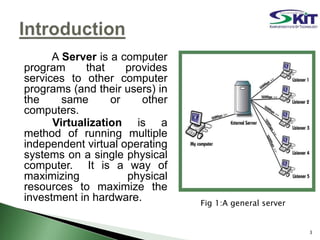
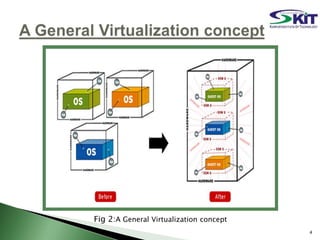
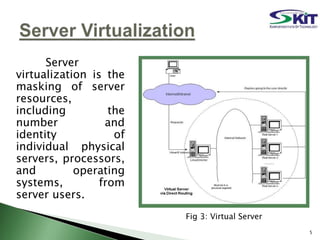
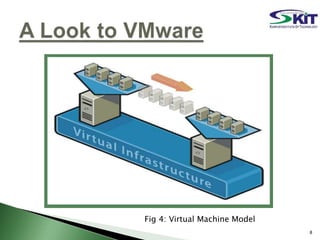
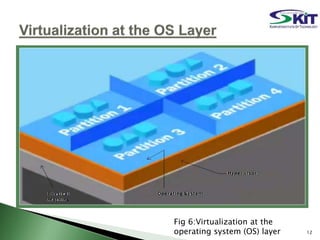
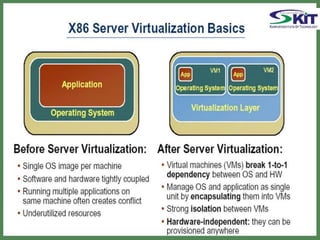
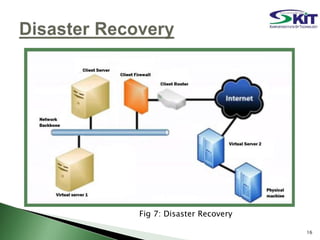
This document discusses server virtualization. It begins by defining server virtualization and describing the key approaches: virtual machine model, para-virtual machine model, and virtualization at the OS layer. Benefits of server virtualization include reduced costs, improved resource utilization, increased availability, and tools to enhance security. Server virtualization can be used for server consolidation, multiple OS/application support, disaster recovery, and centralizing administration. It concludes by discussing future applications of server virtualization like establishing large organizations at low cost and improving data security.