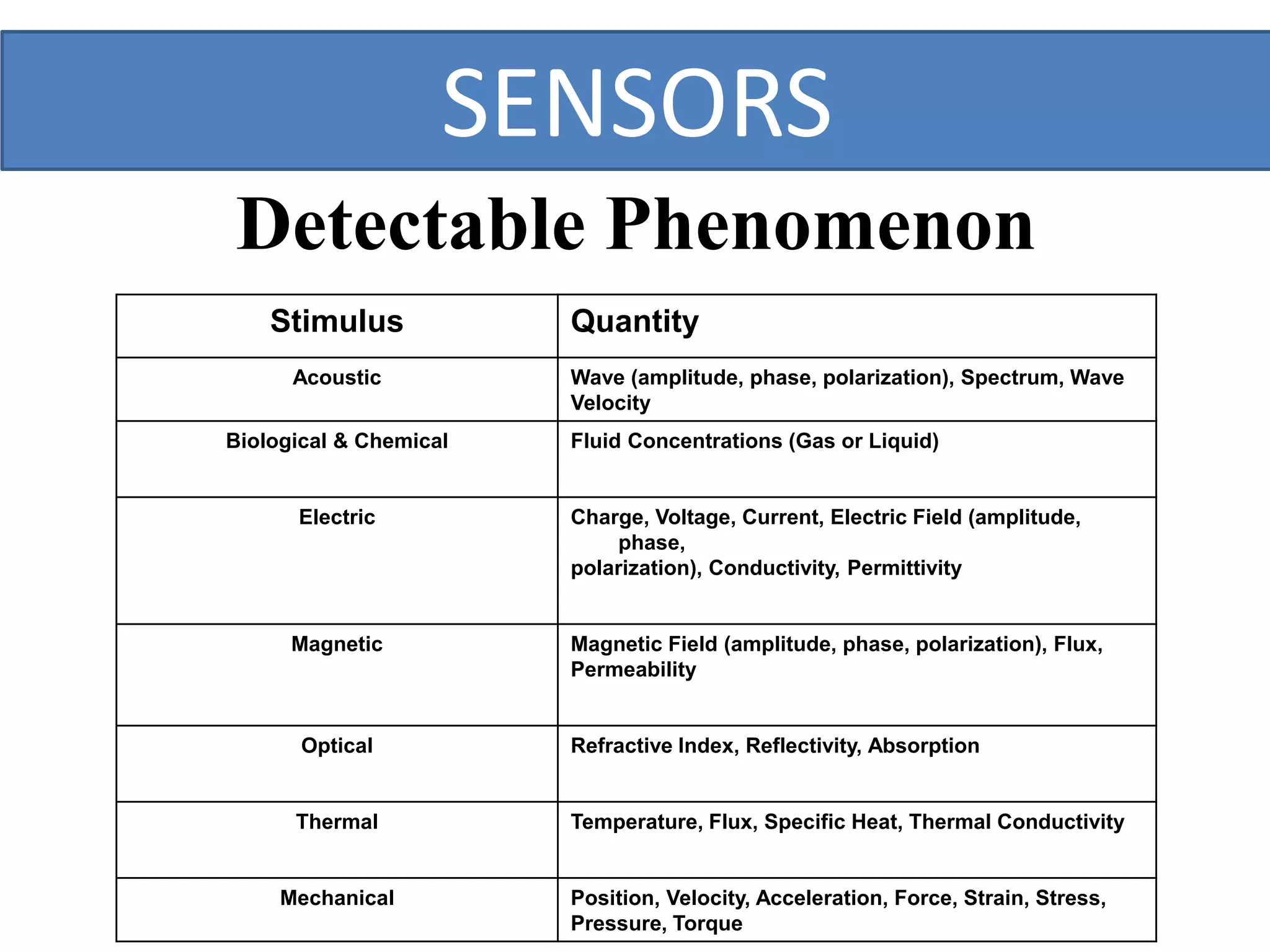
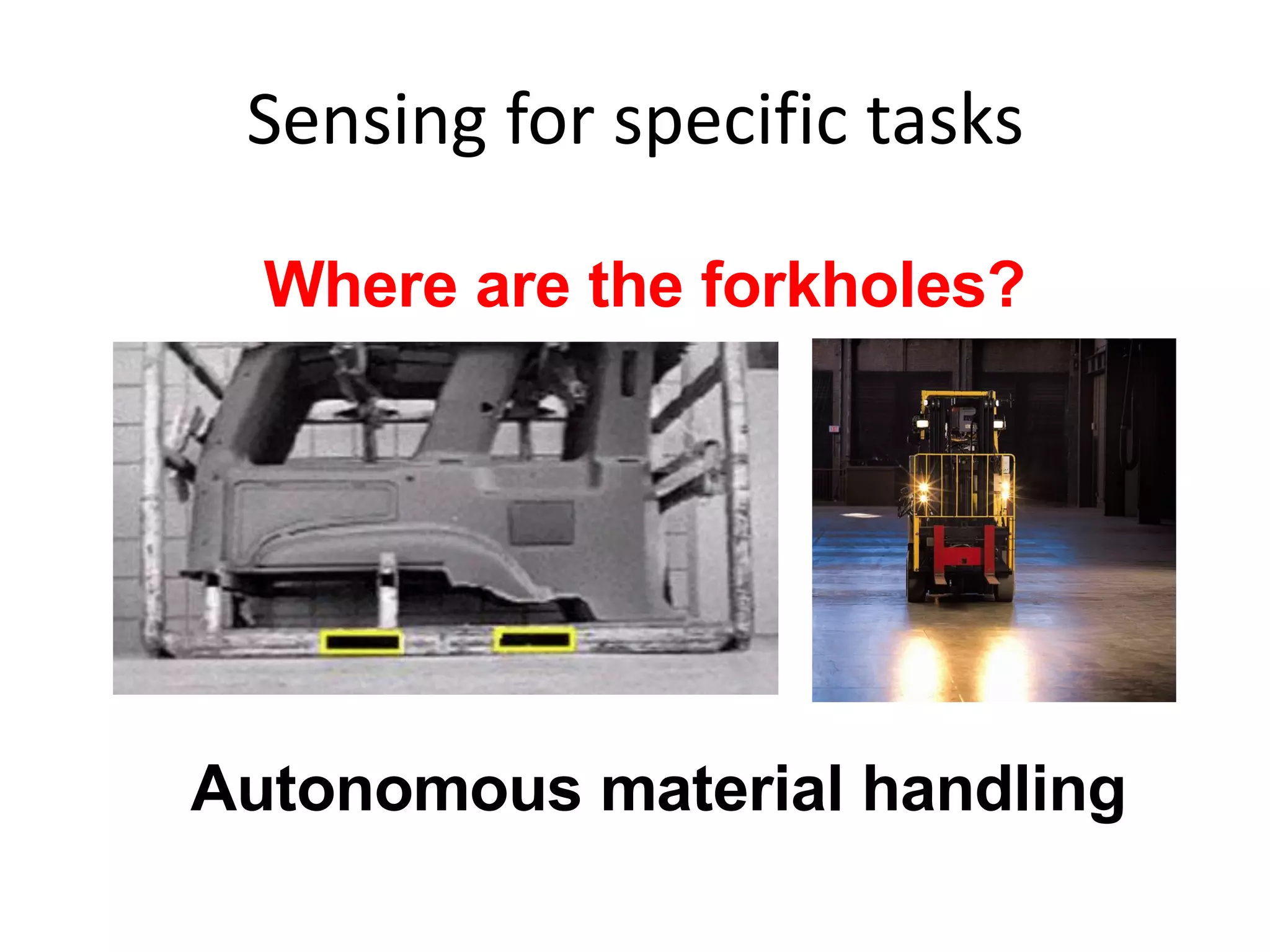
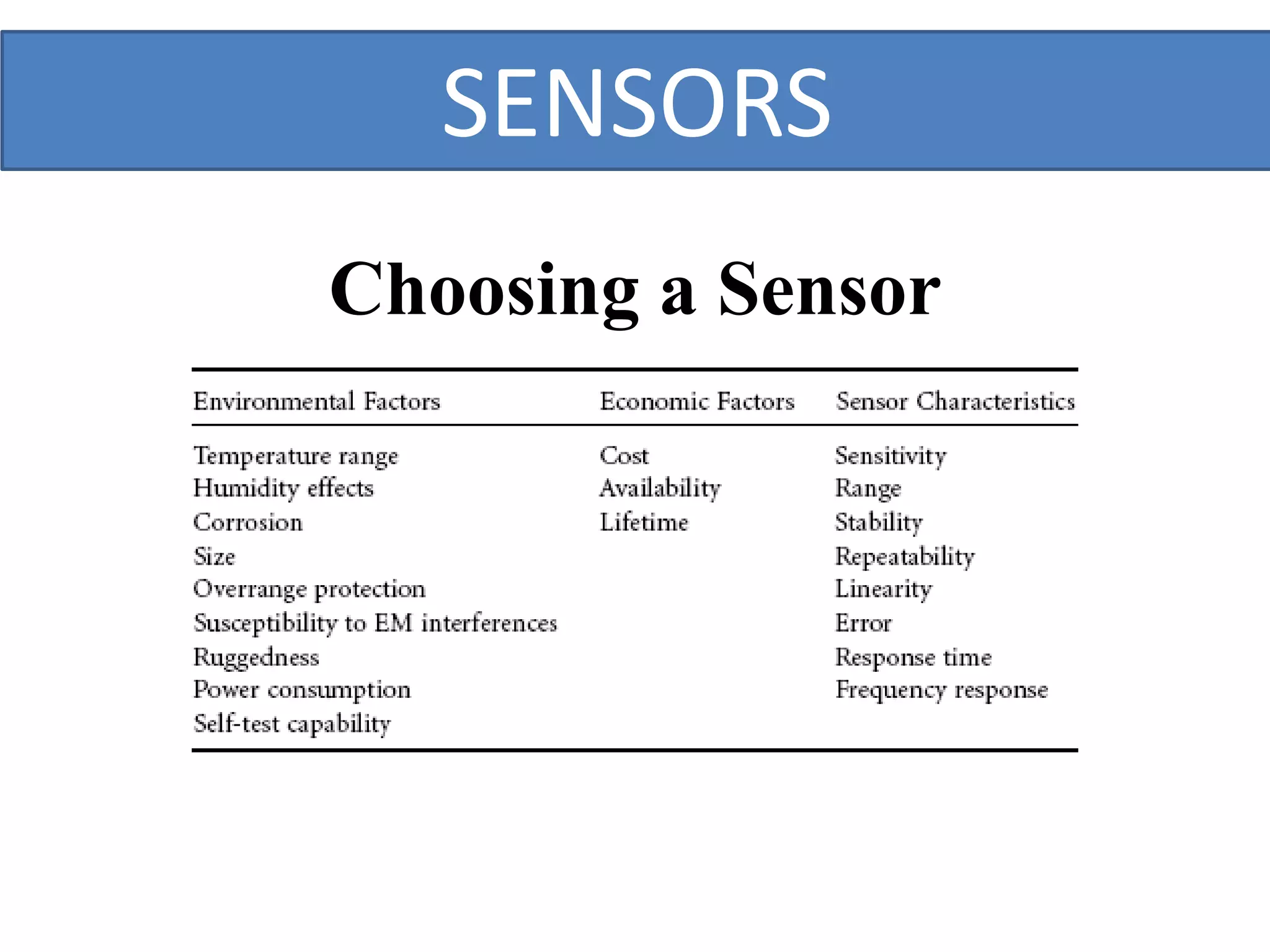
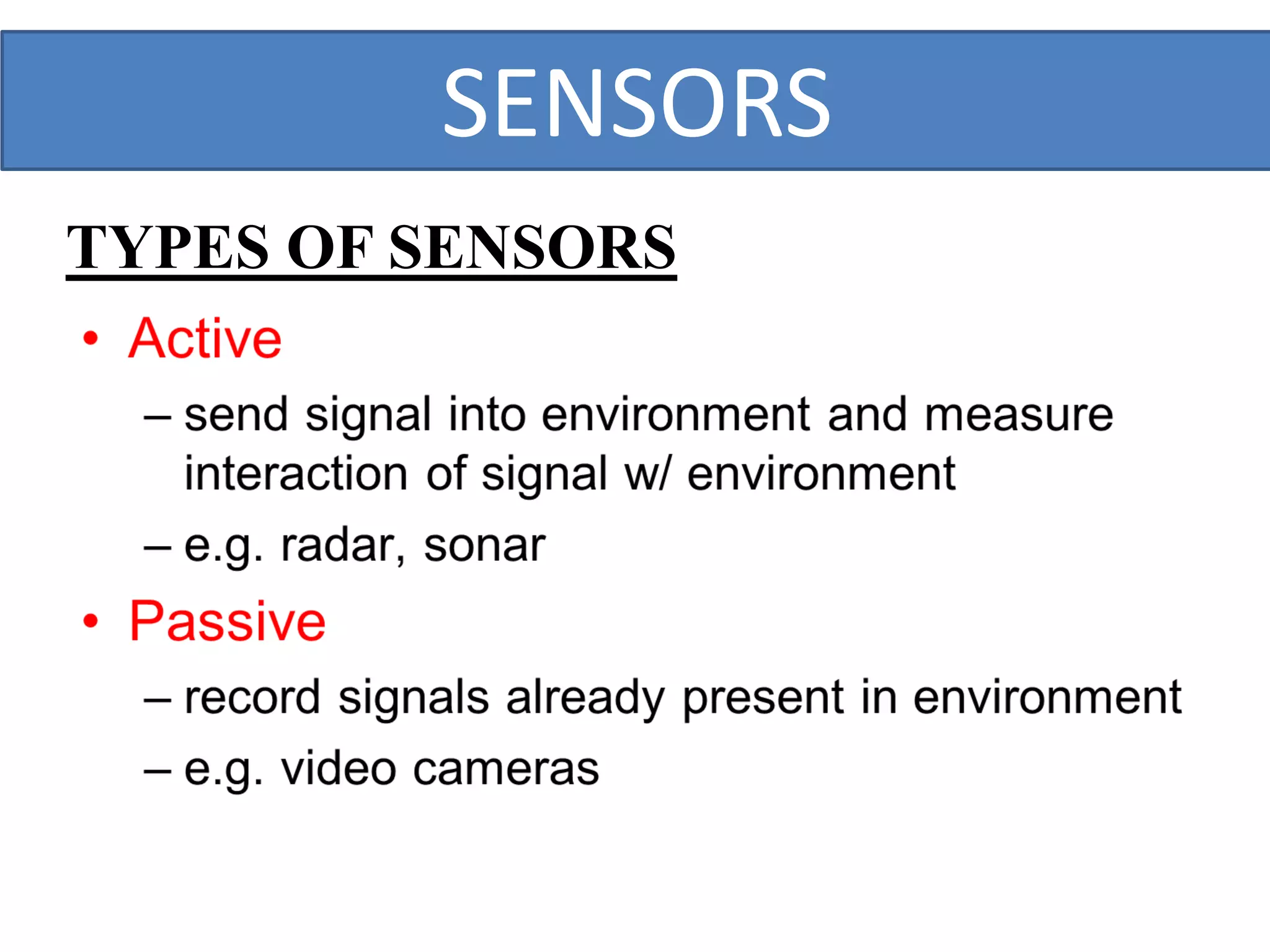
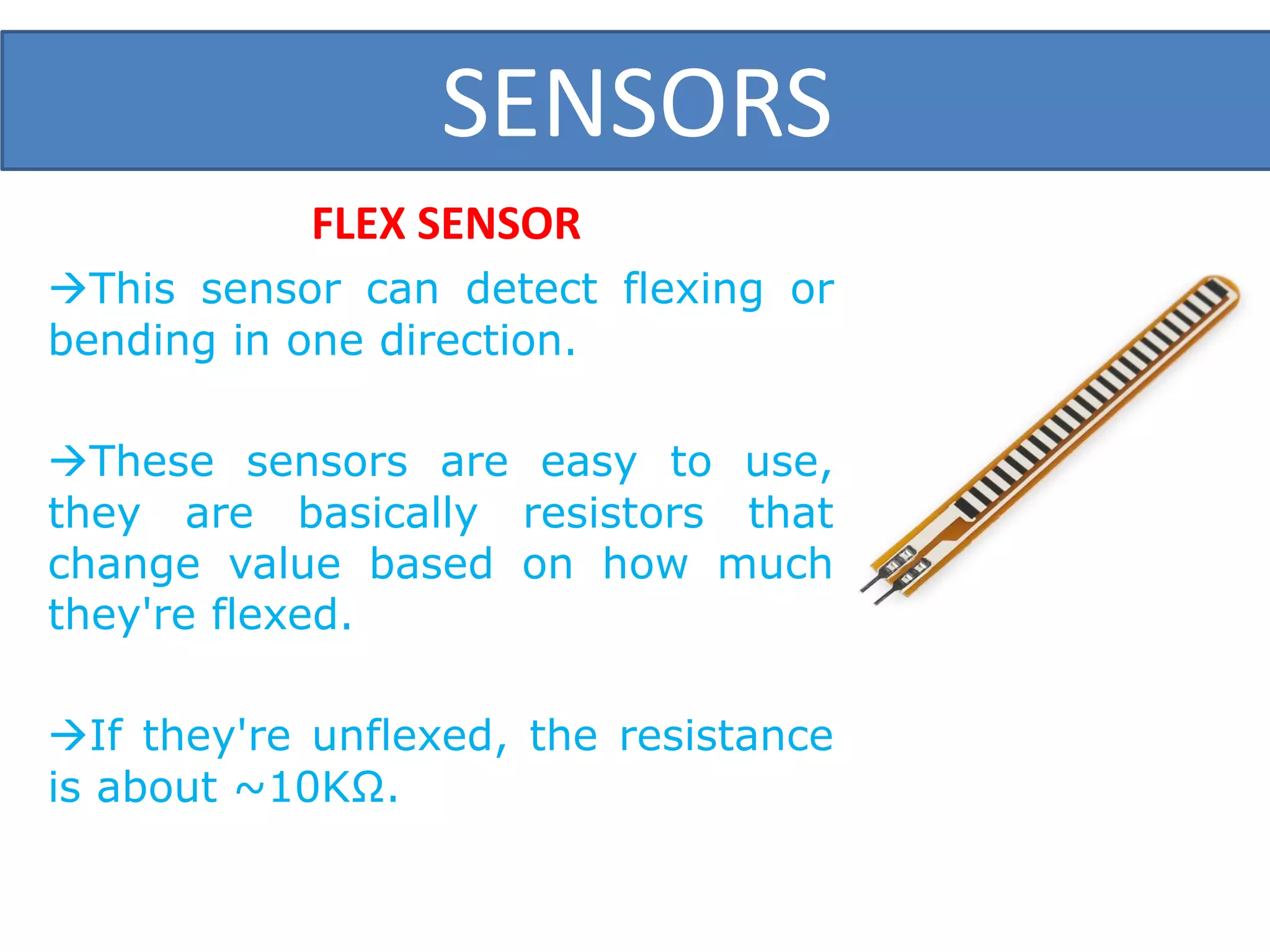
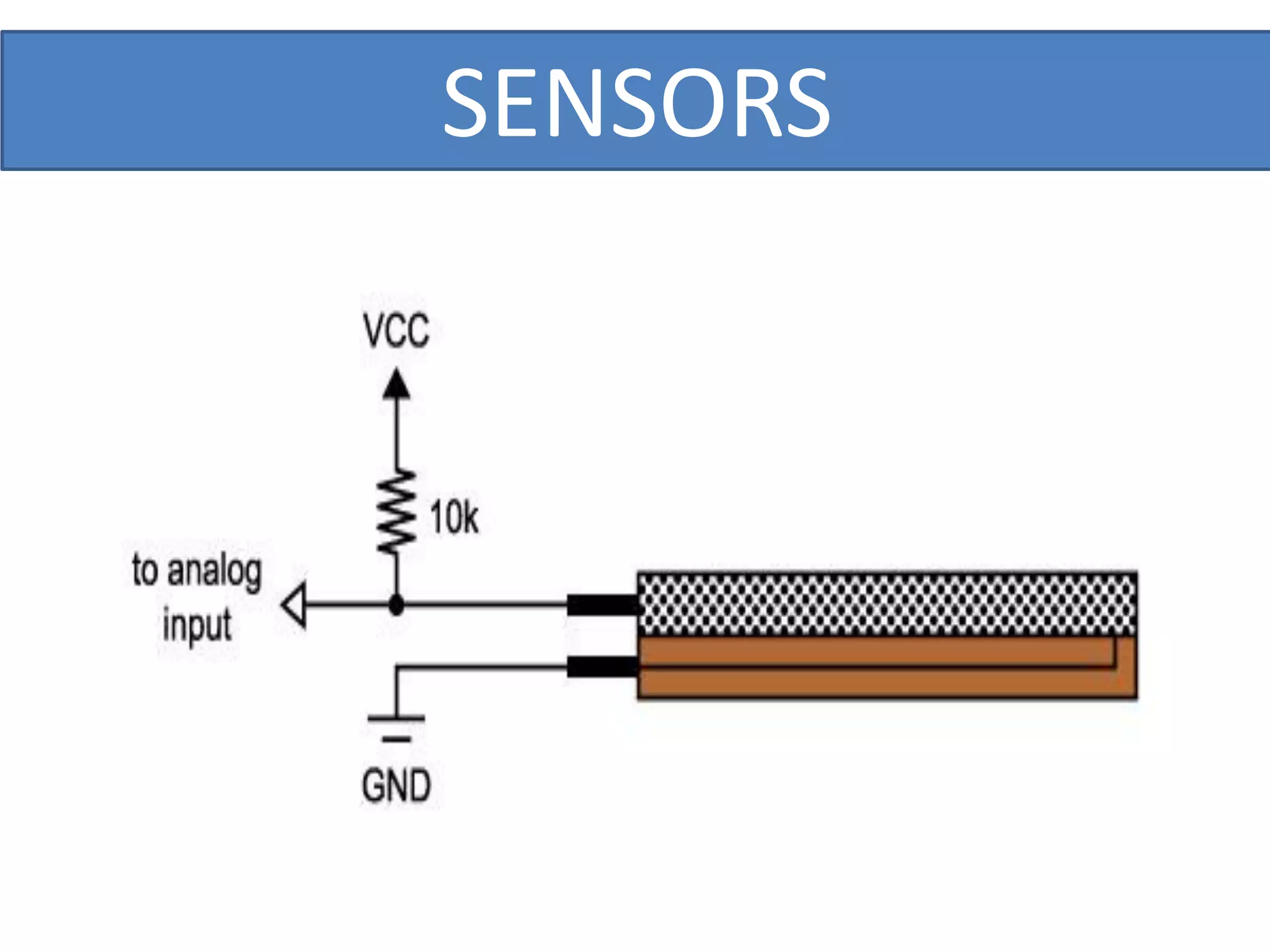
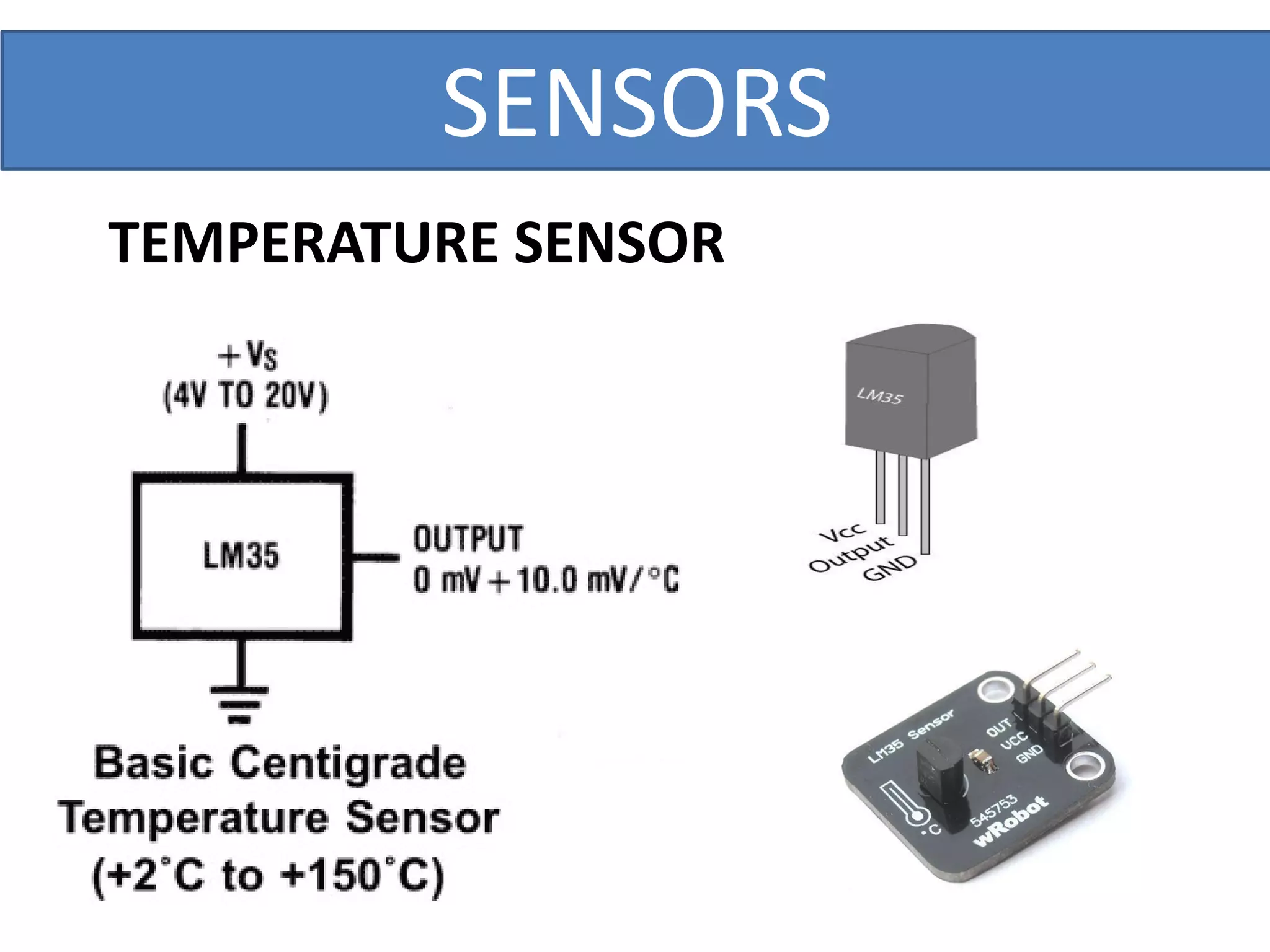
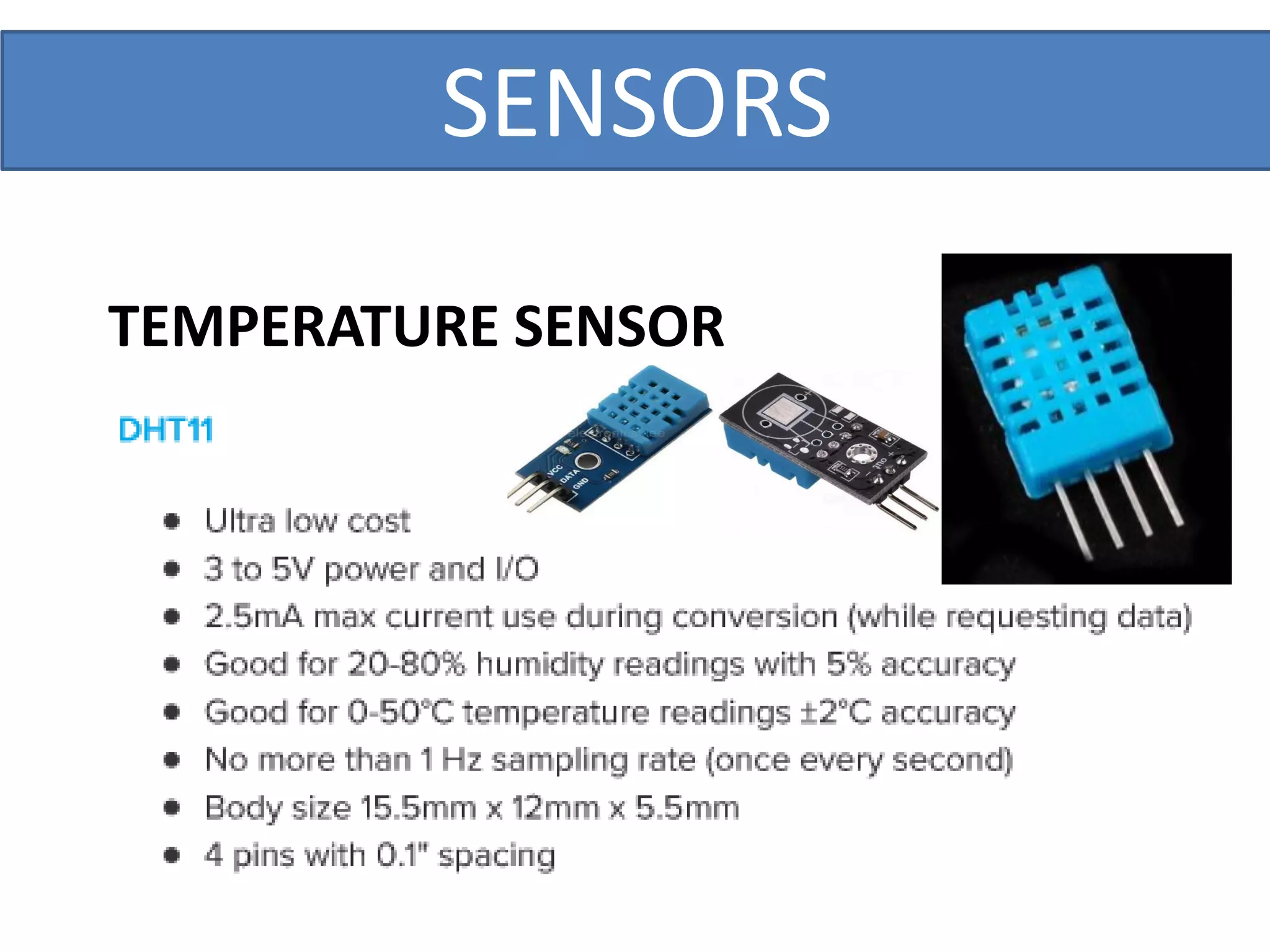
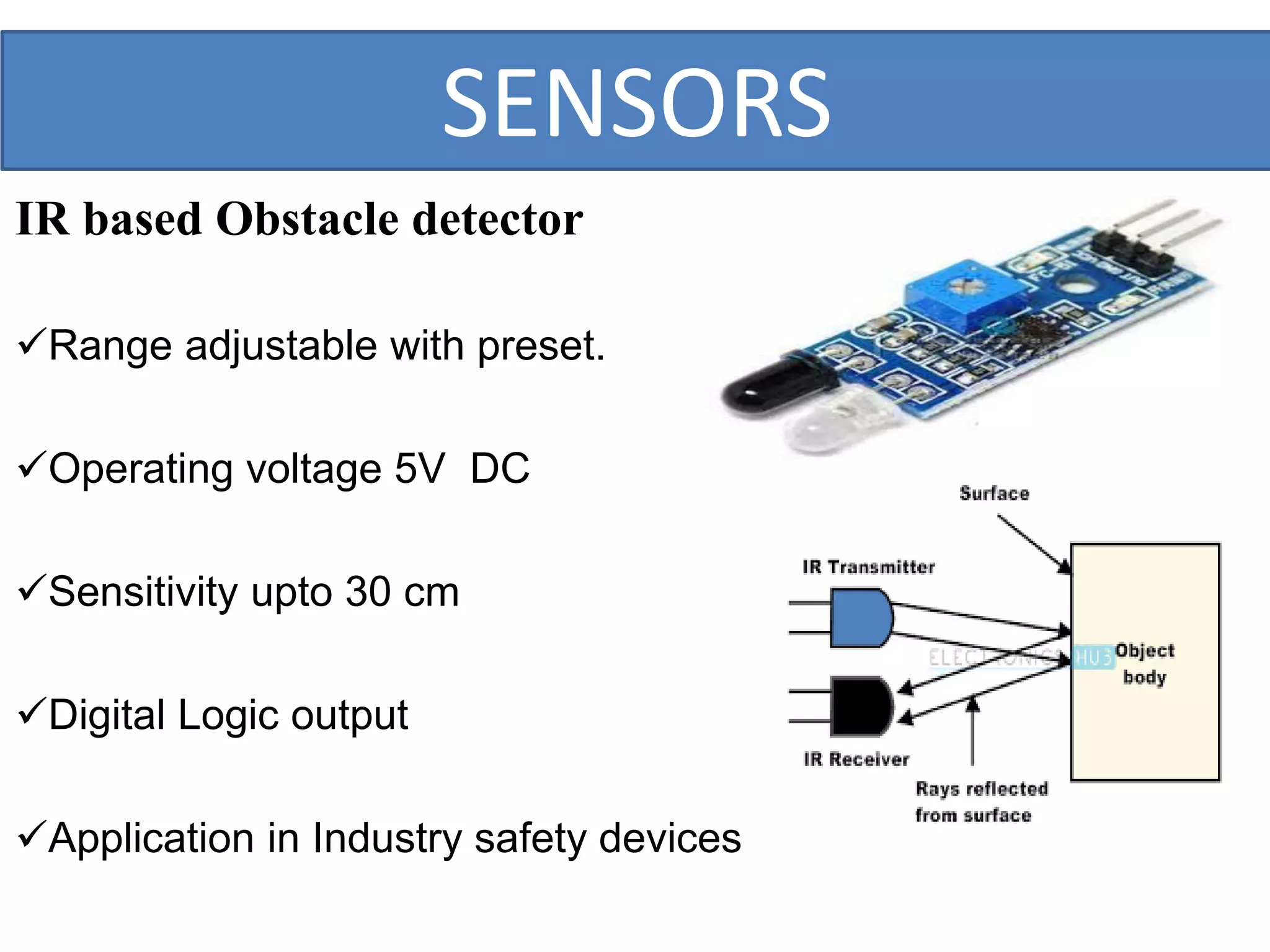
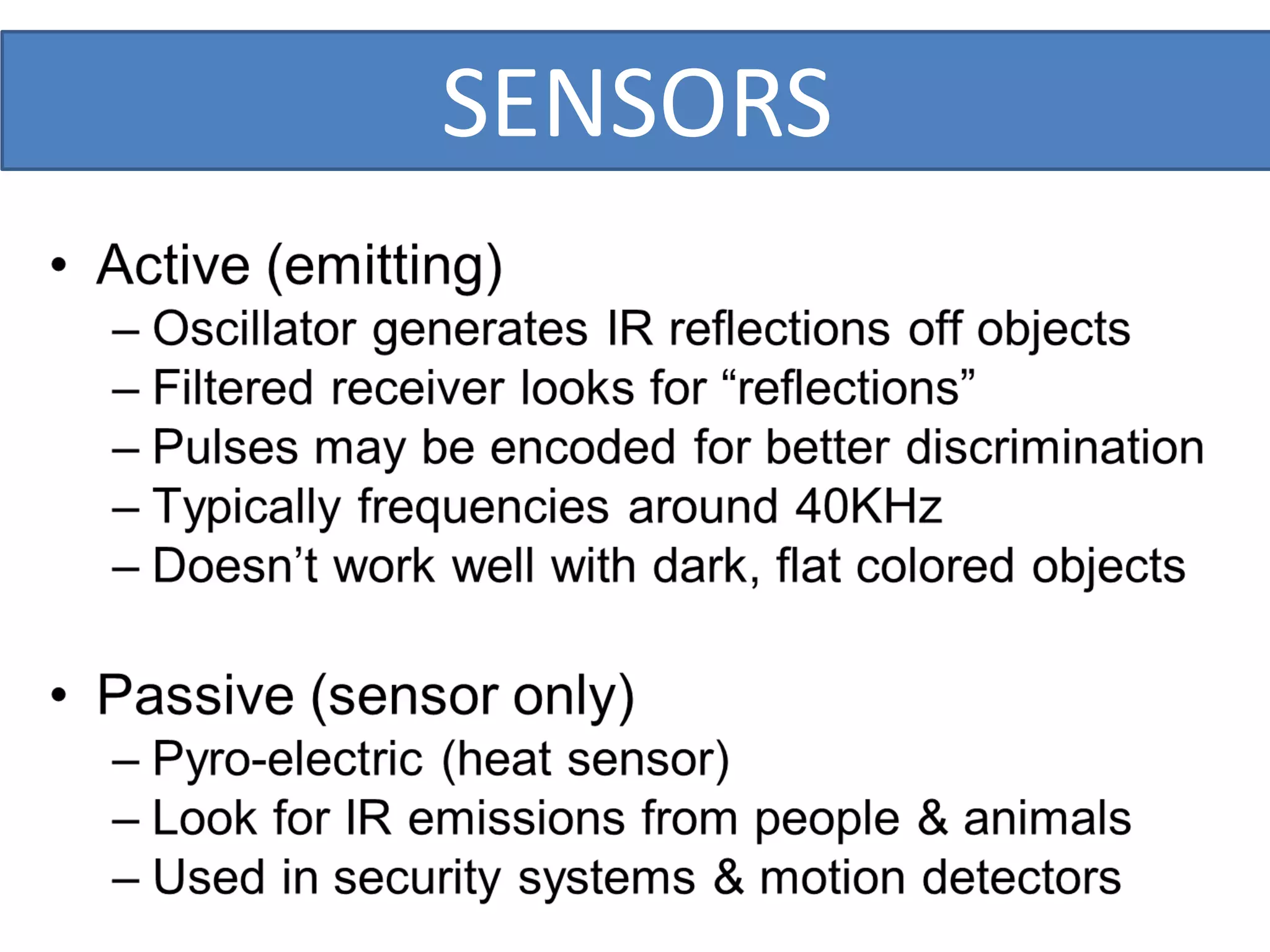
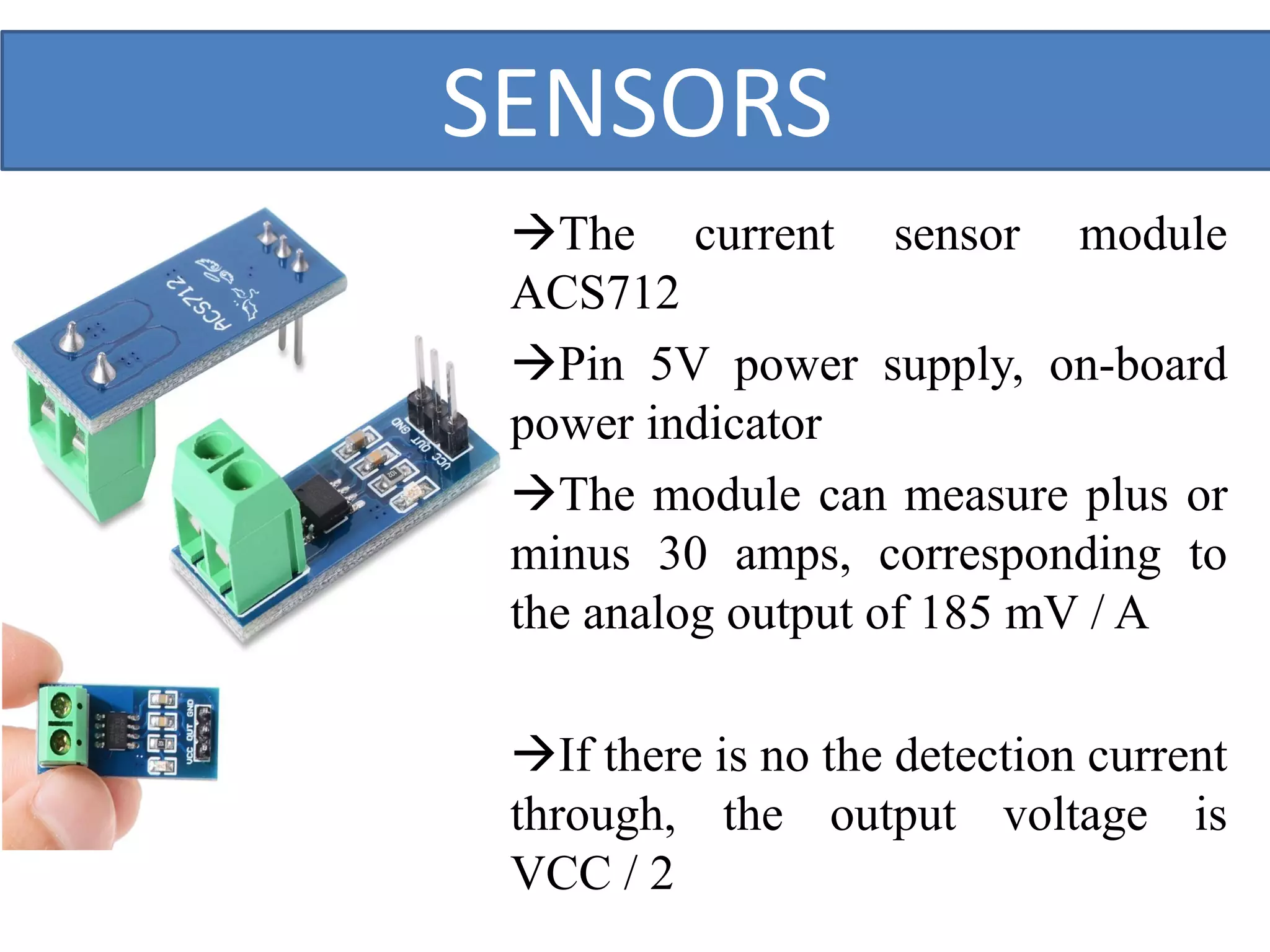
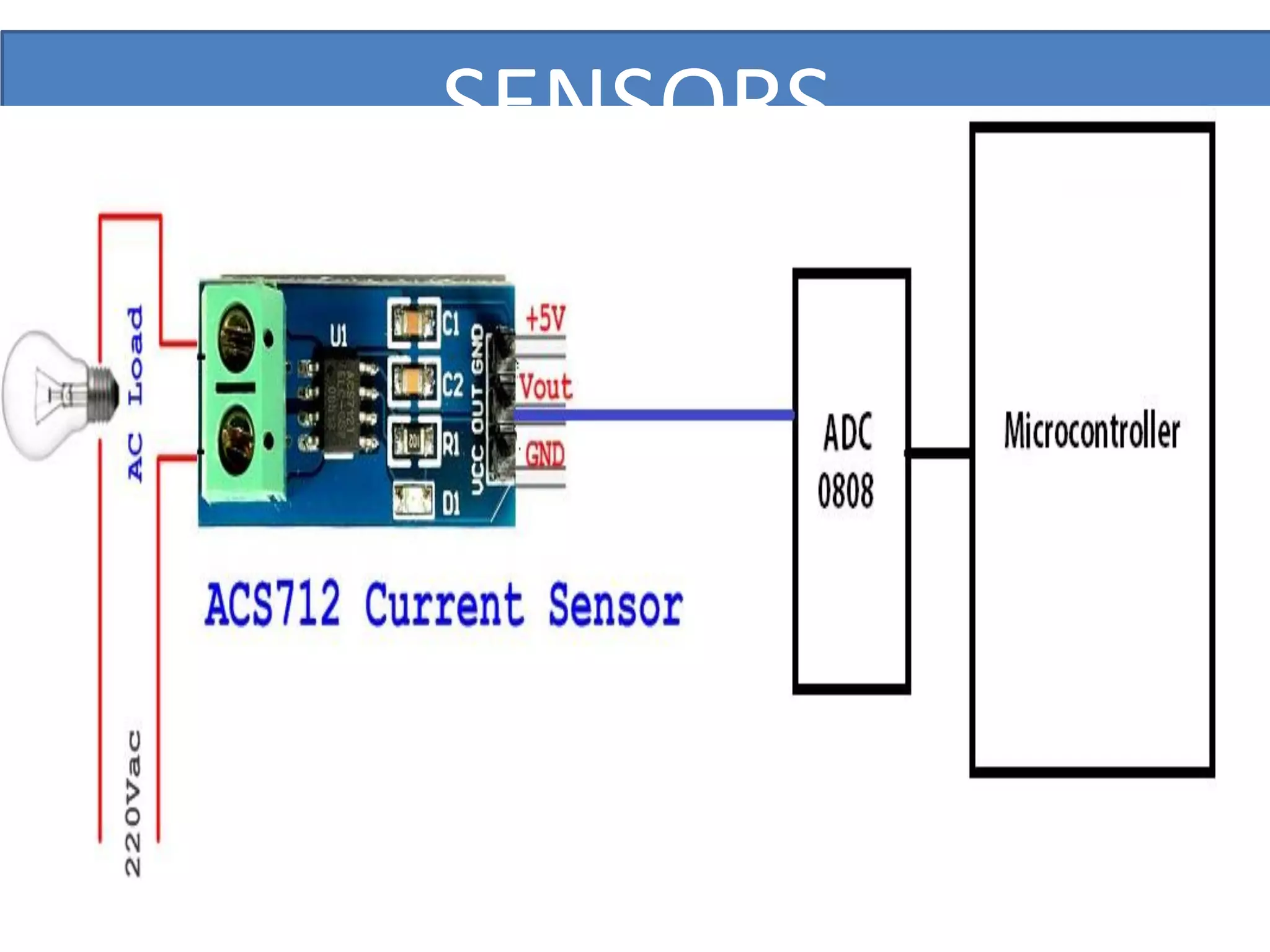
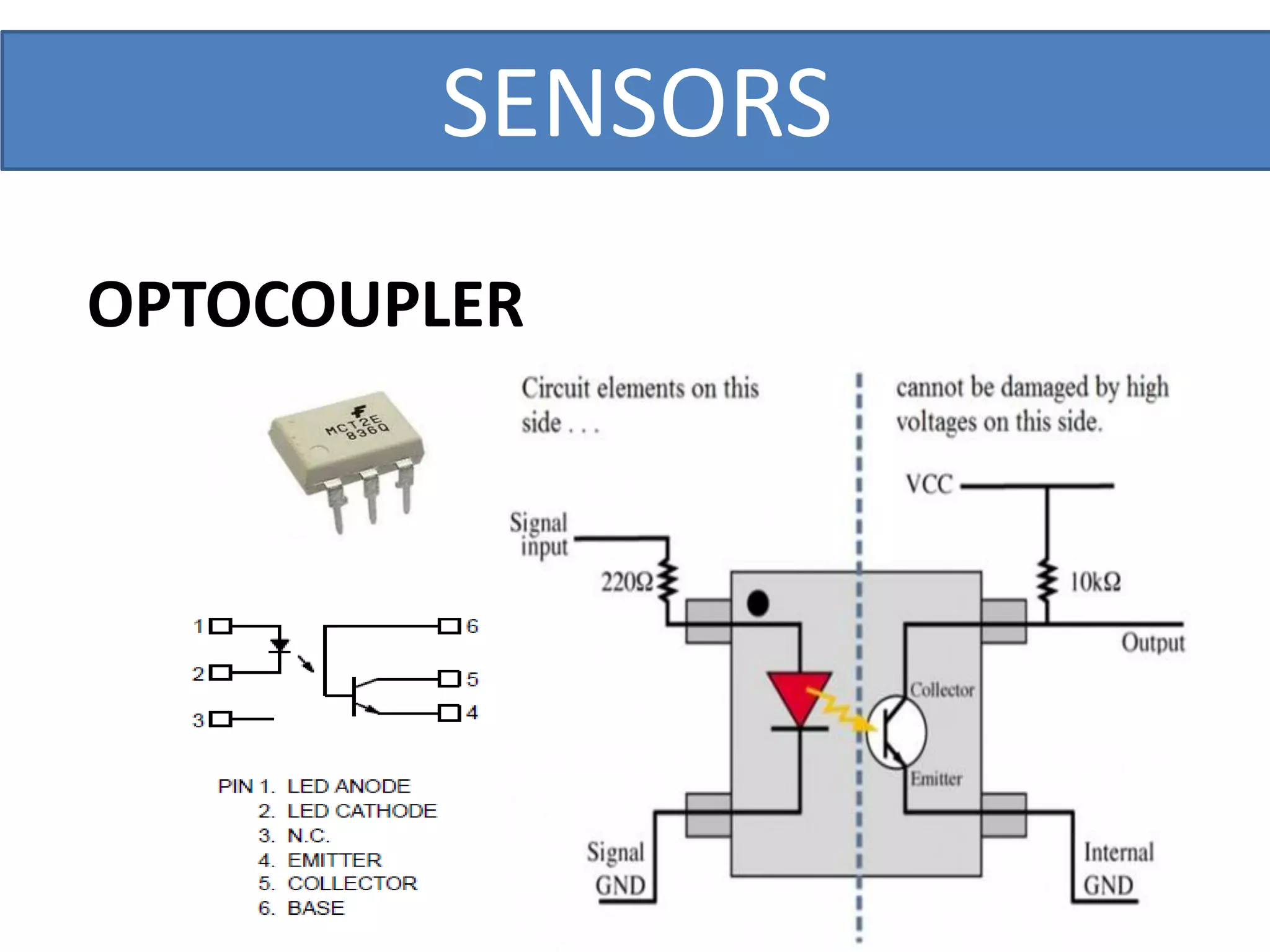
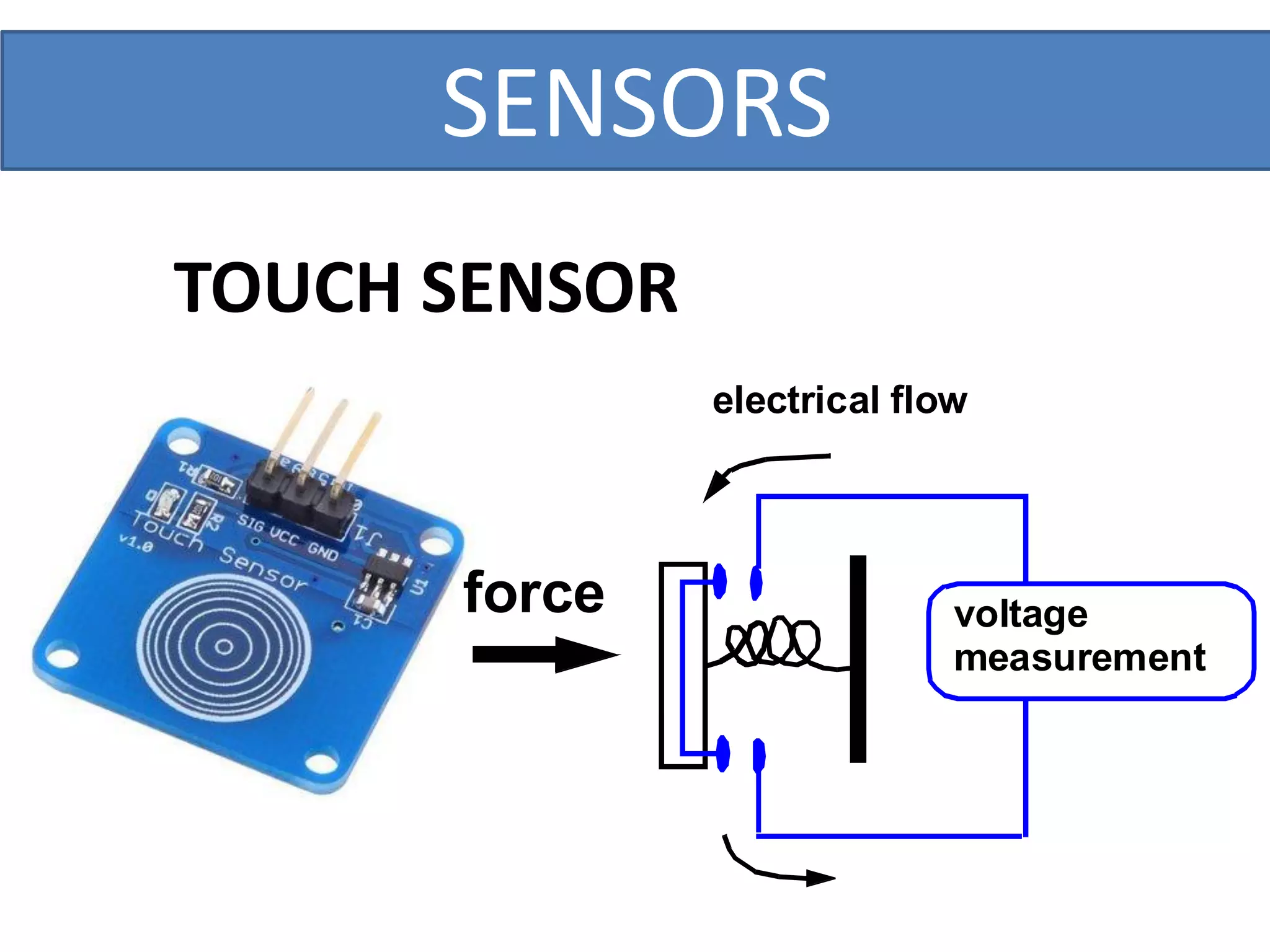
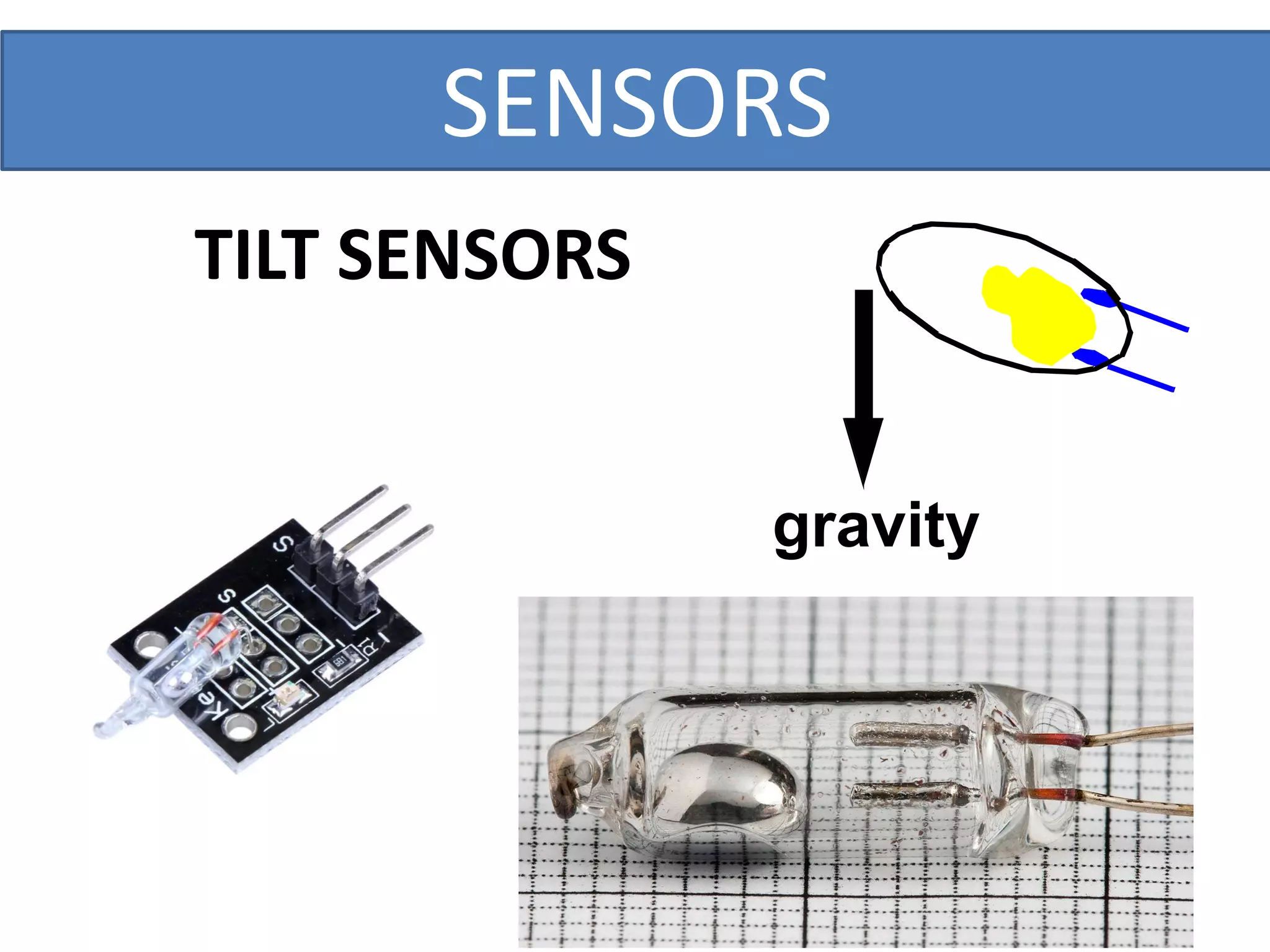
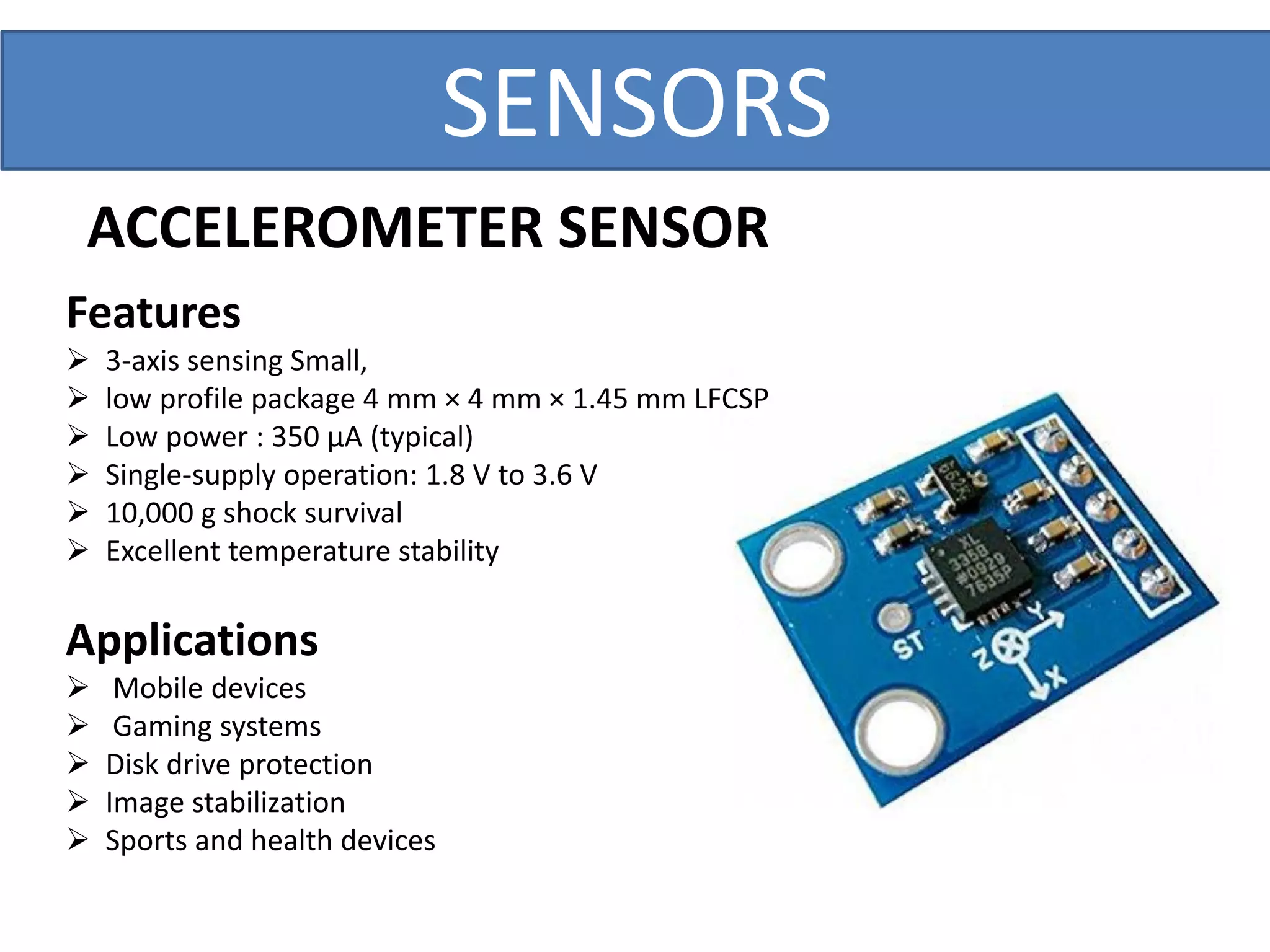
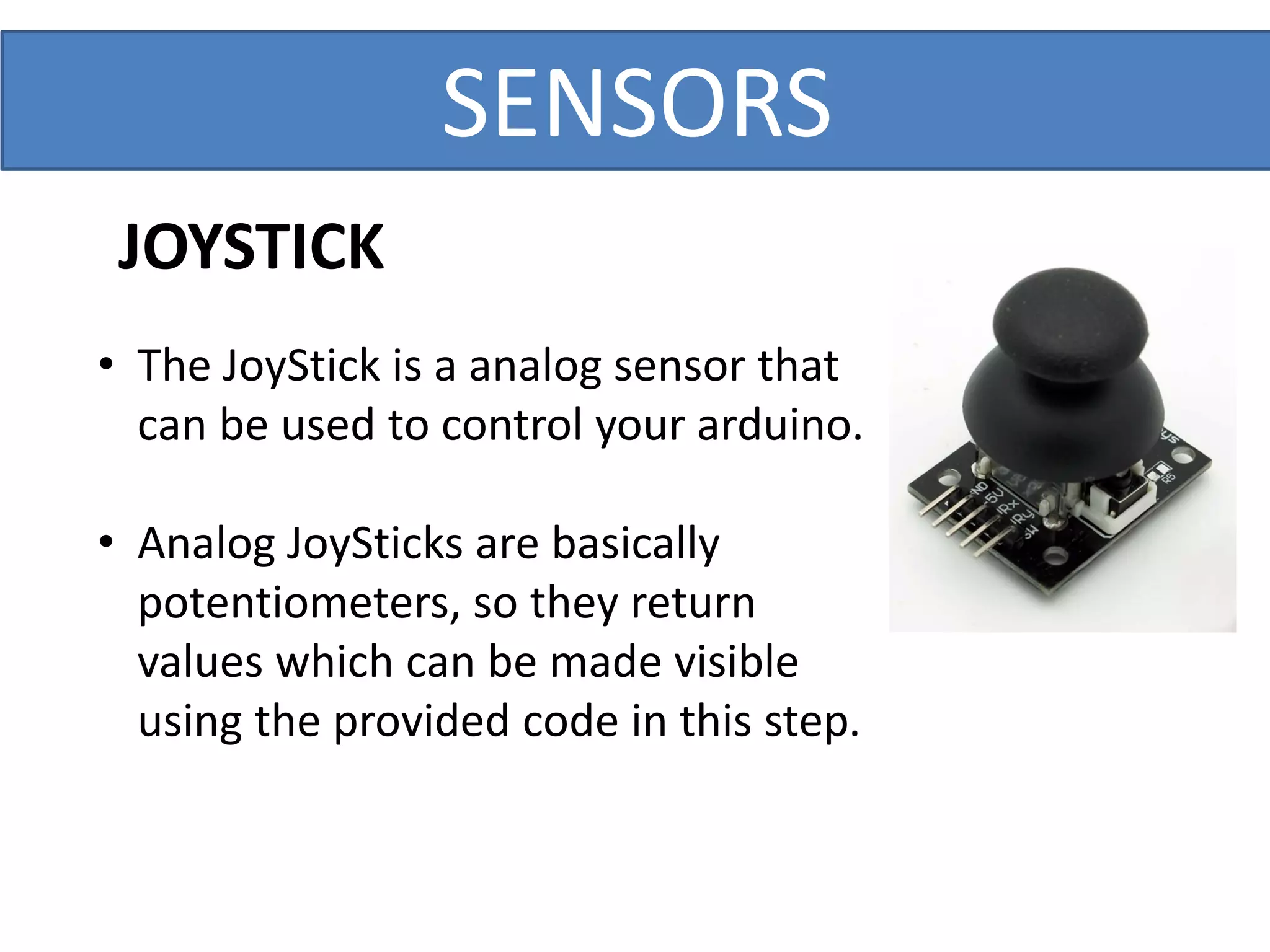
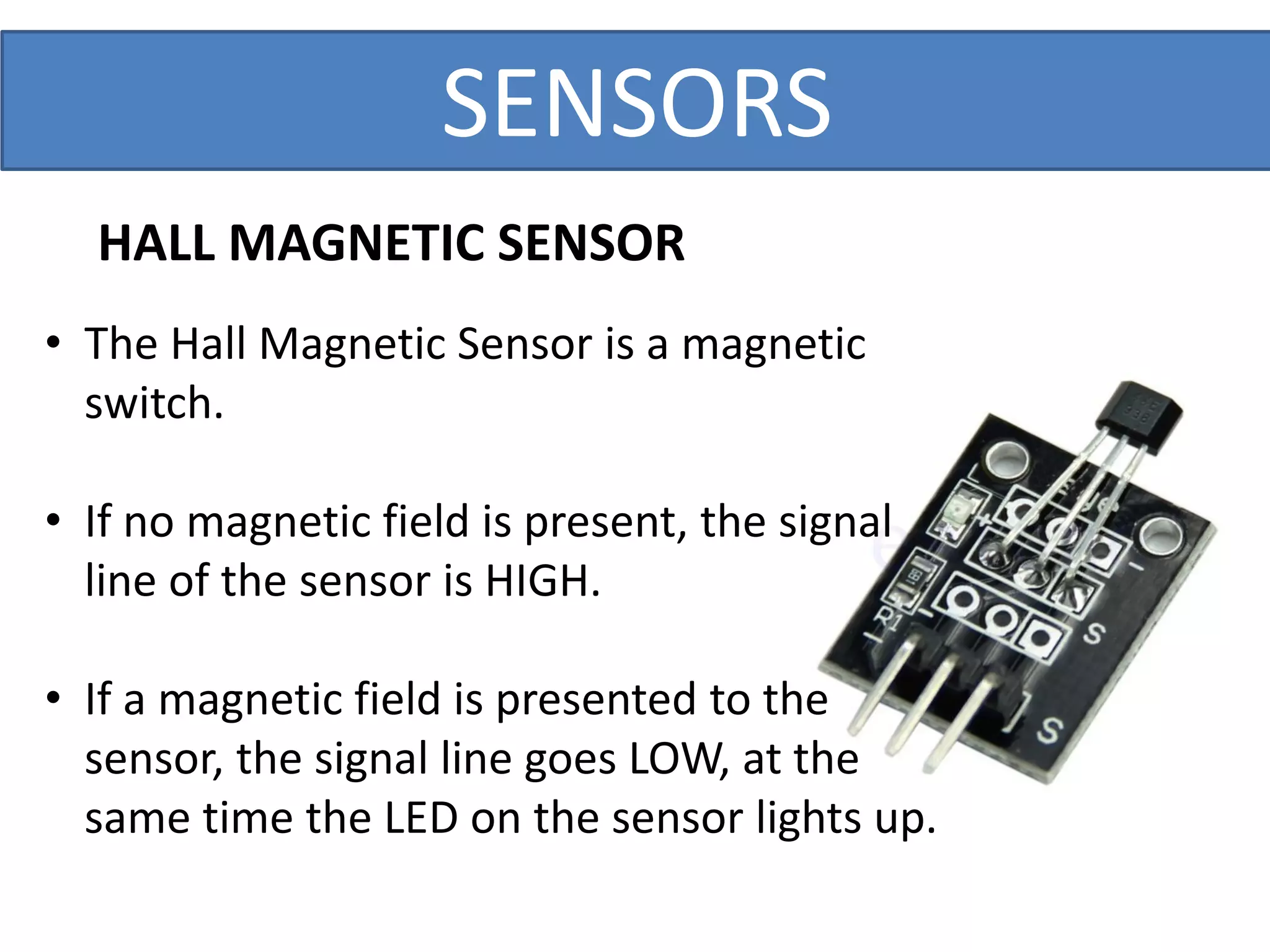
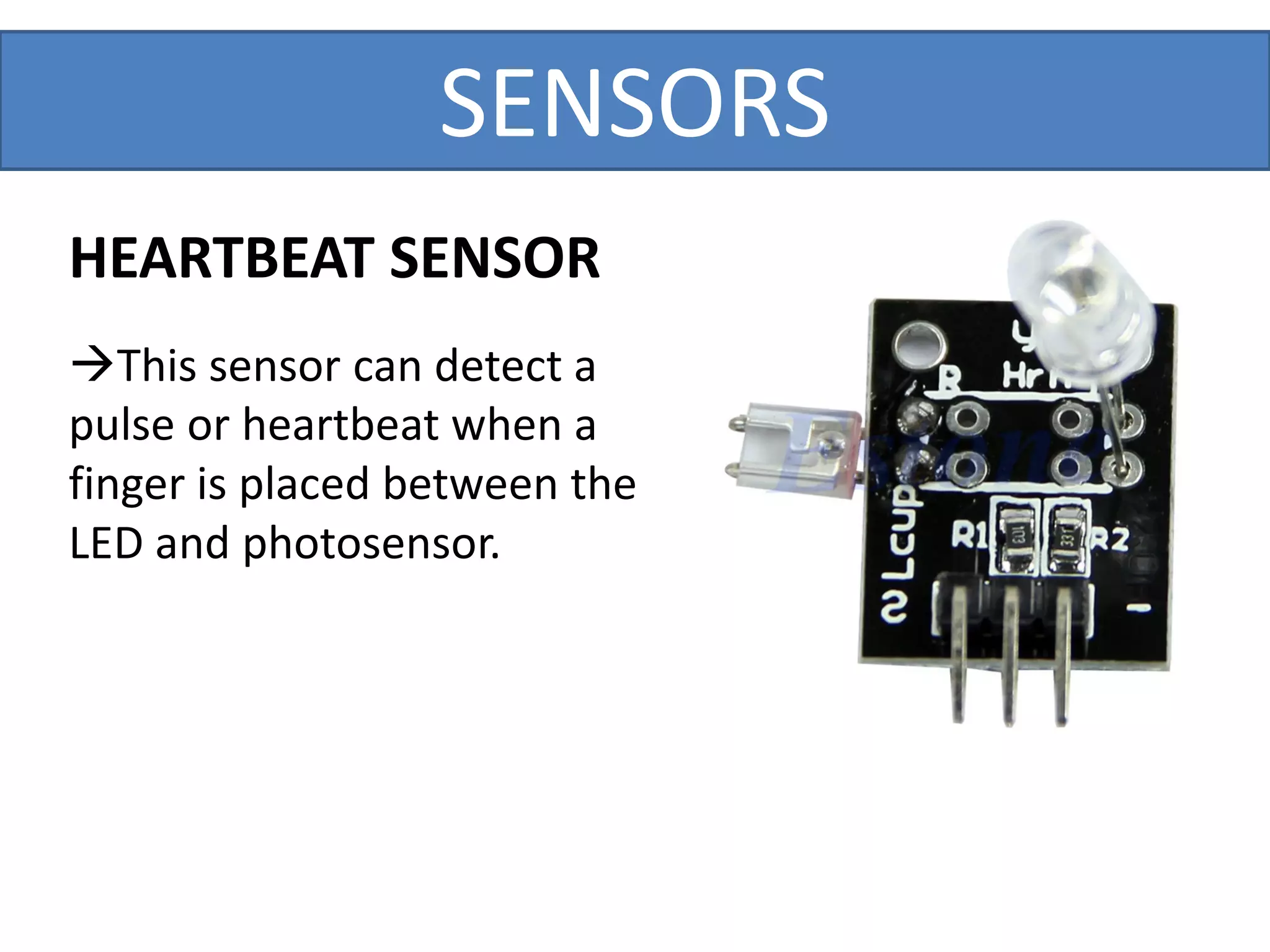
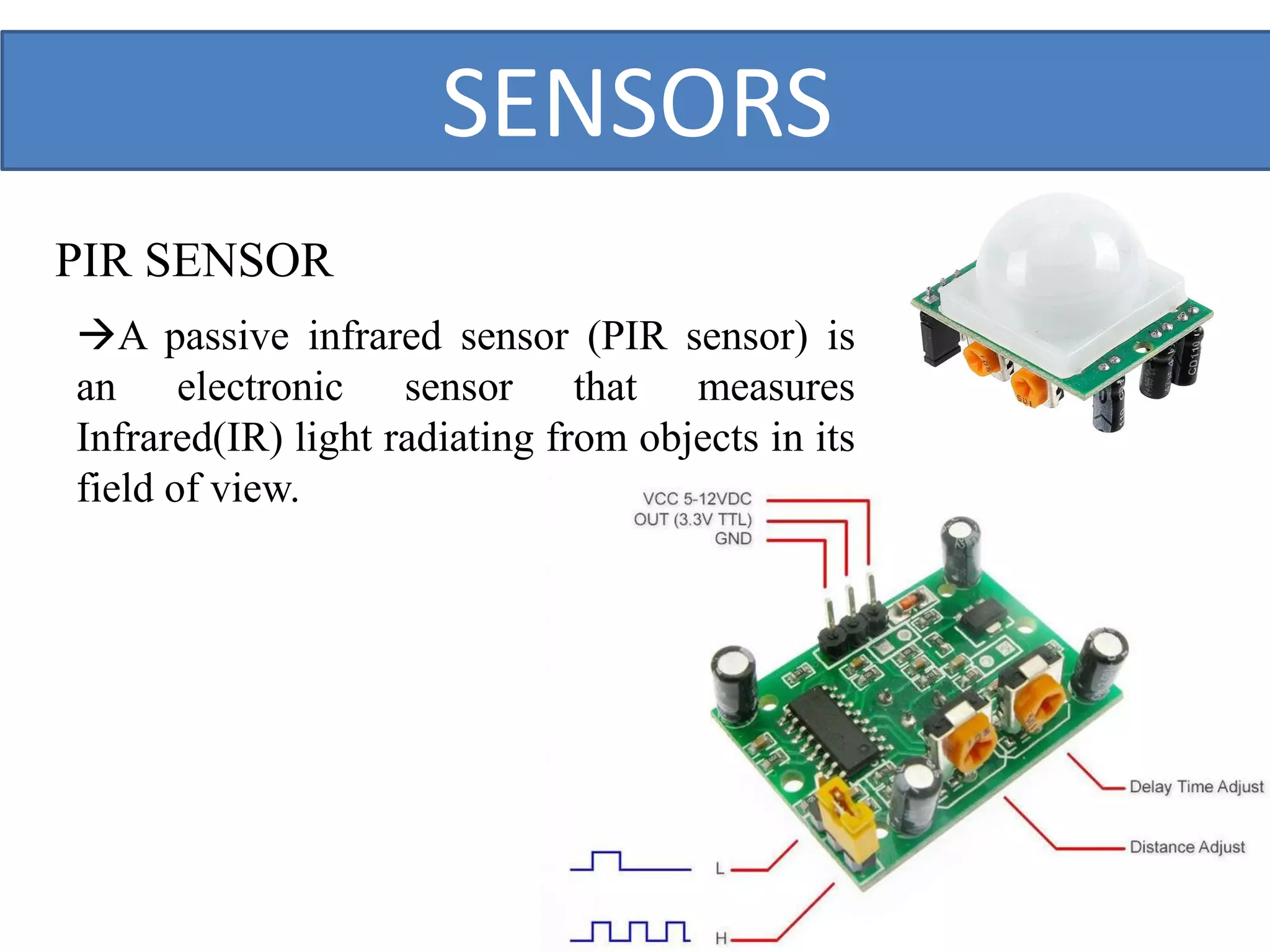
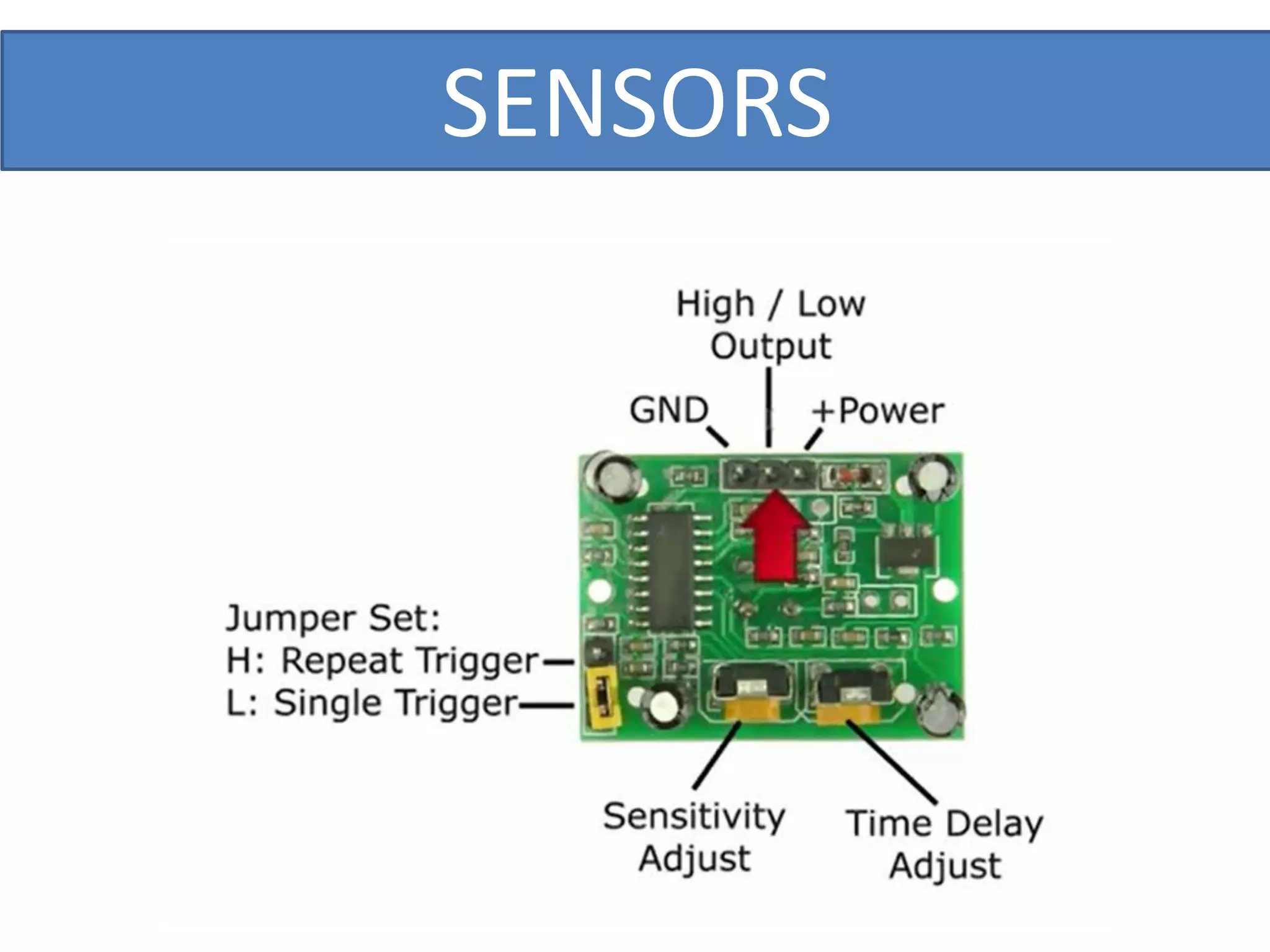
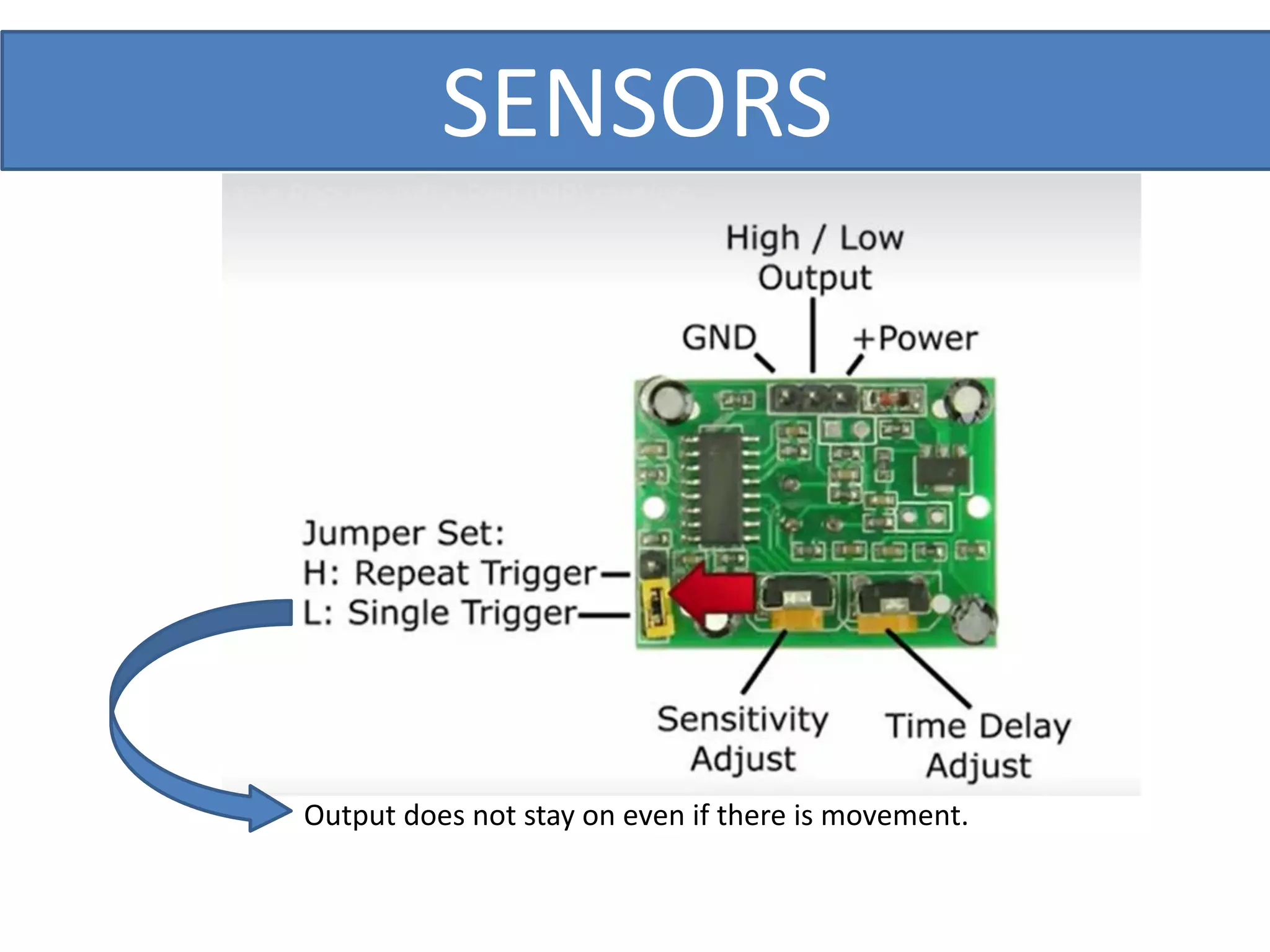
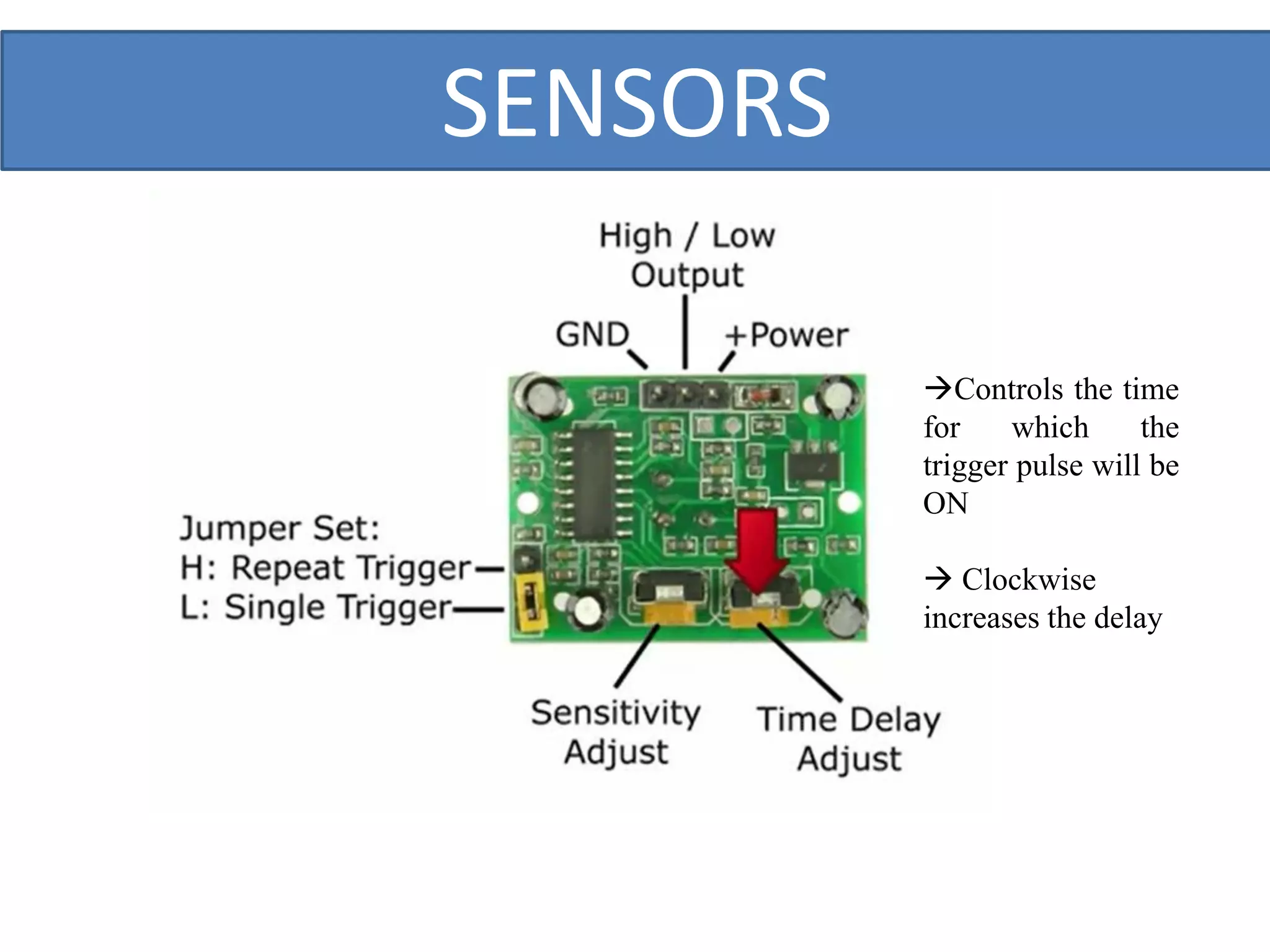
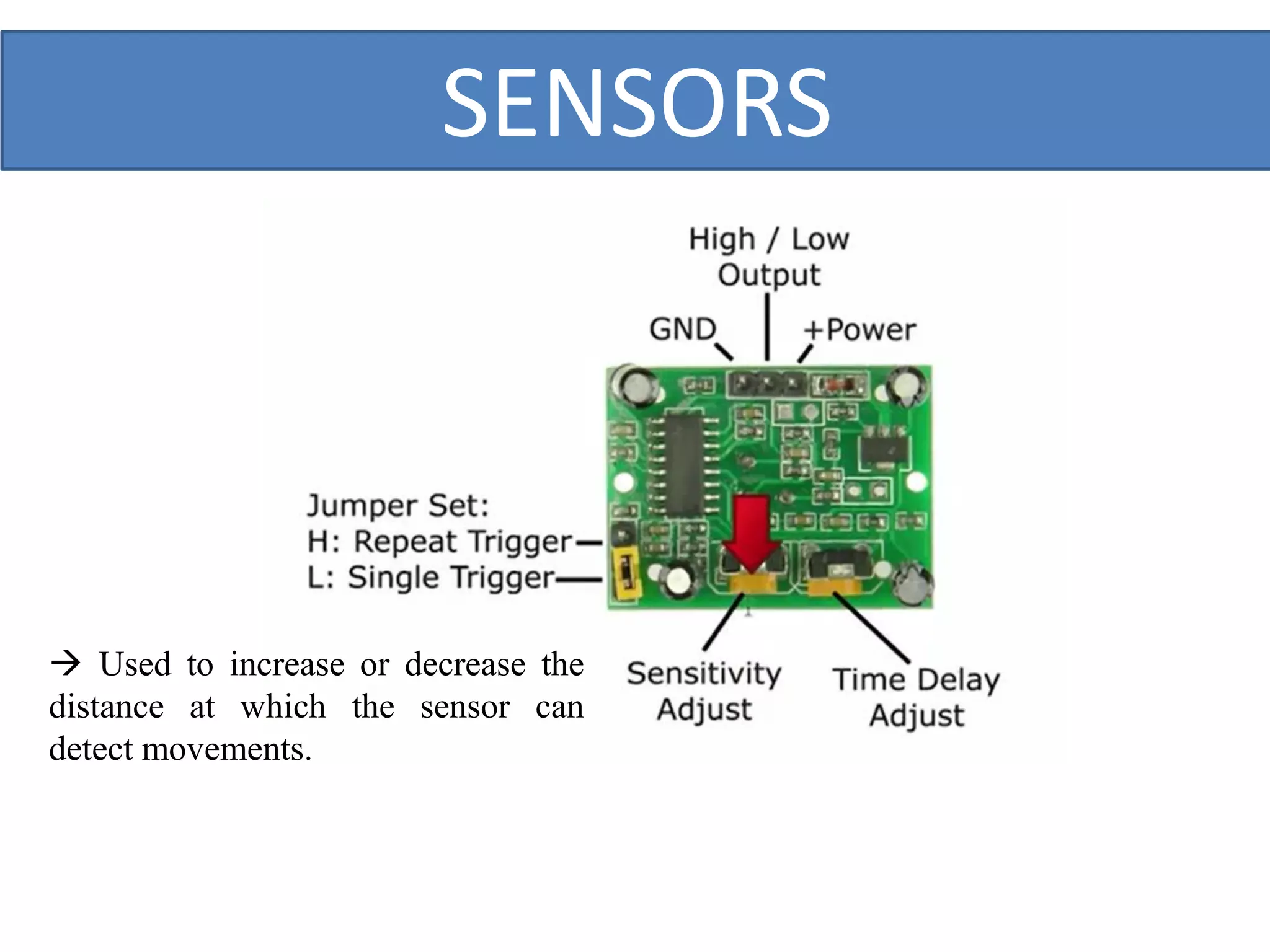
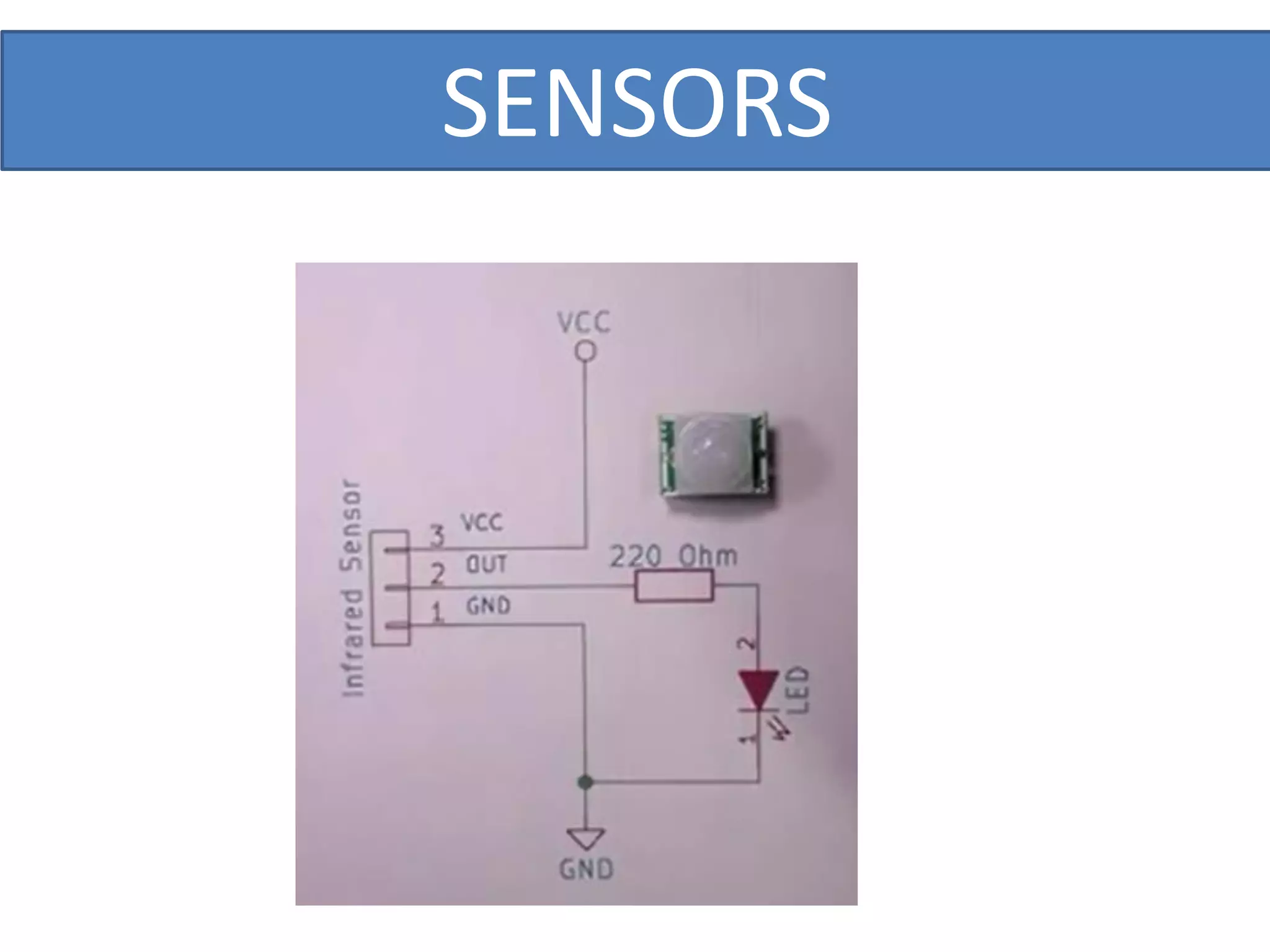
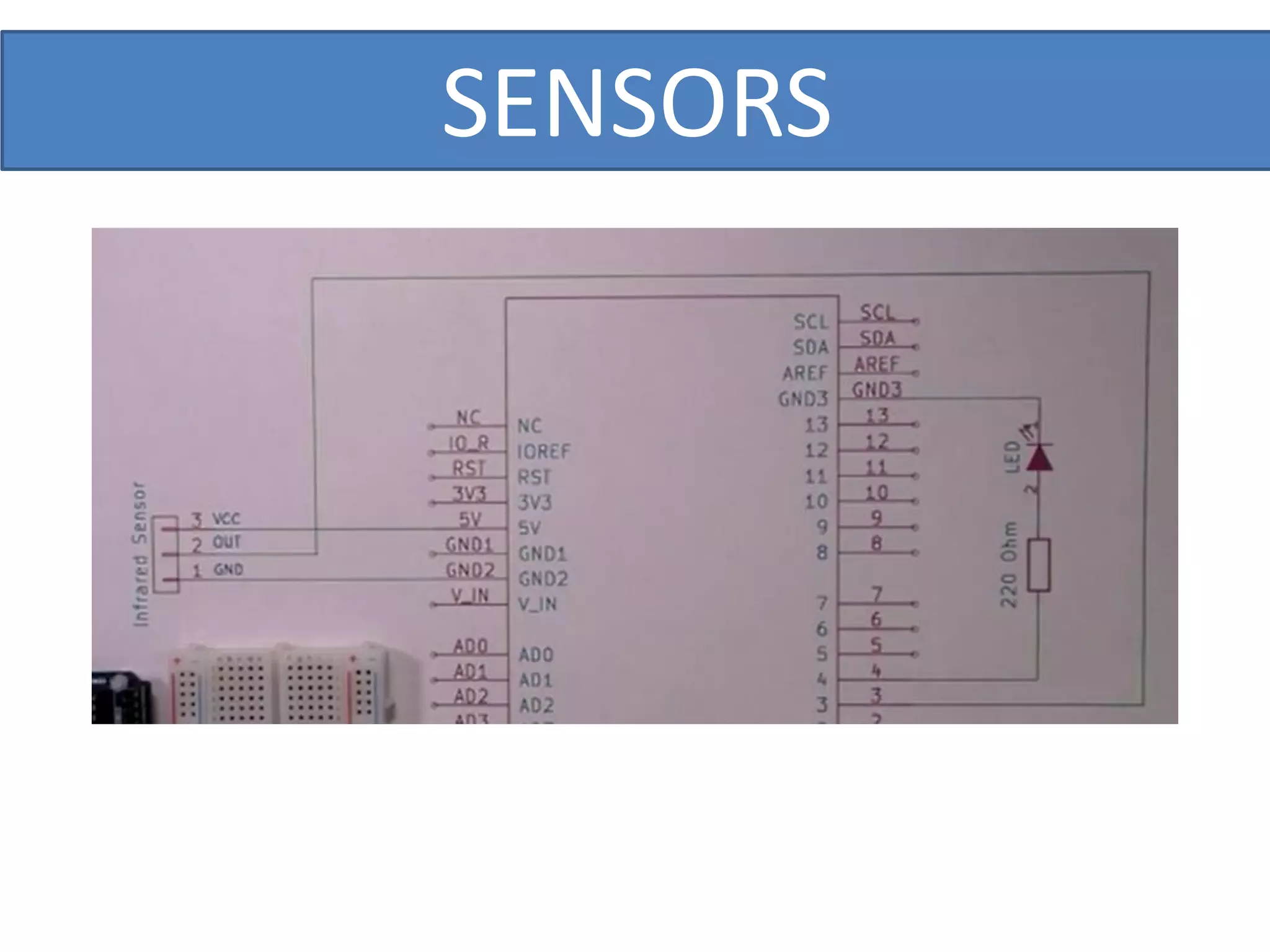
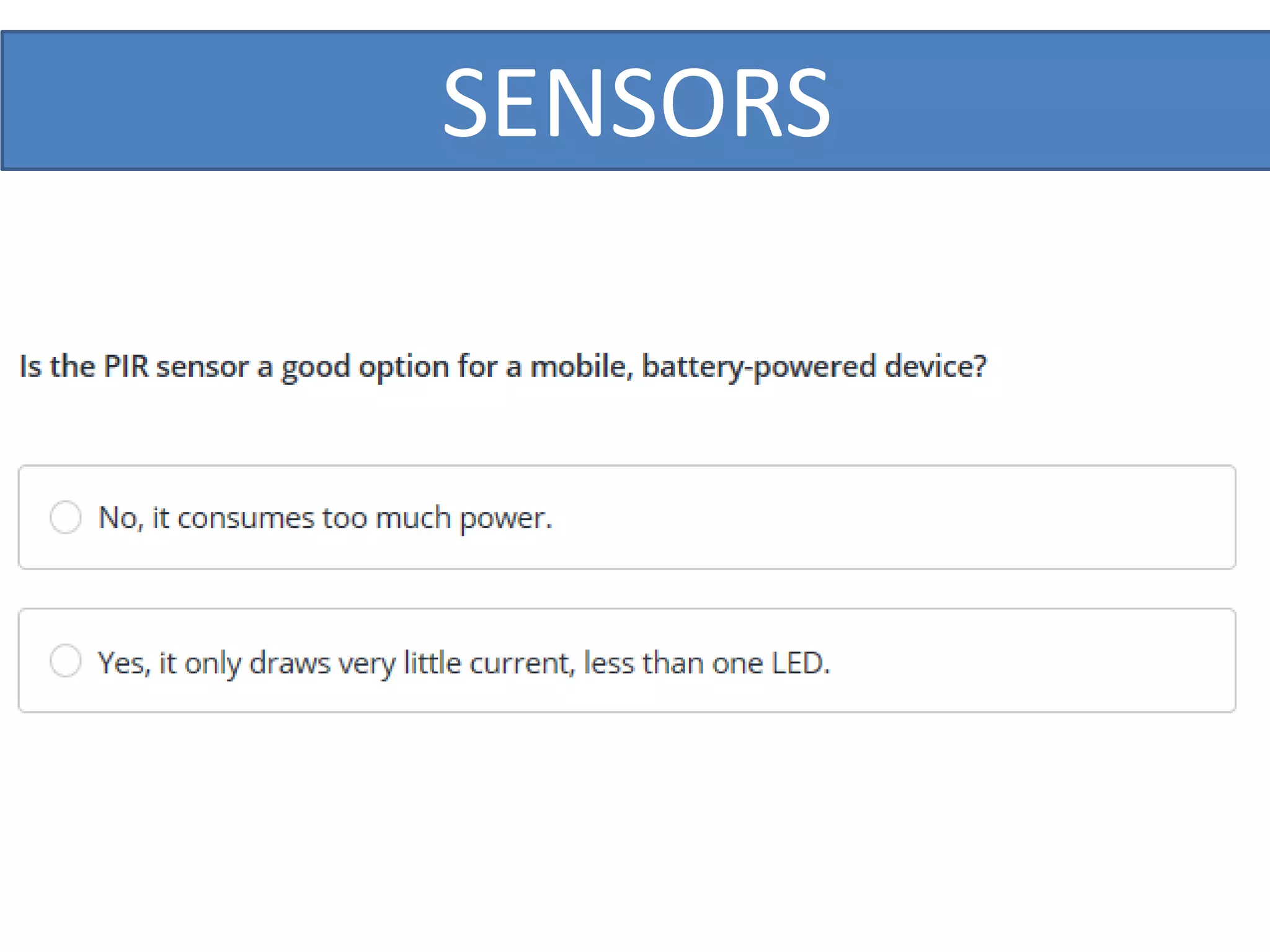
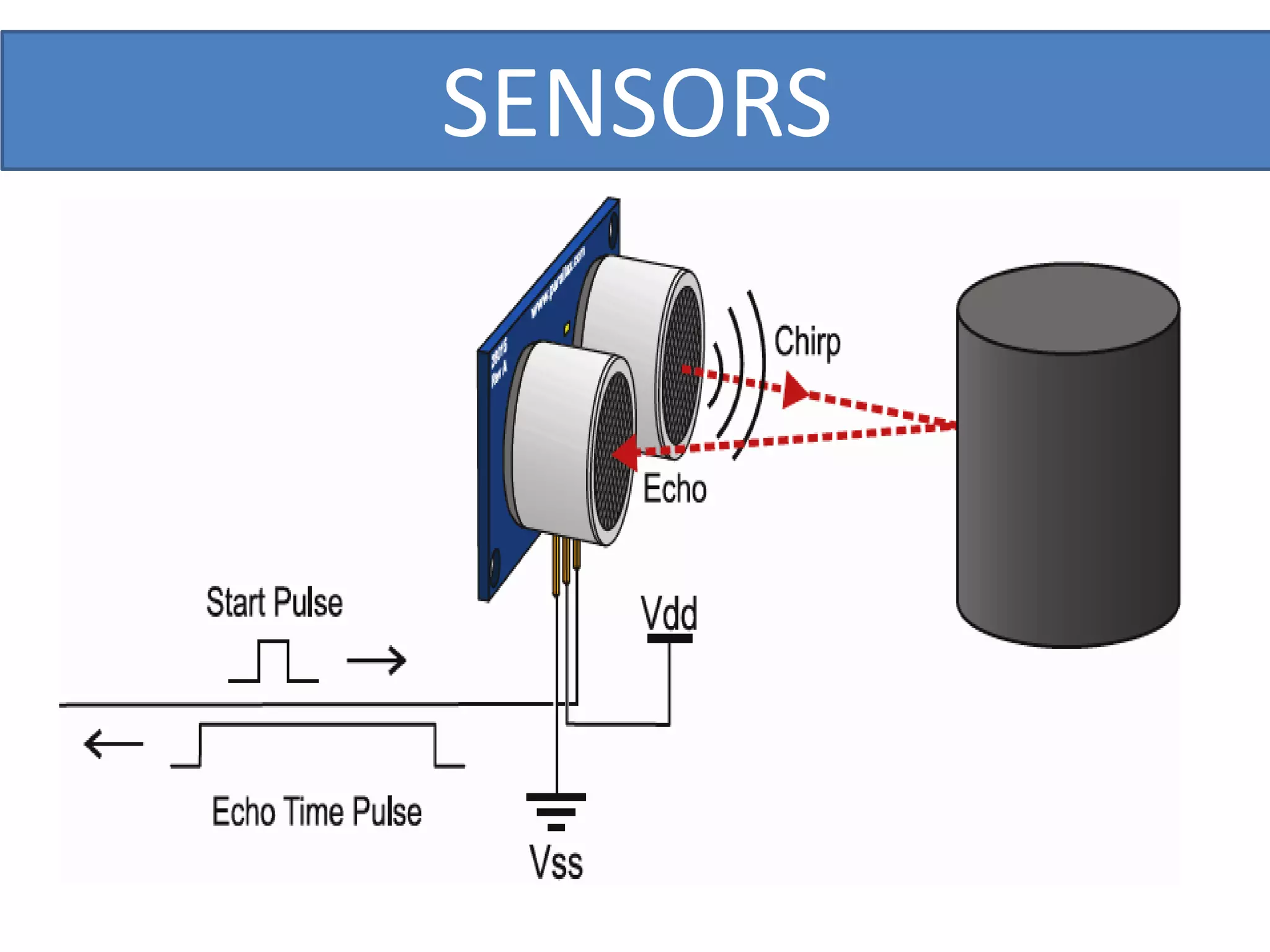
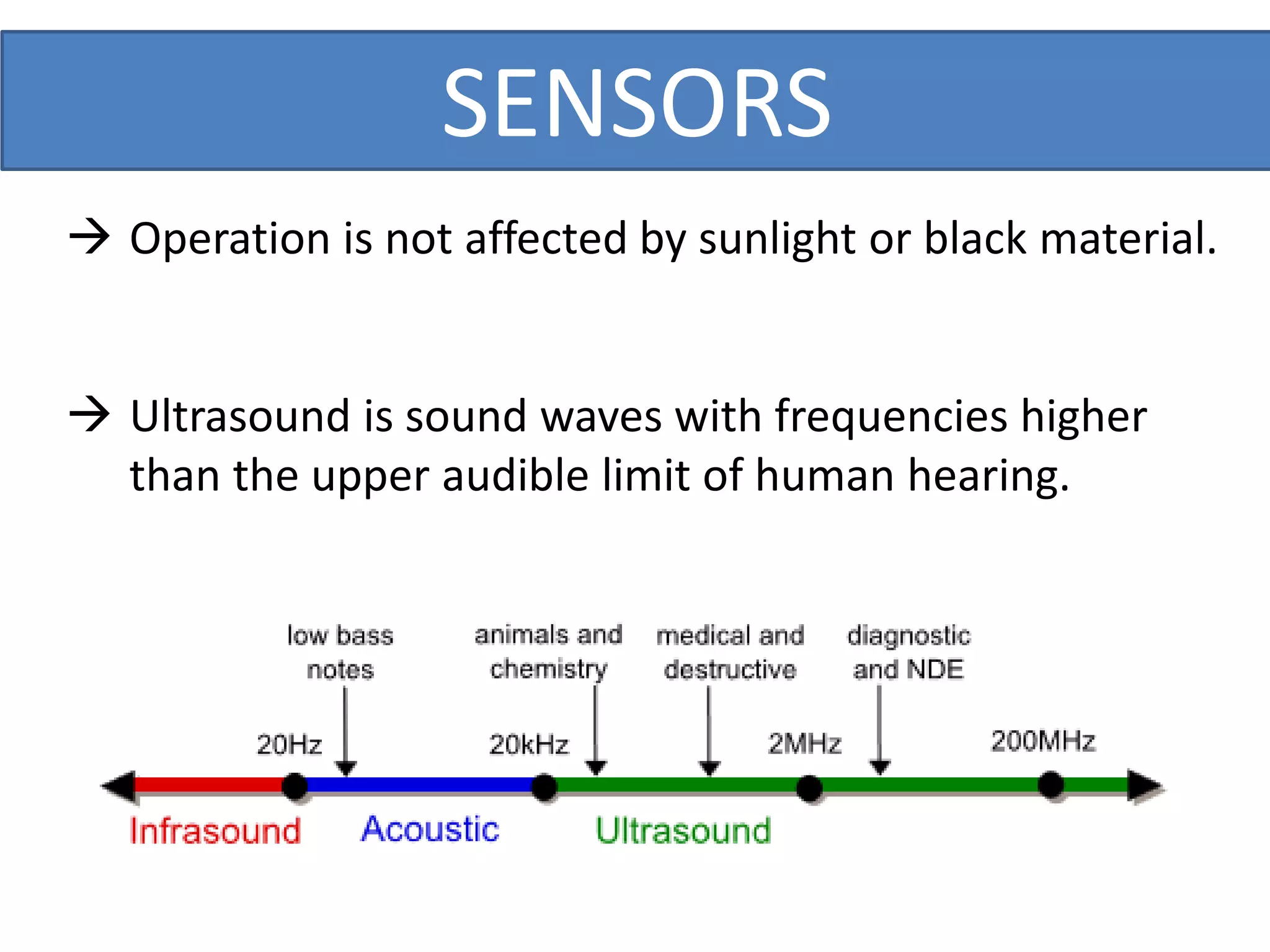
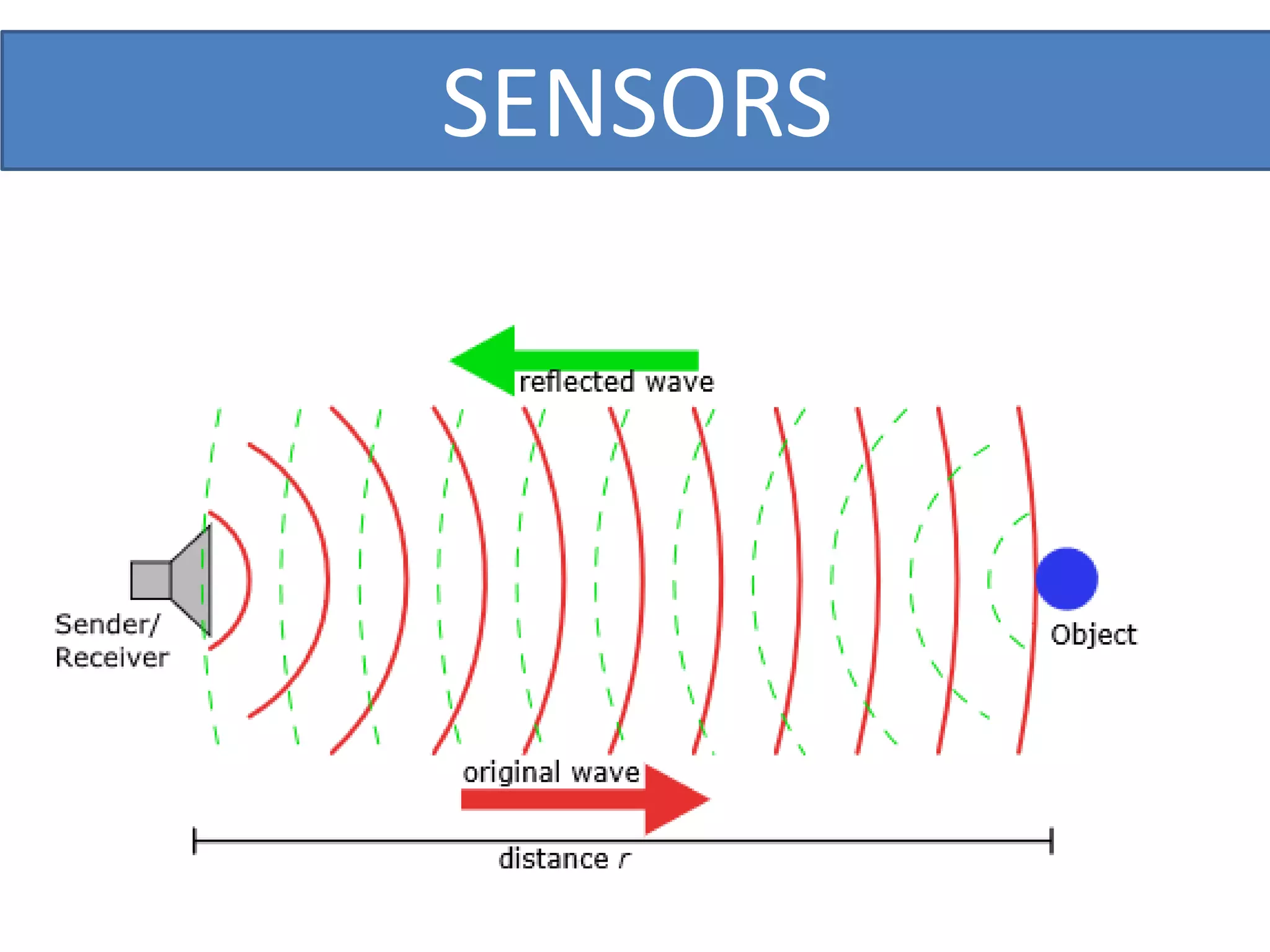
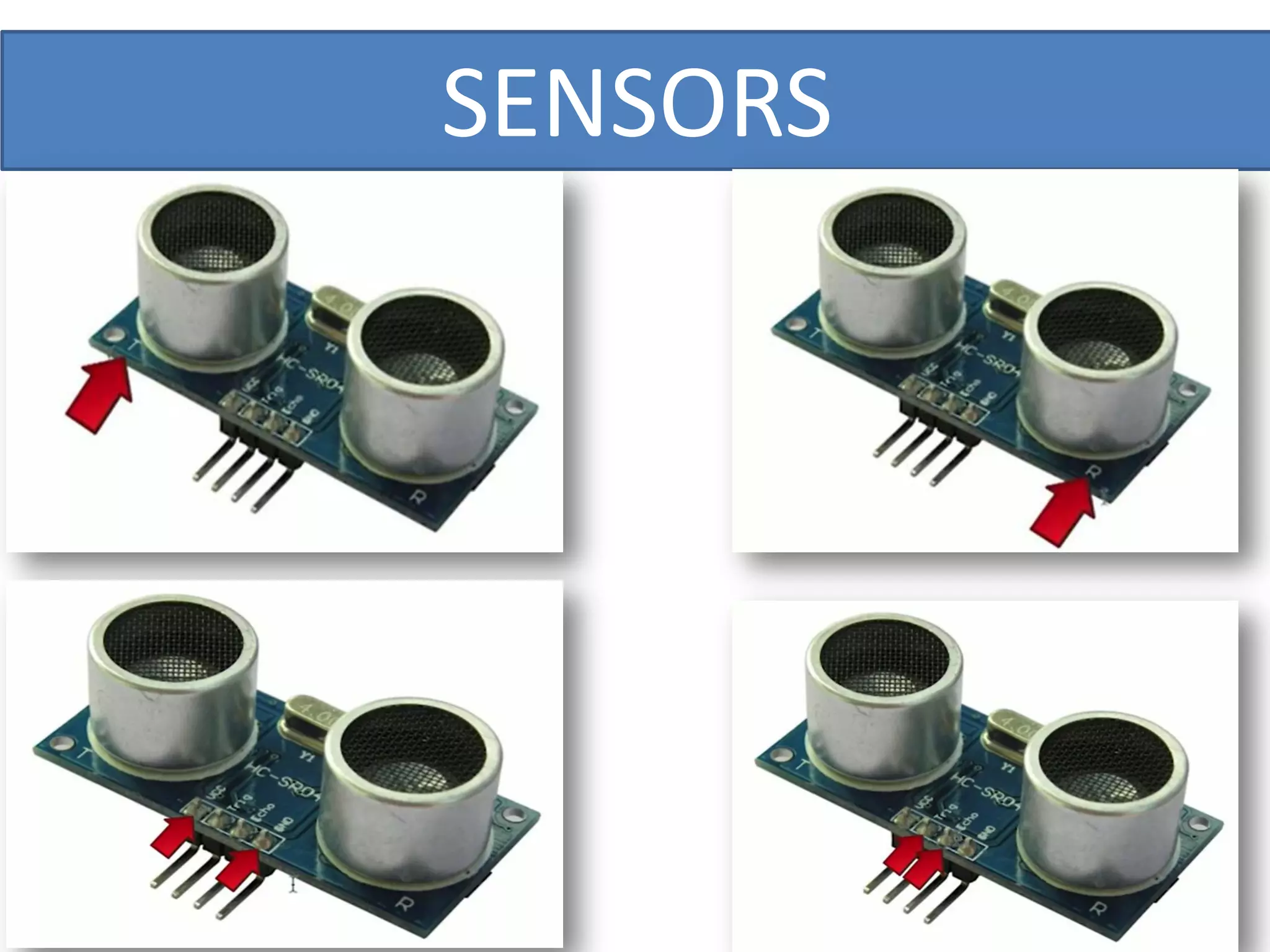
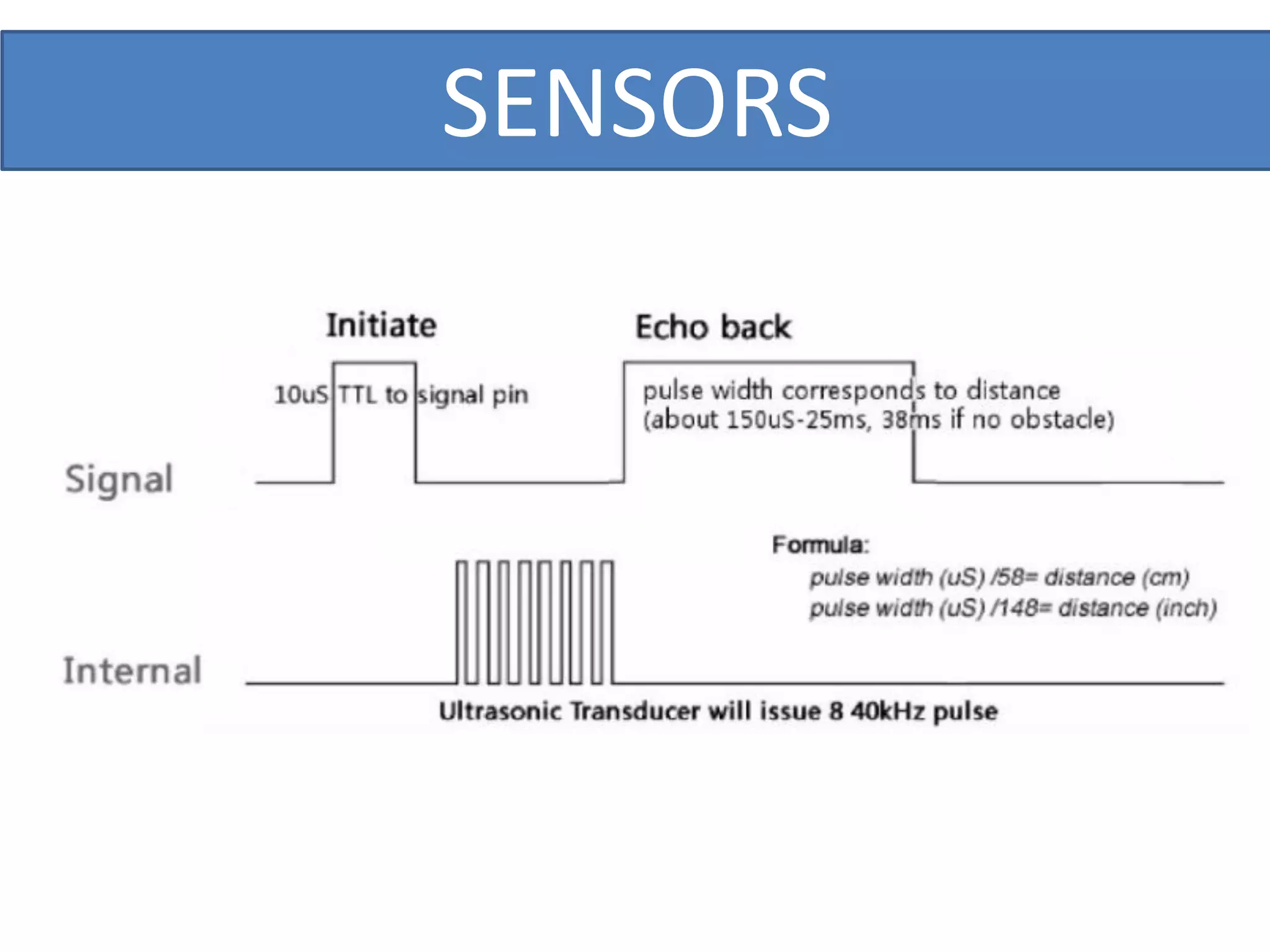
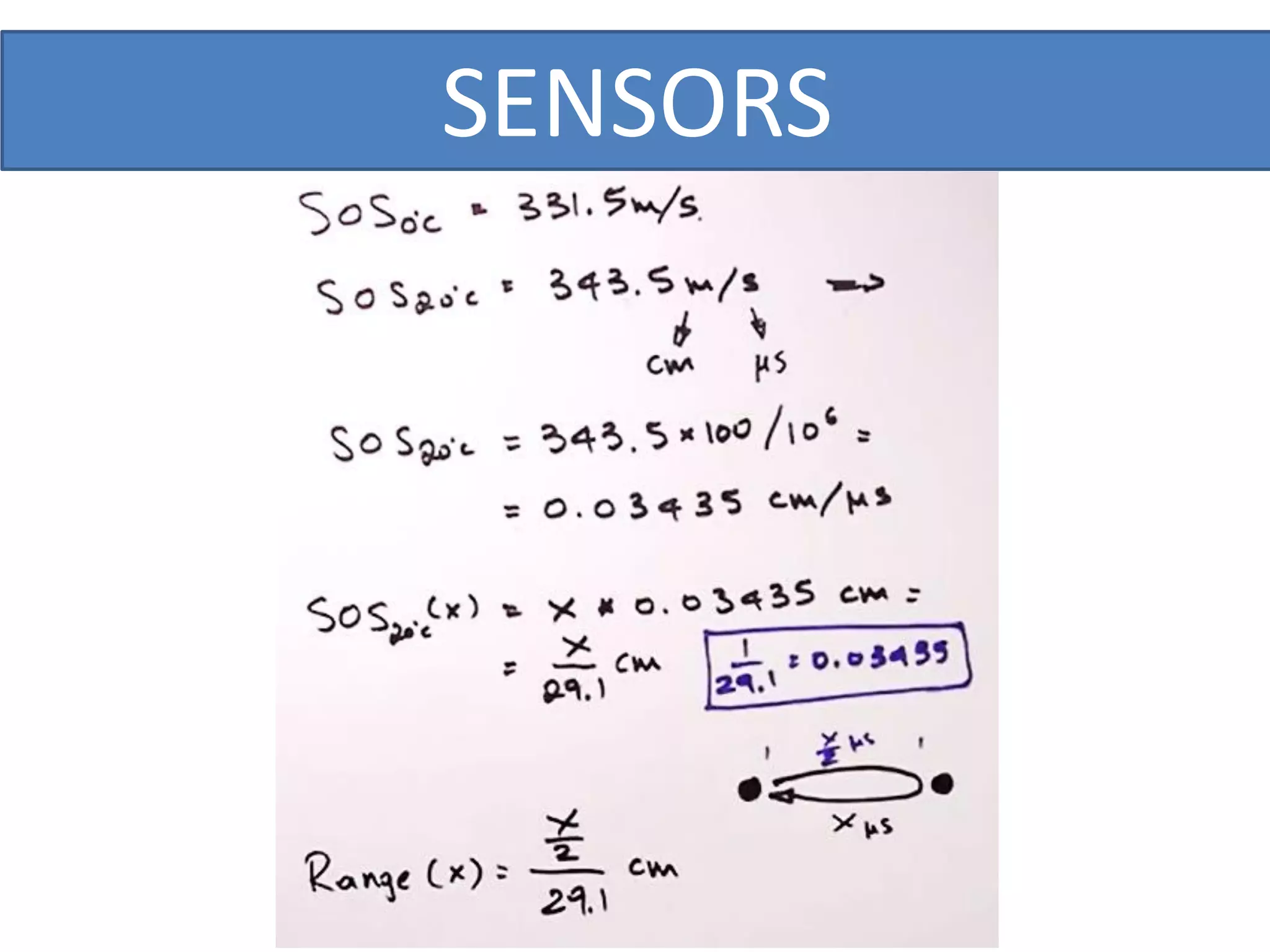
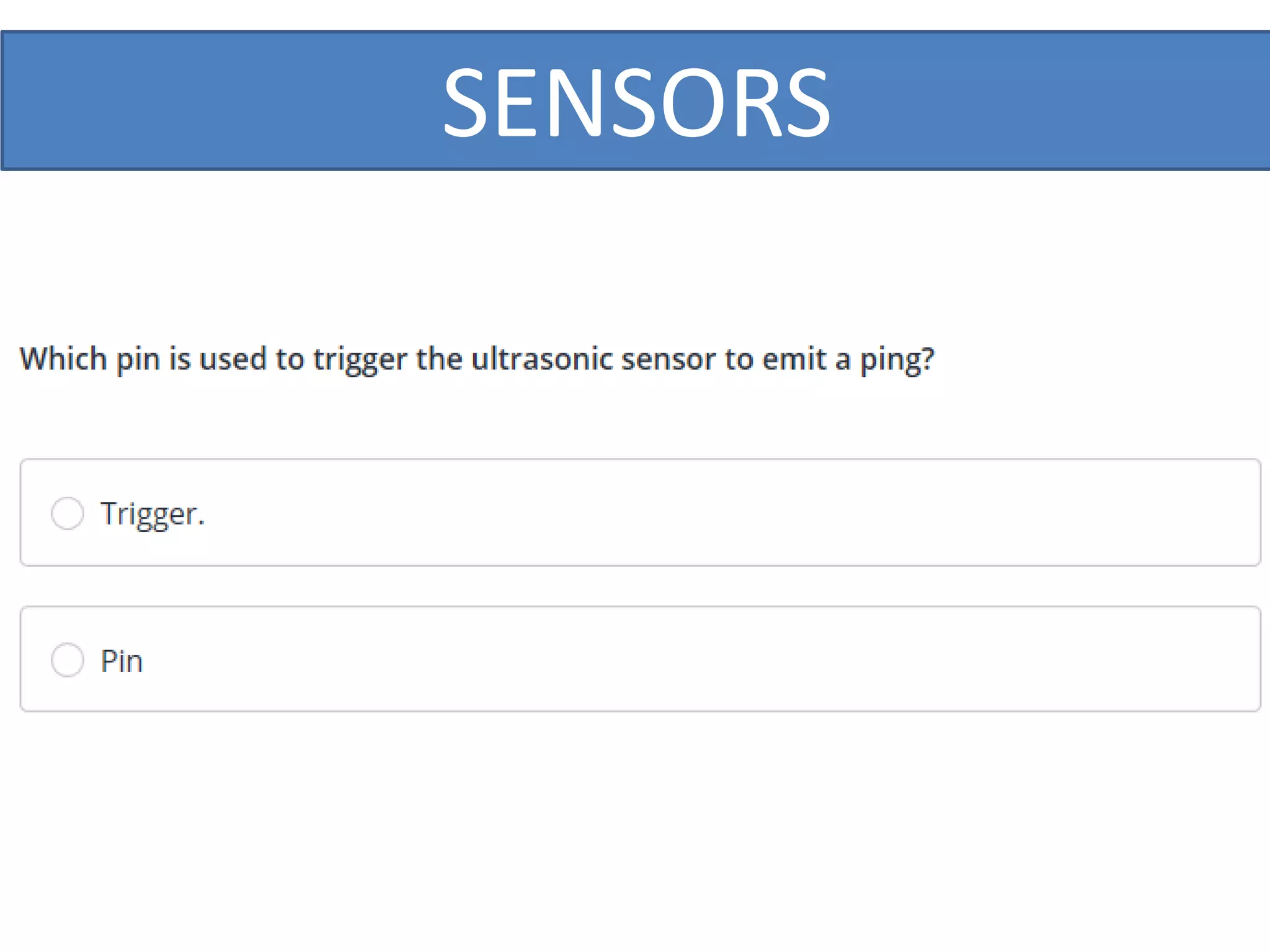
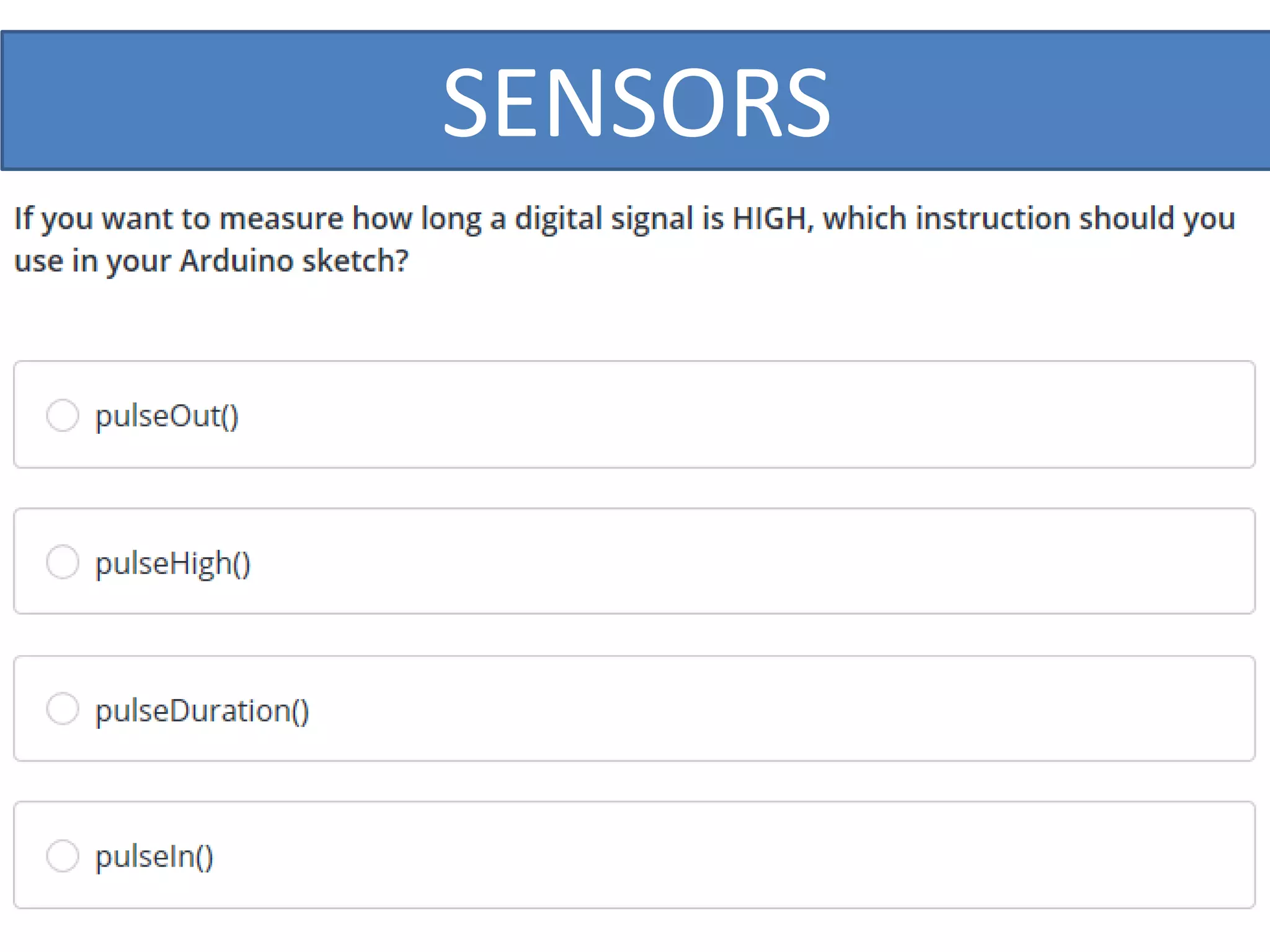
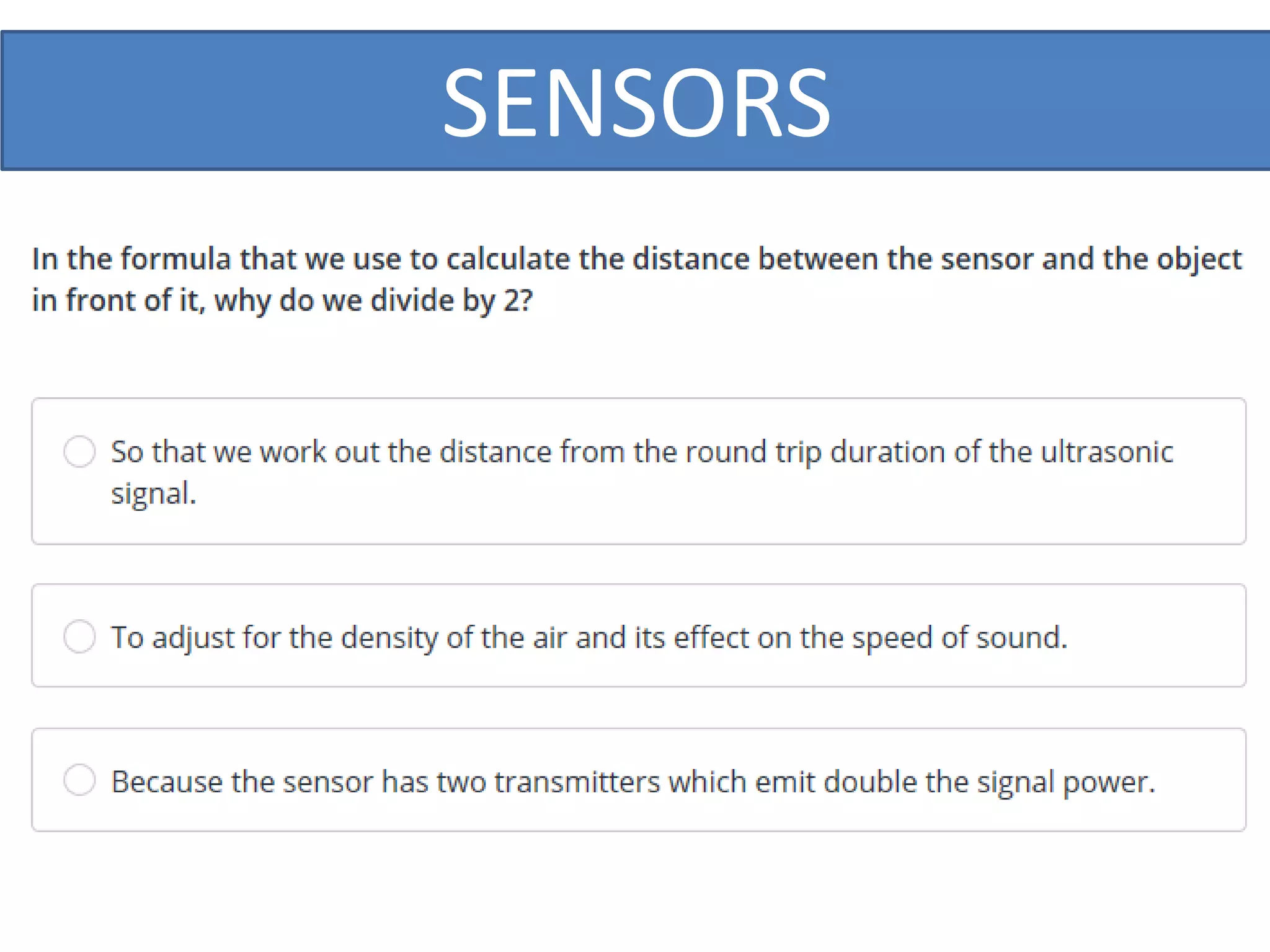
This document outlines a five-day short course on Arduino programming fundamentals and the Proteus Design Suite, focusing on various types of sensors and their applications in robotics and automation. It explains the principles behind different sensors, such as LDR, flex, temperature, and accelerometer sensors, and their necessity for providing environmental awareness, localization, and task-specific sensing in robotic systems. The document also details specific sensor functionalities and includes examples of applications in both industry and domestic settings.