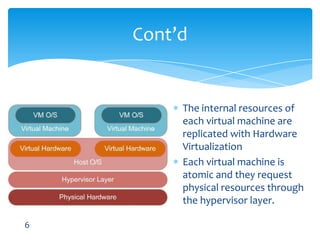
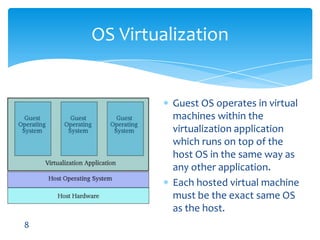
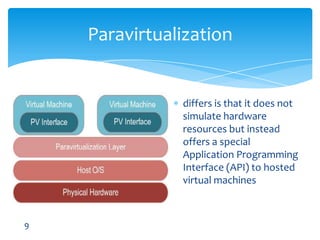
This document discusses various types of virtualization including hardware virtualization, OS virtualization, and desktop virtualization. It provides examples of virtualization software including VMware, QEMU, and Microsoft Virtual PC. VMware is highlighted as the industry leader with products like ESX that run as hypervisors on hardware. The document also performs a SWOT analysis of virtualization, noting strengths like adaptability and live migration, weaknesses like cost, and threats like security breaches and new competition.