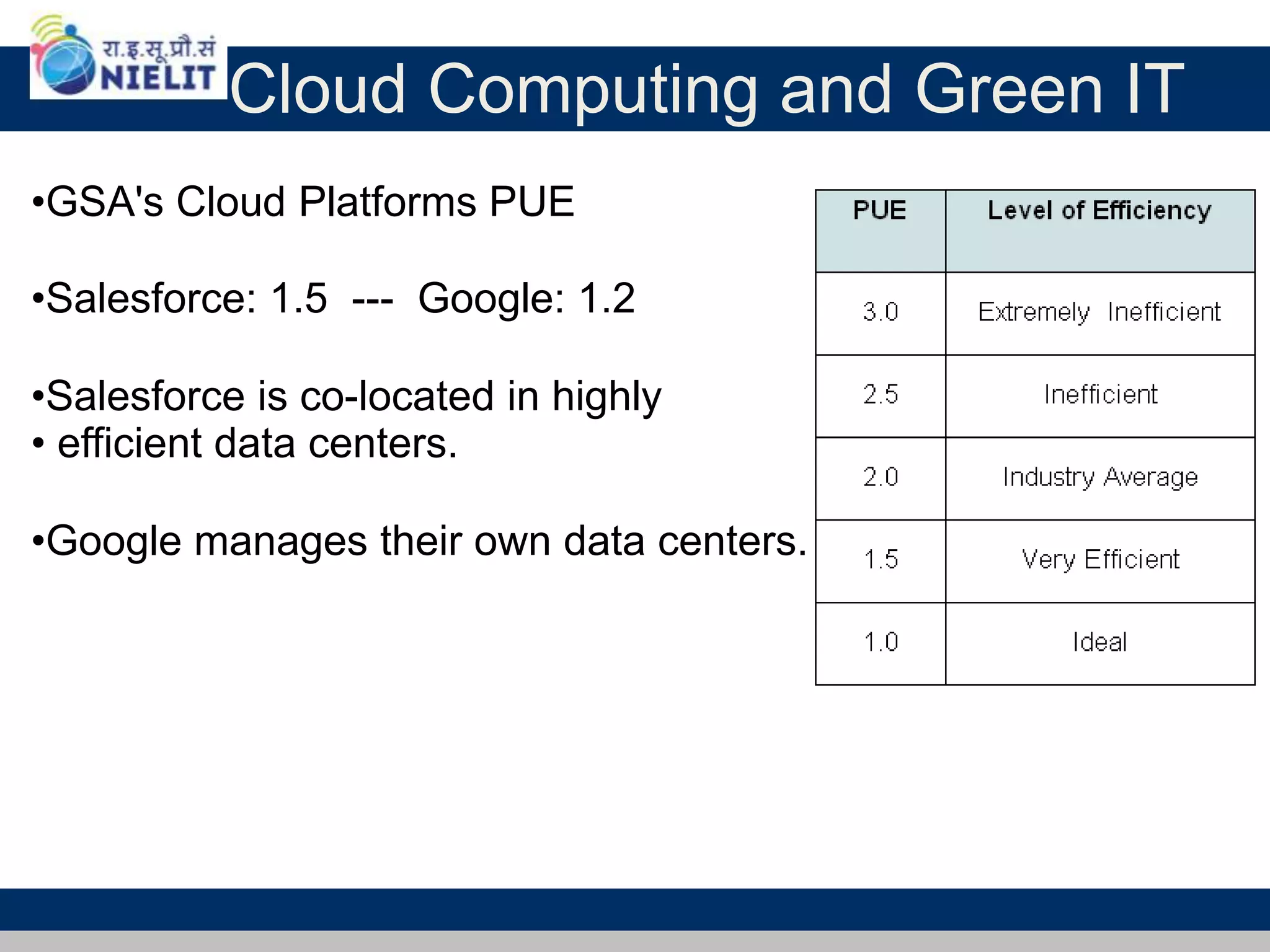
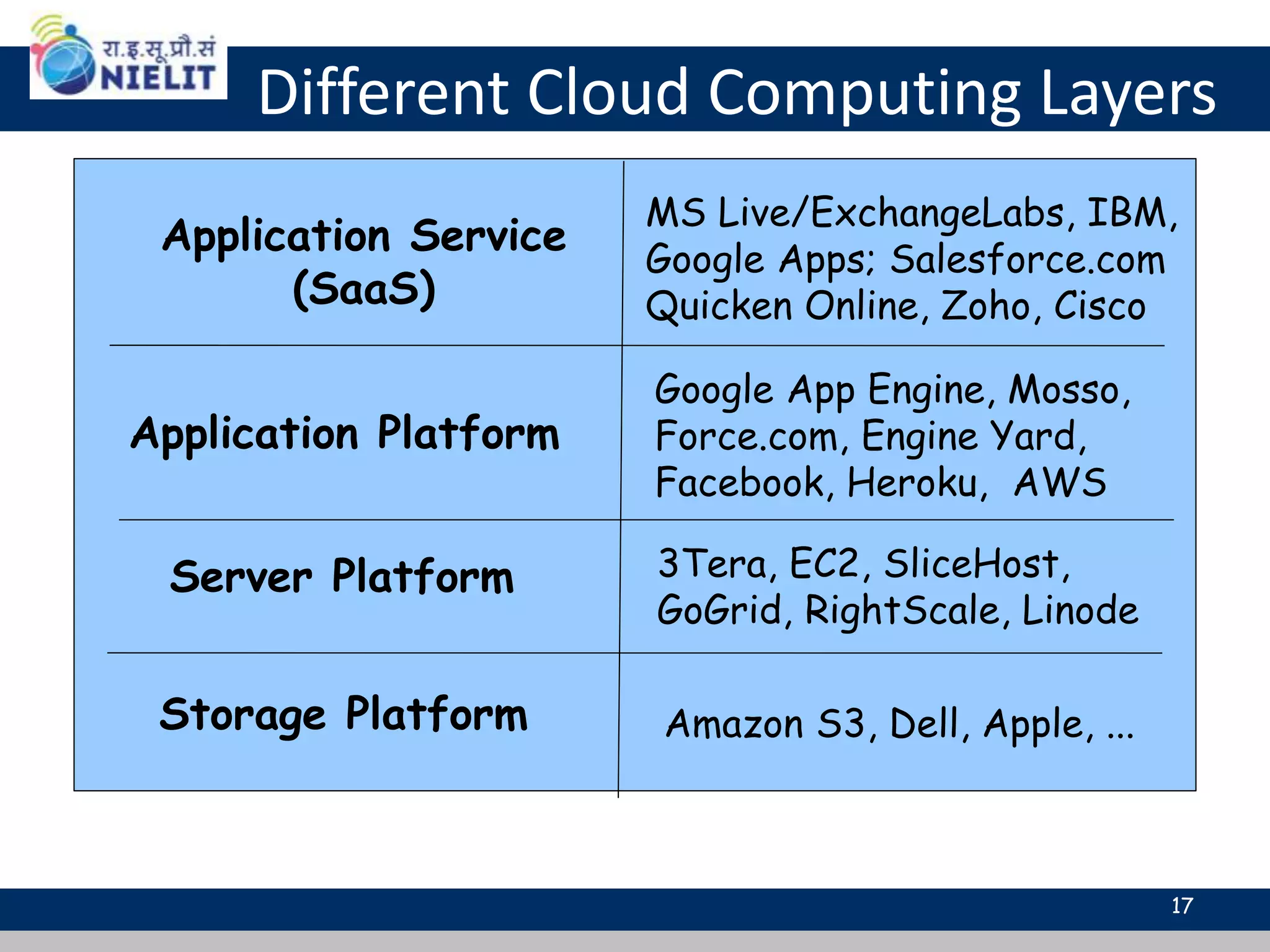
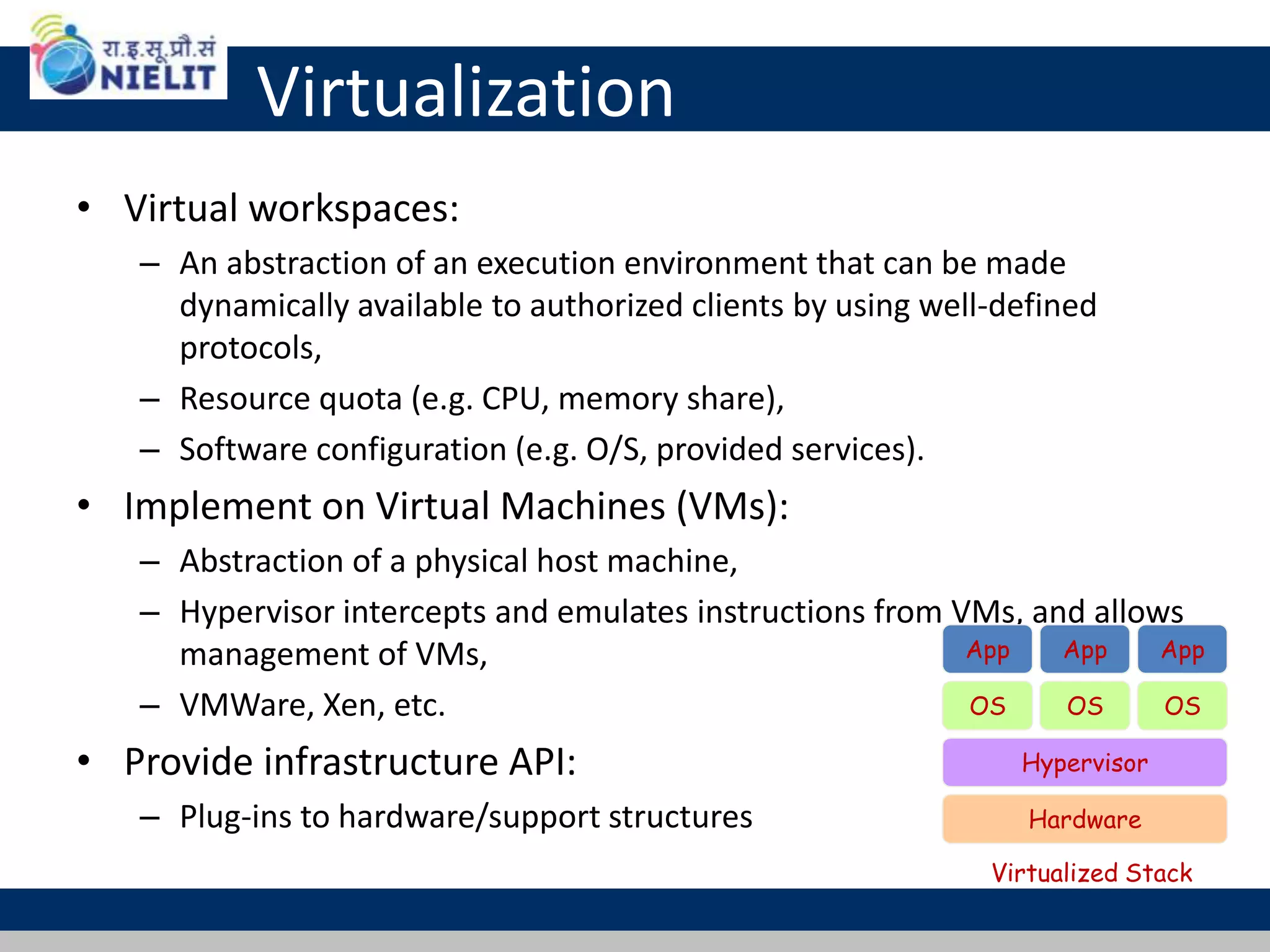
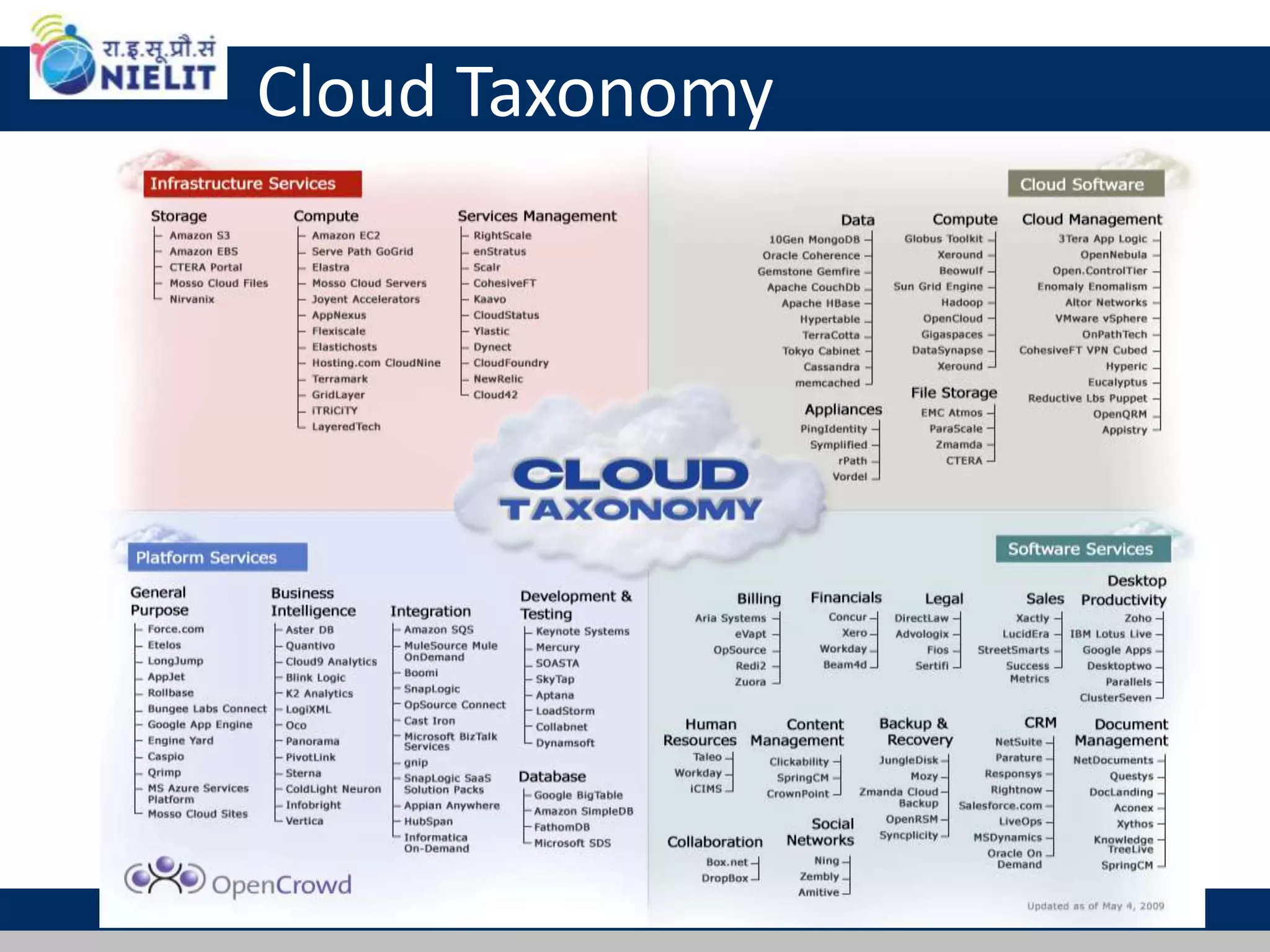
Cloud computing refers to on-demand delivery of computing resources such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software and analytics over the internet. It provides flexibility and cost savings by allowing users to pay for only the resources they need. Virtualization is a key technology that allows multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical machine, improving utilization rates. The main cloud service models are infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS) and software as a service (SaaS). Cloud computing provides many benefits including reduced costs, increased flexibility and scalability, and environmental benefits from more efficient data centers.