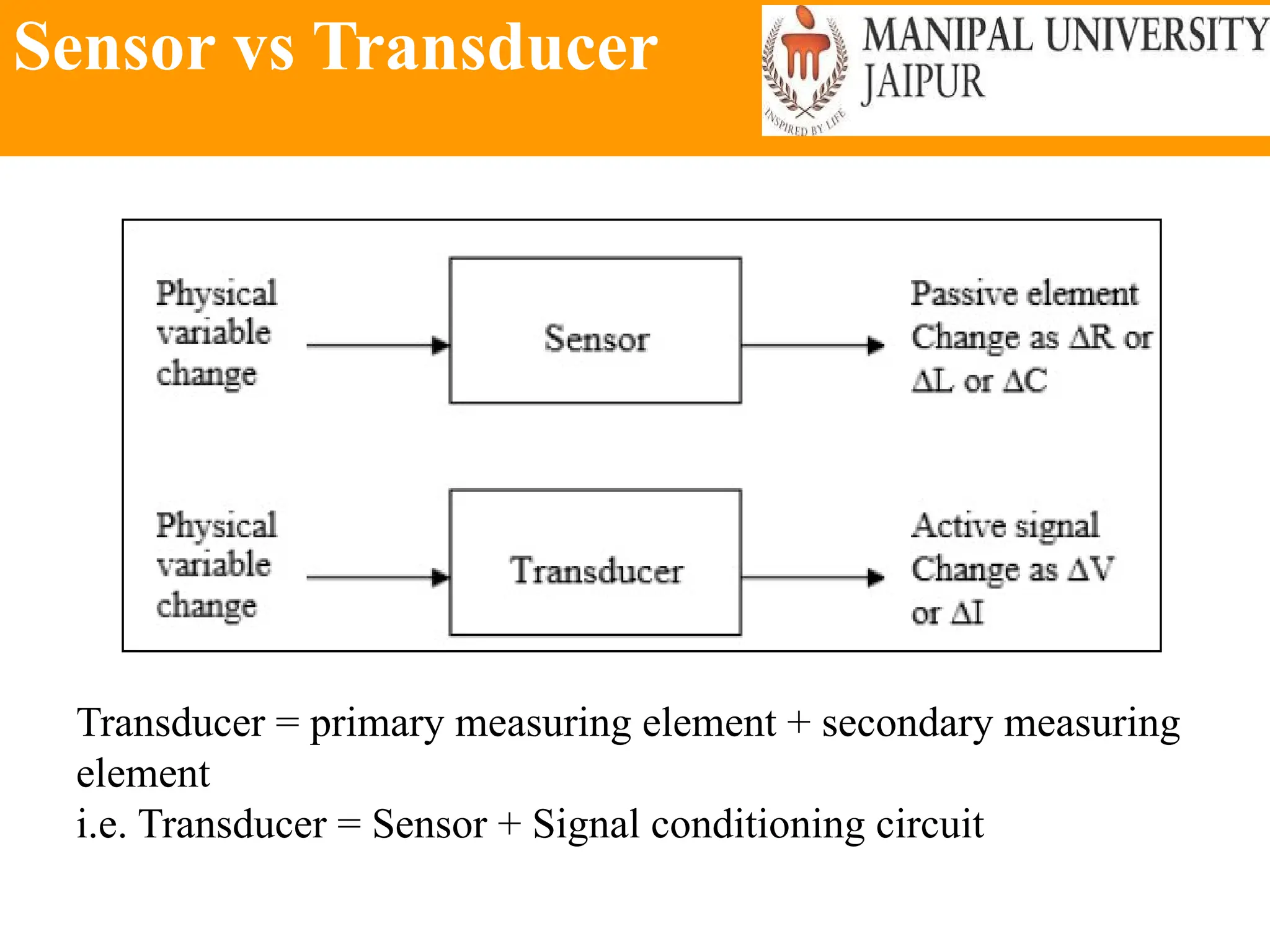
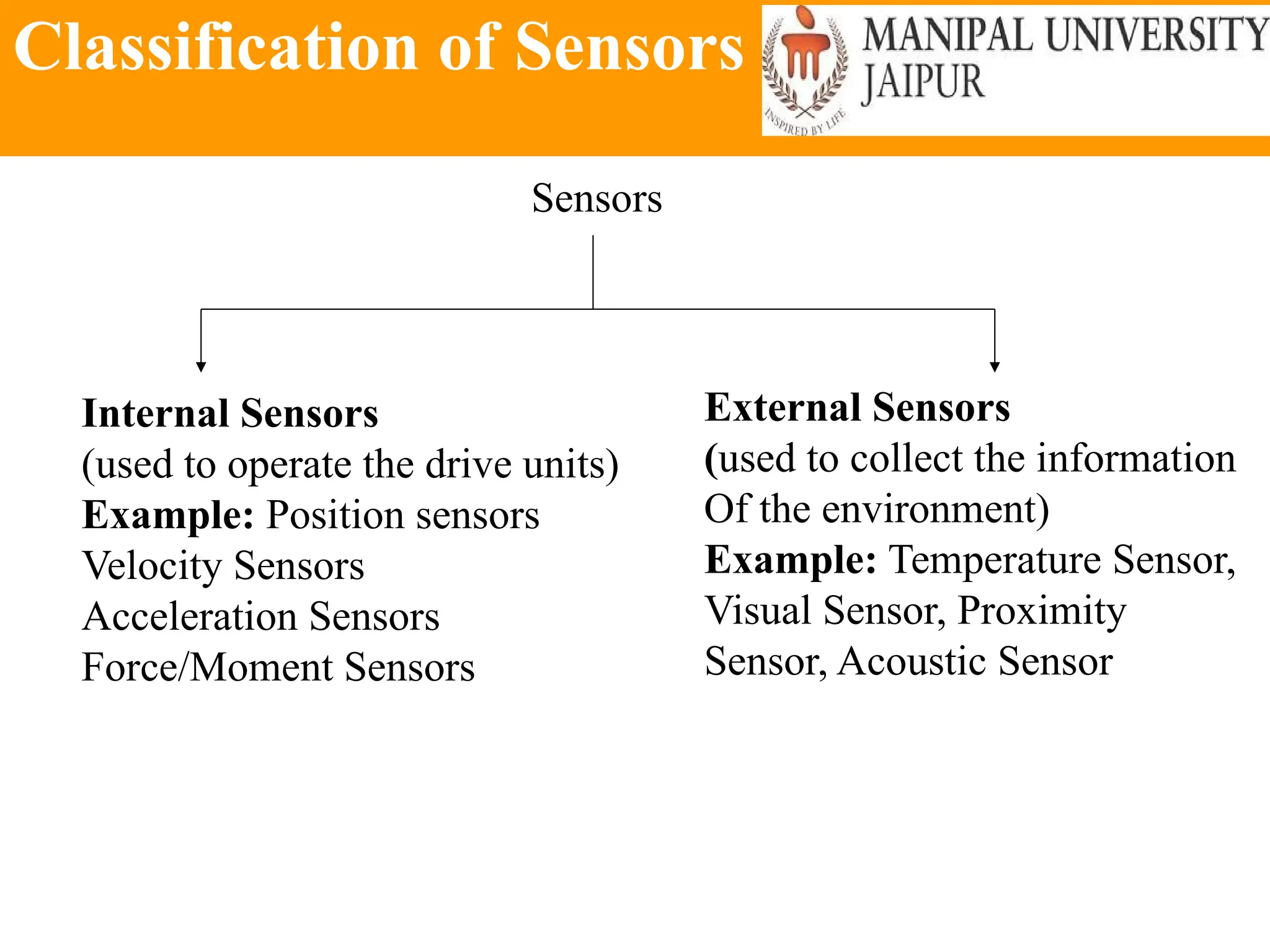
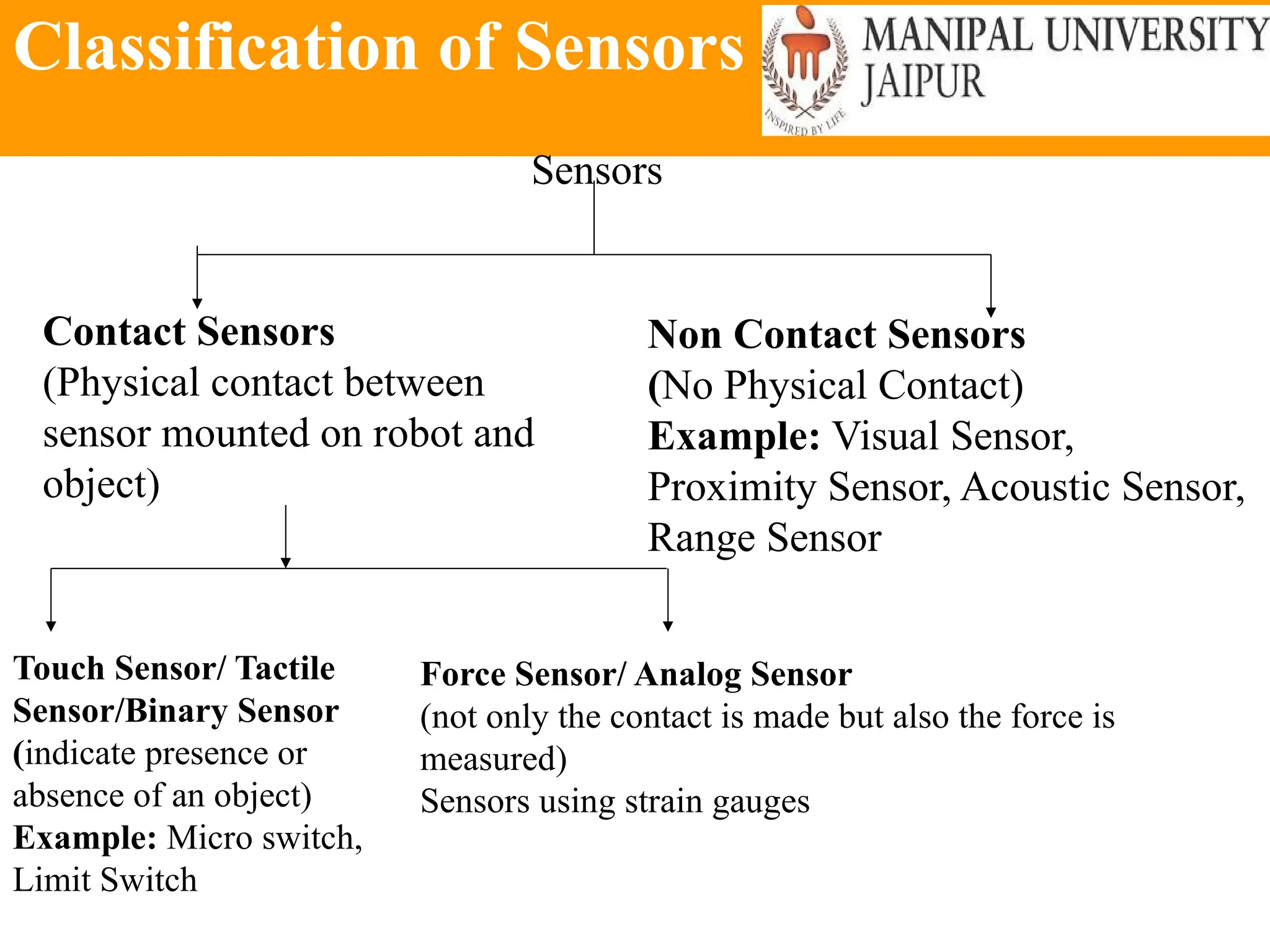
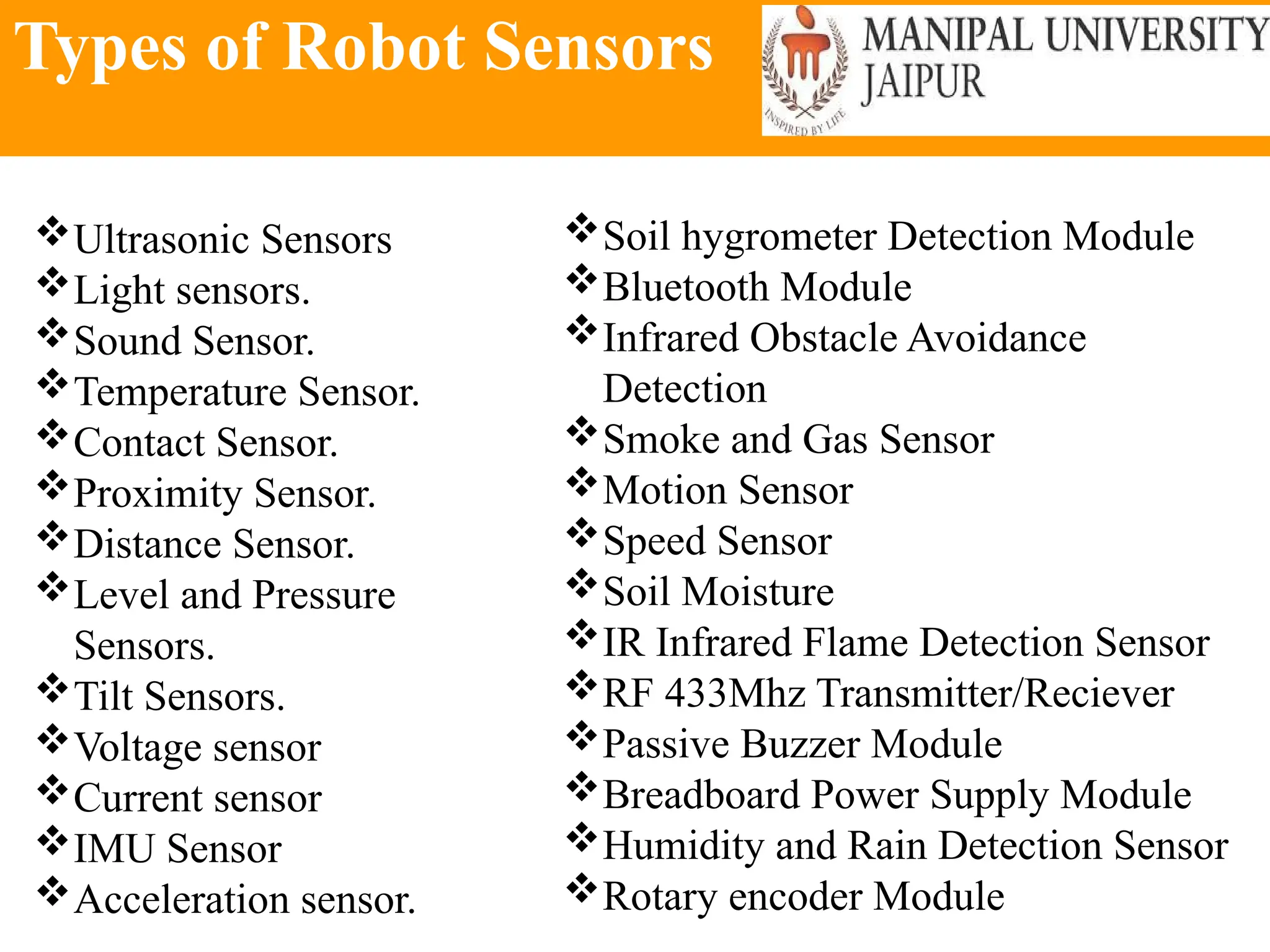
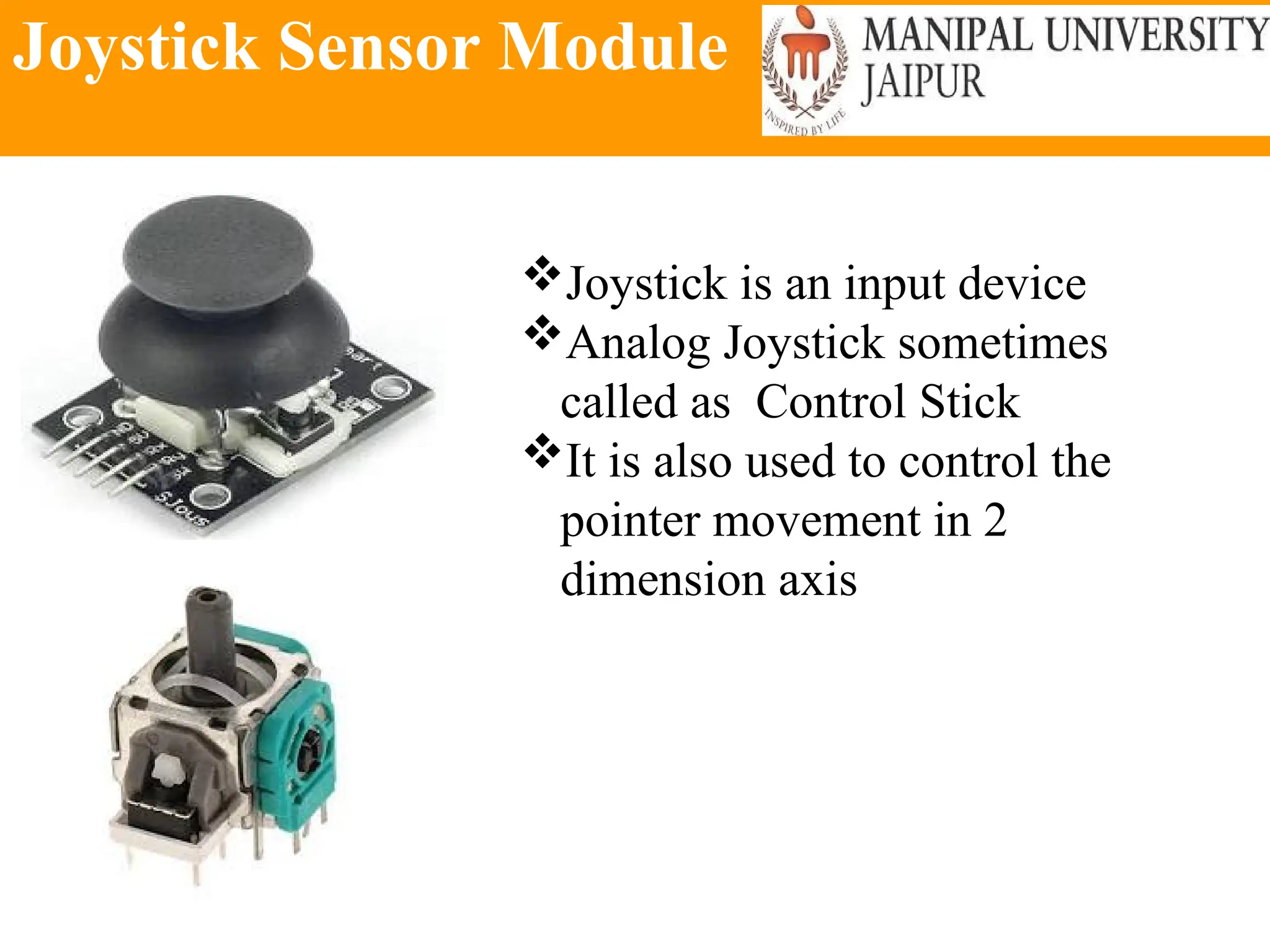
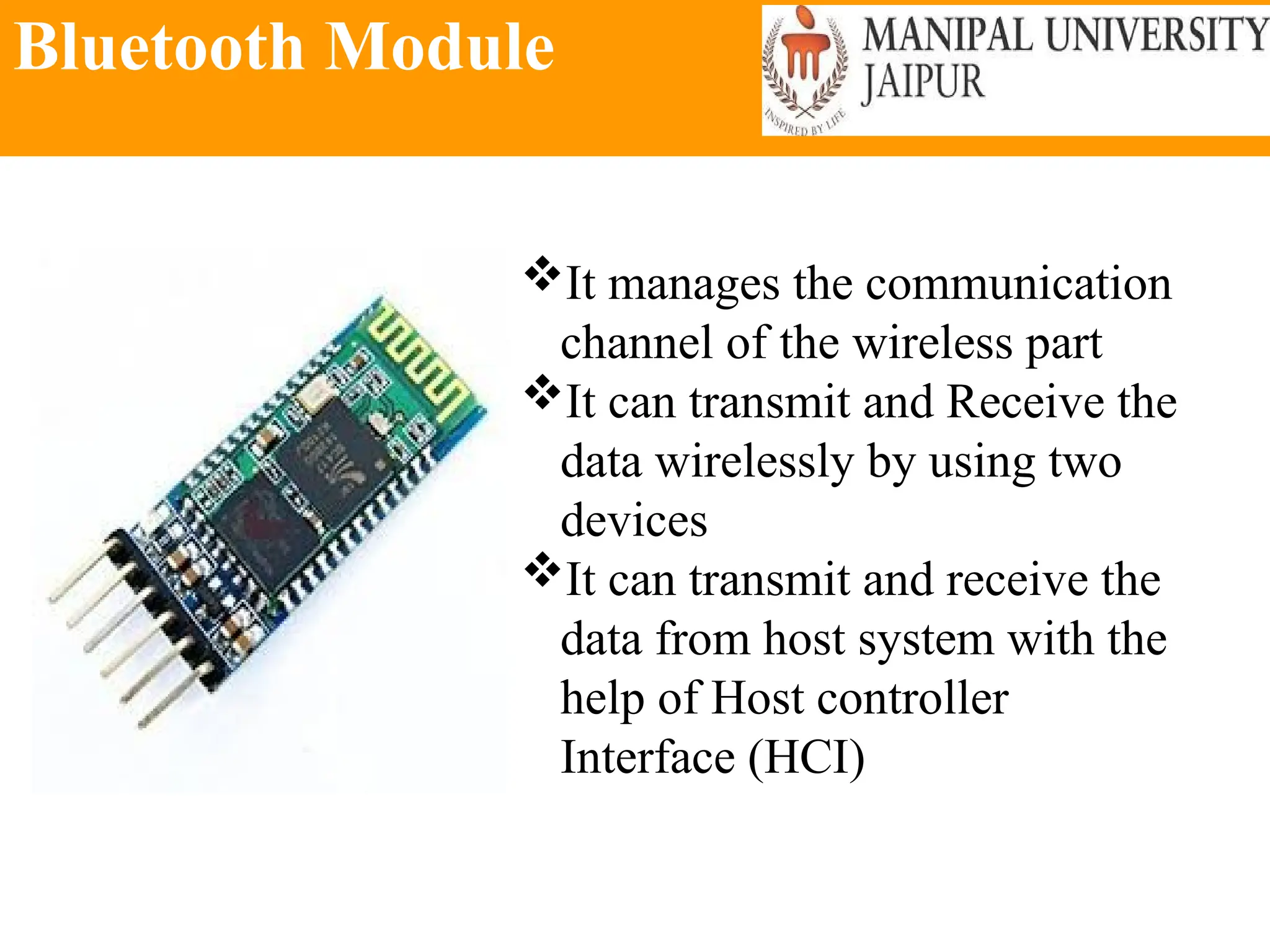
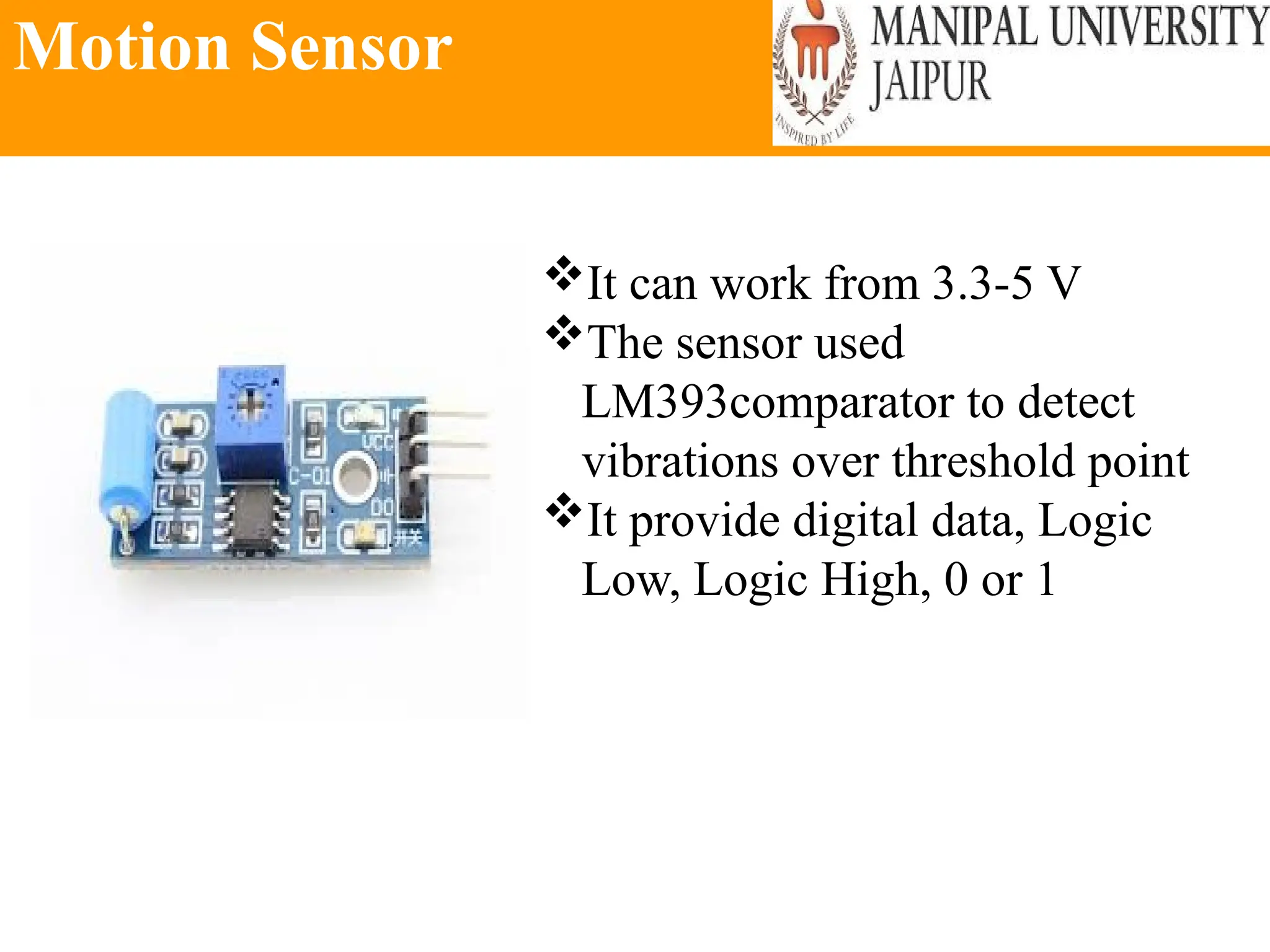
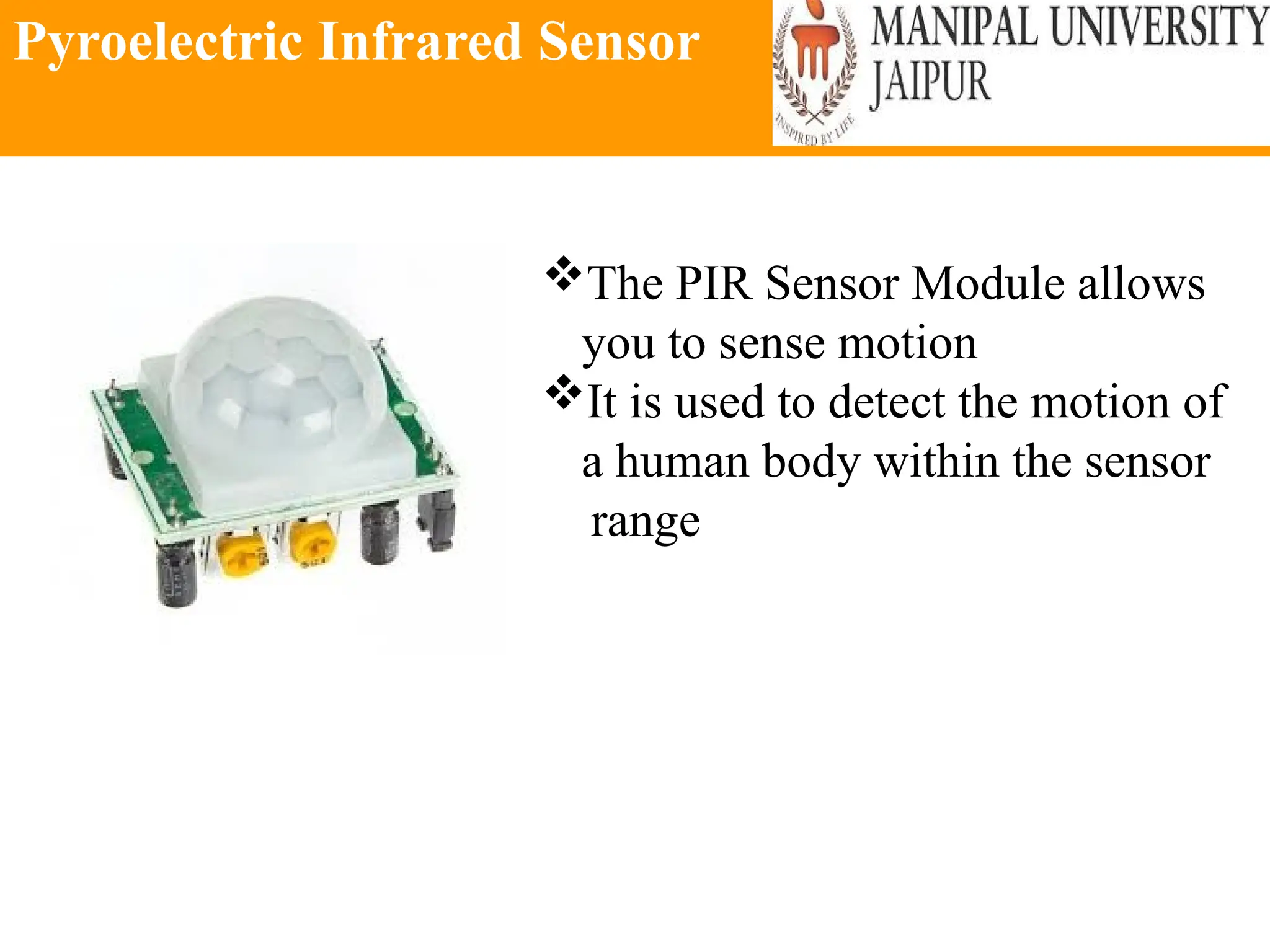
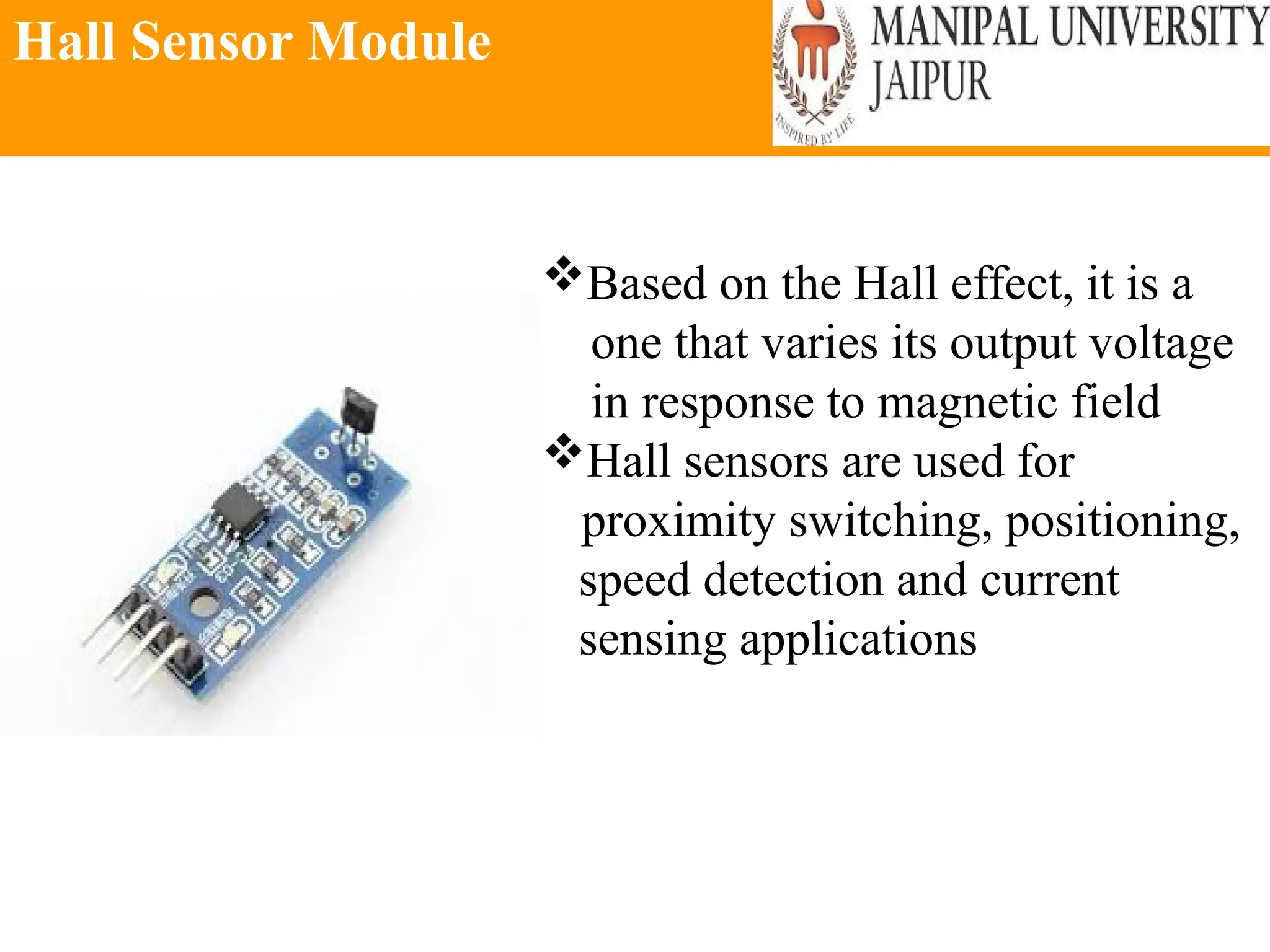
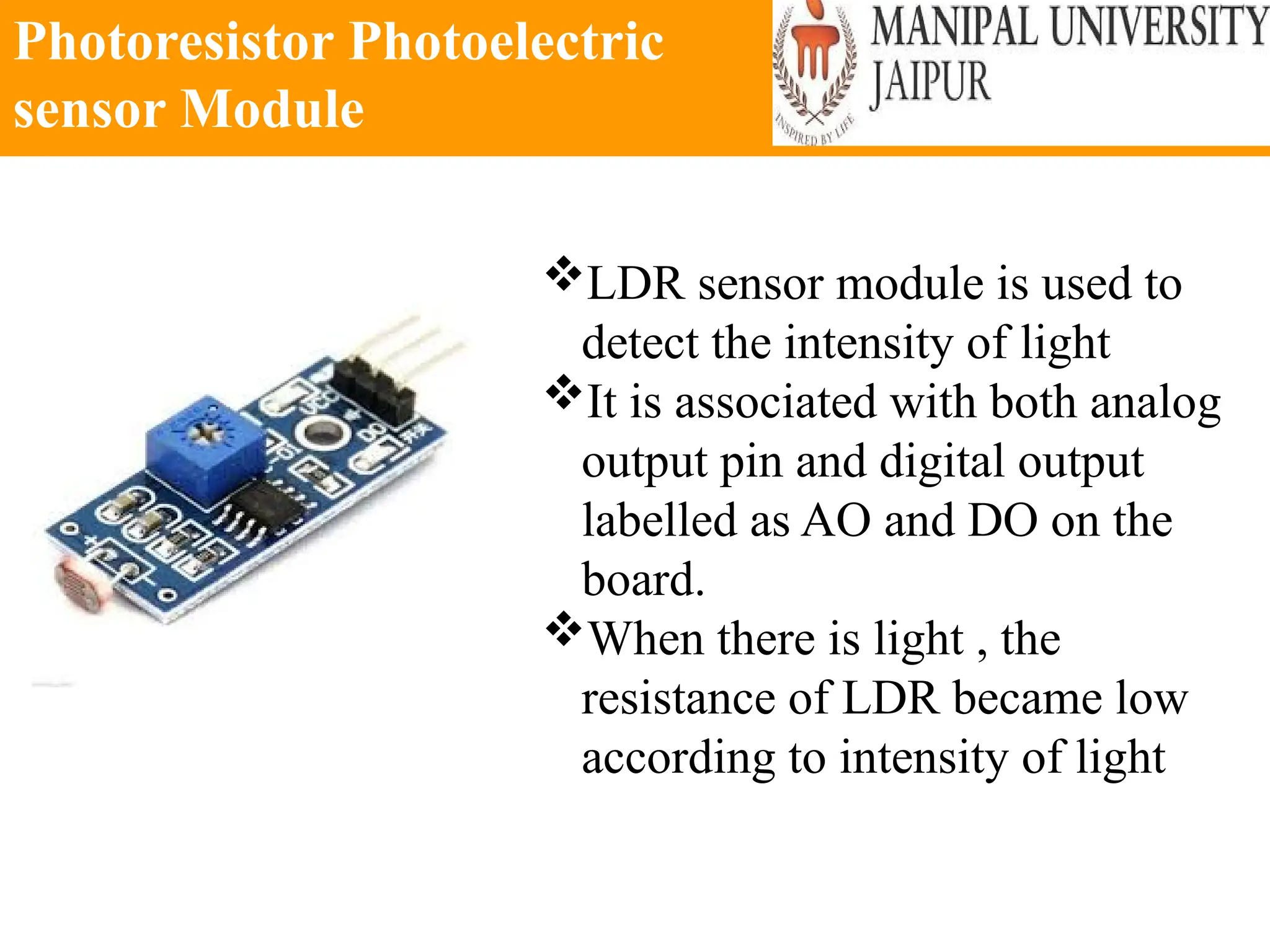
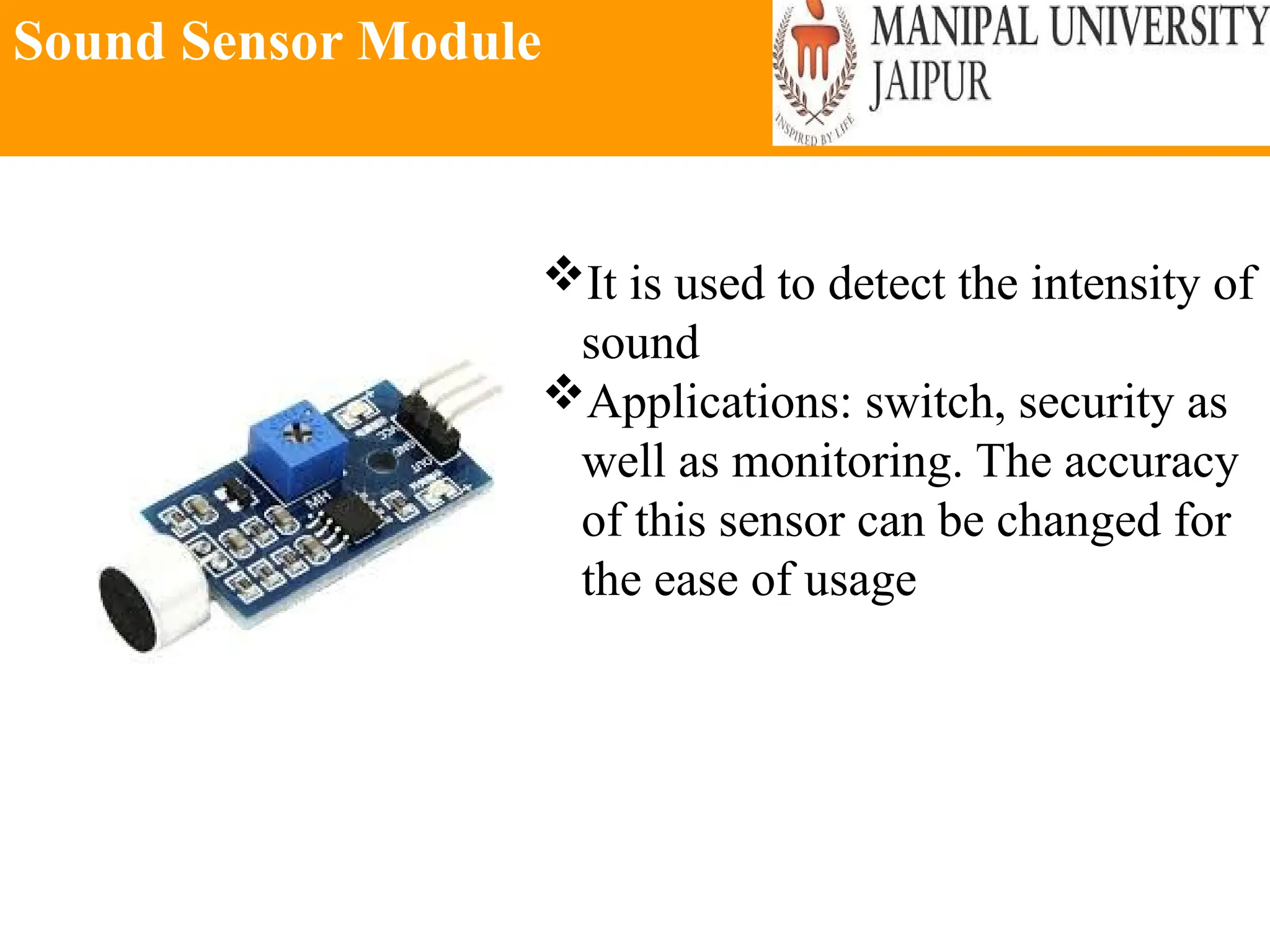
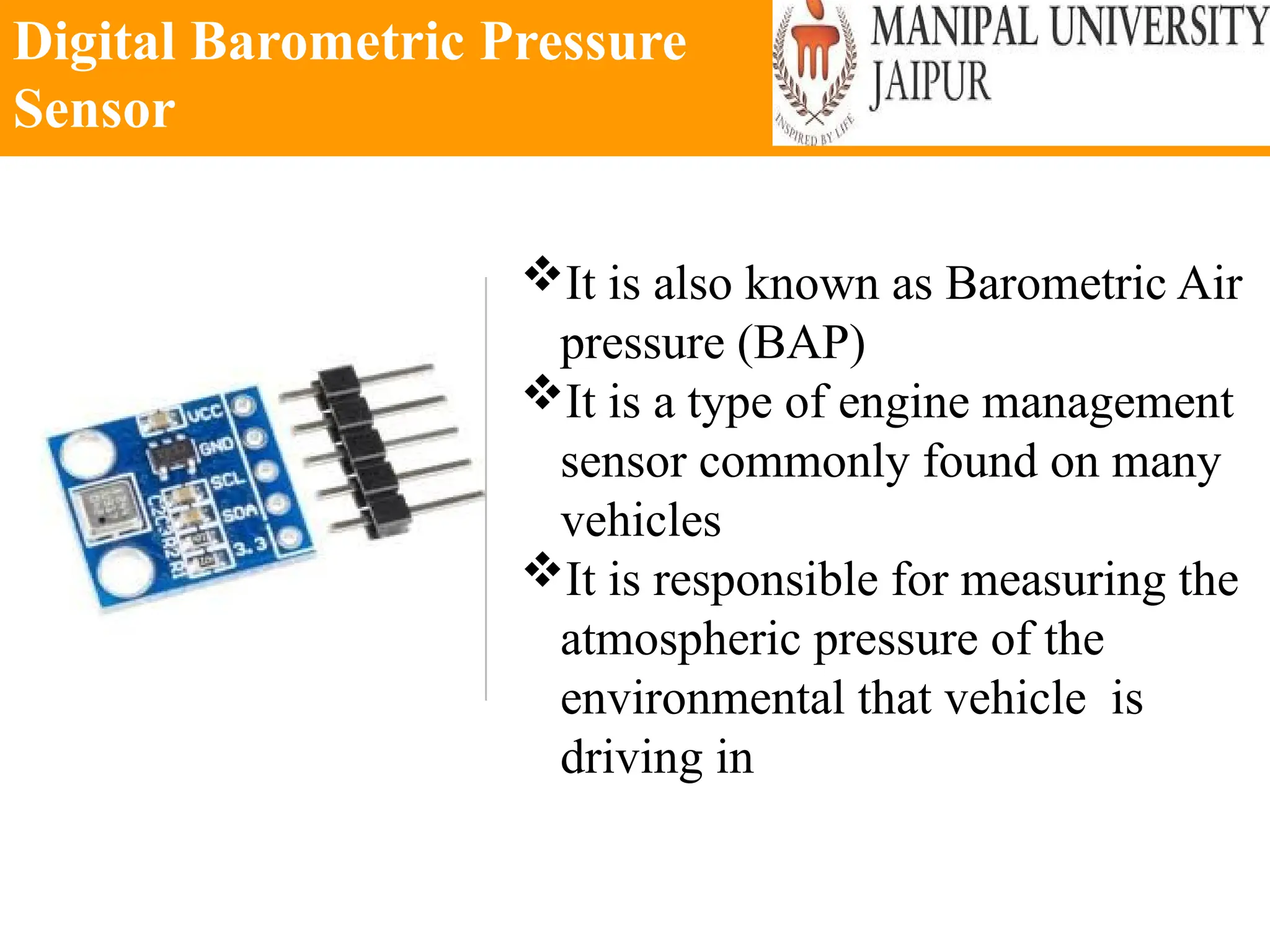
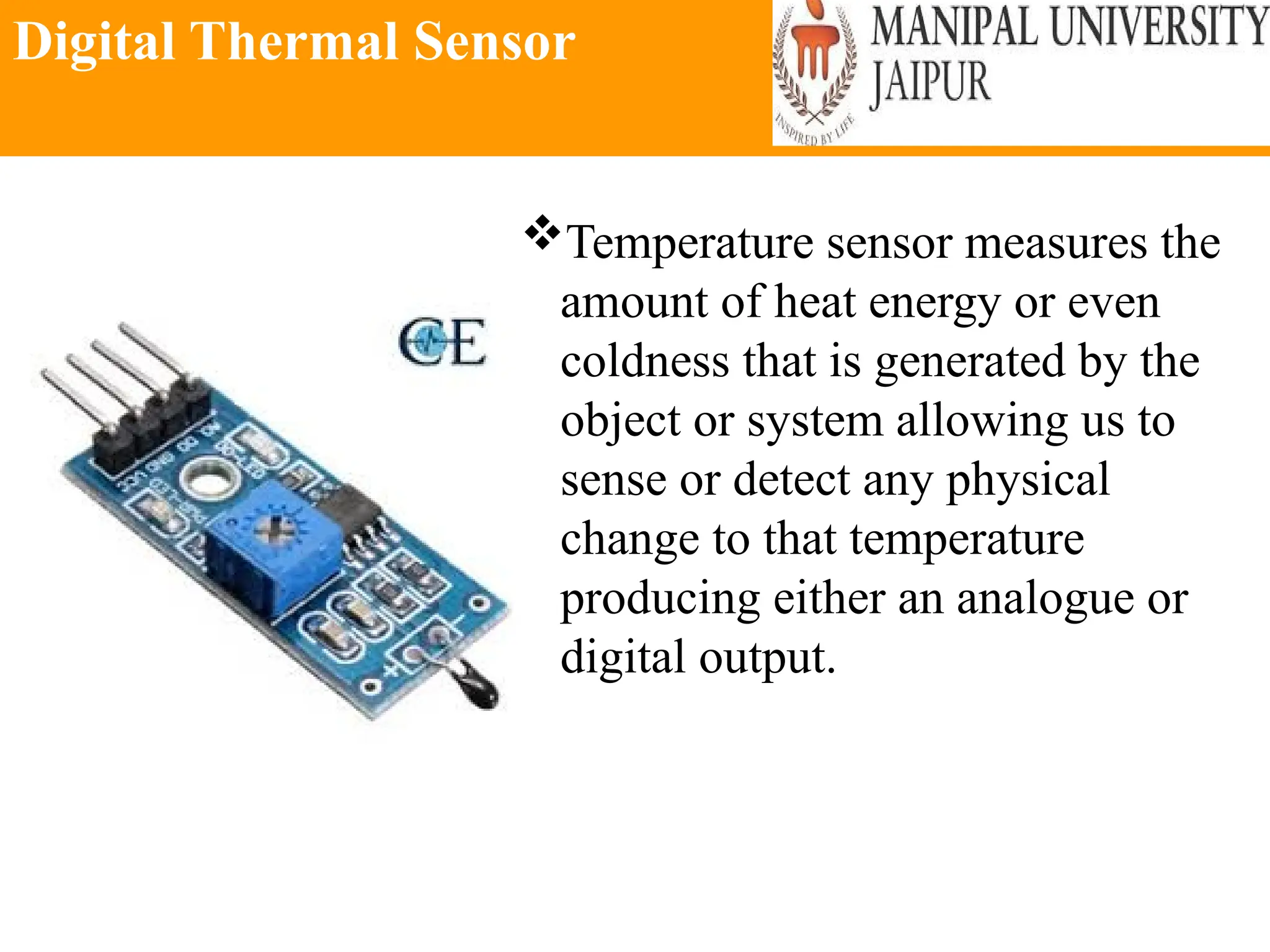
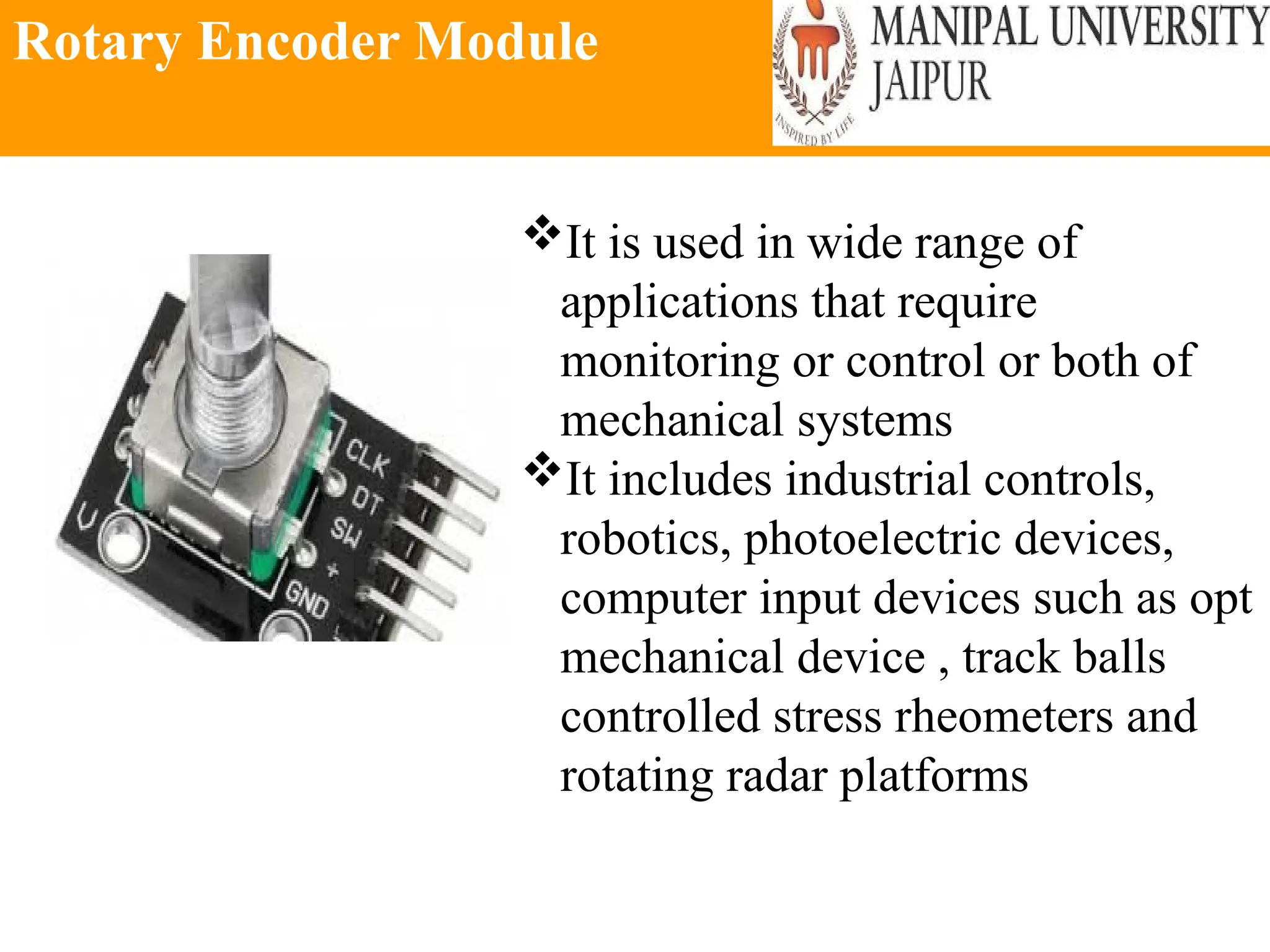
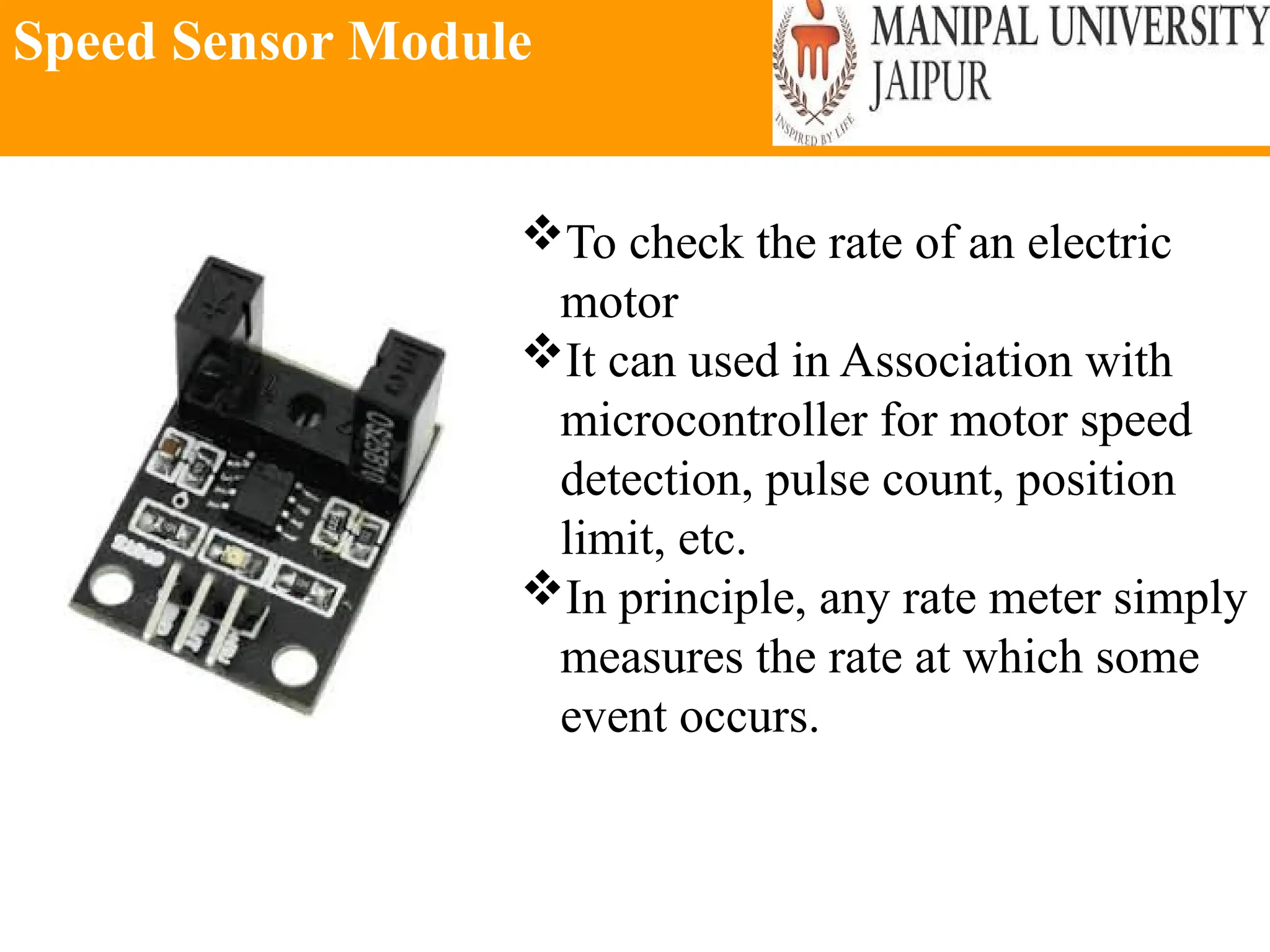
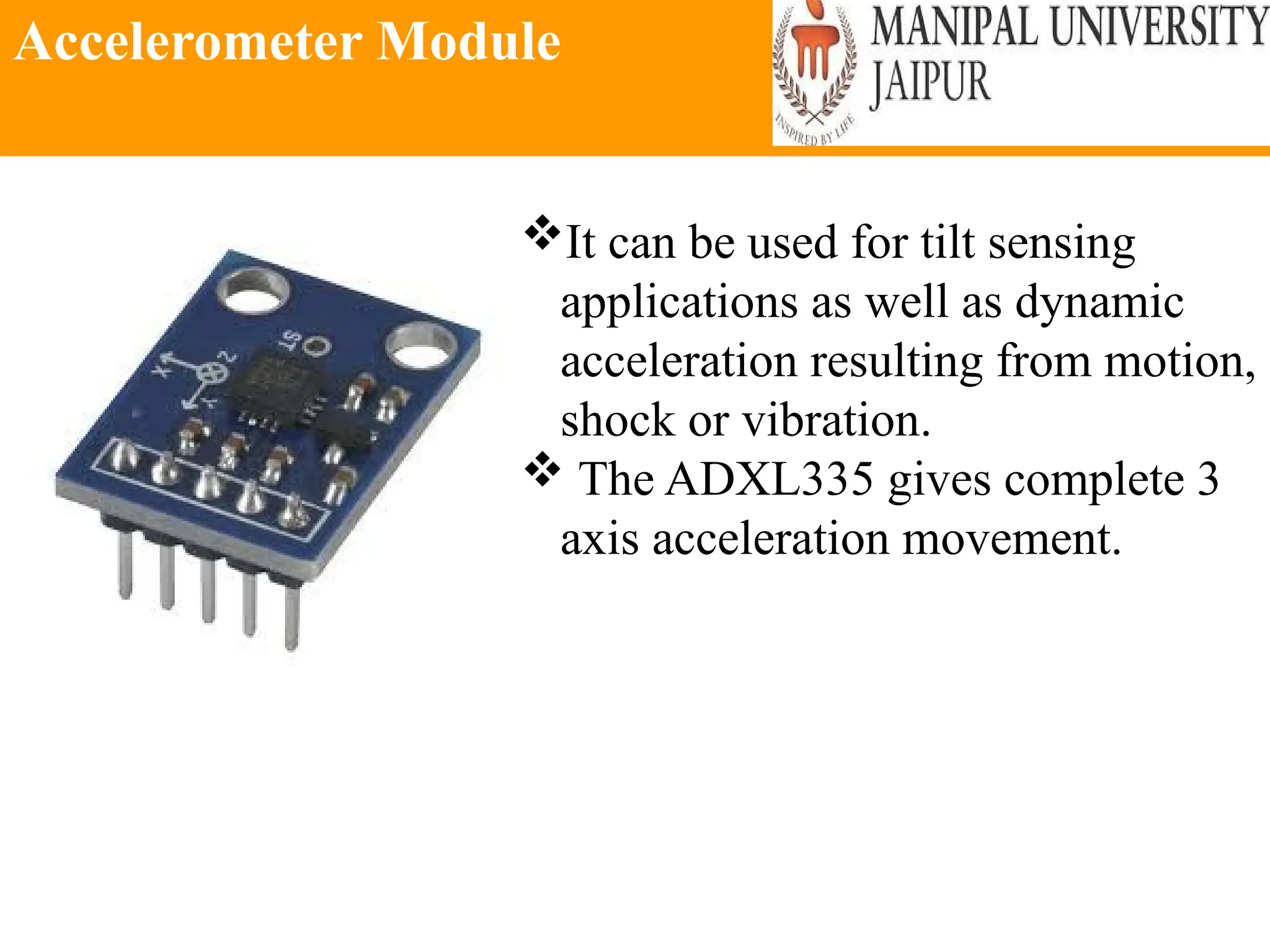
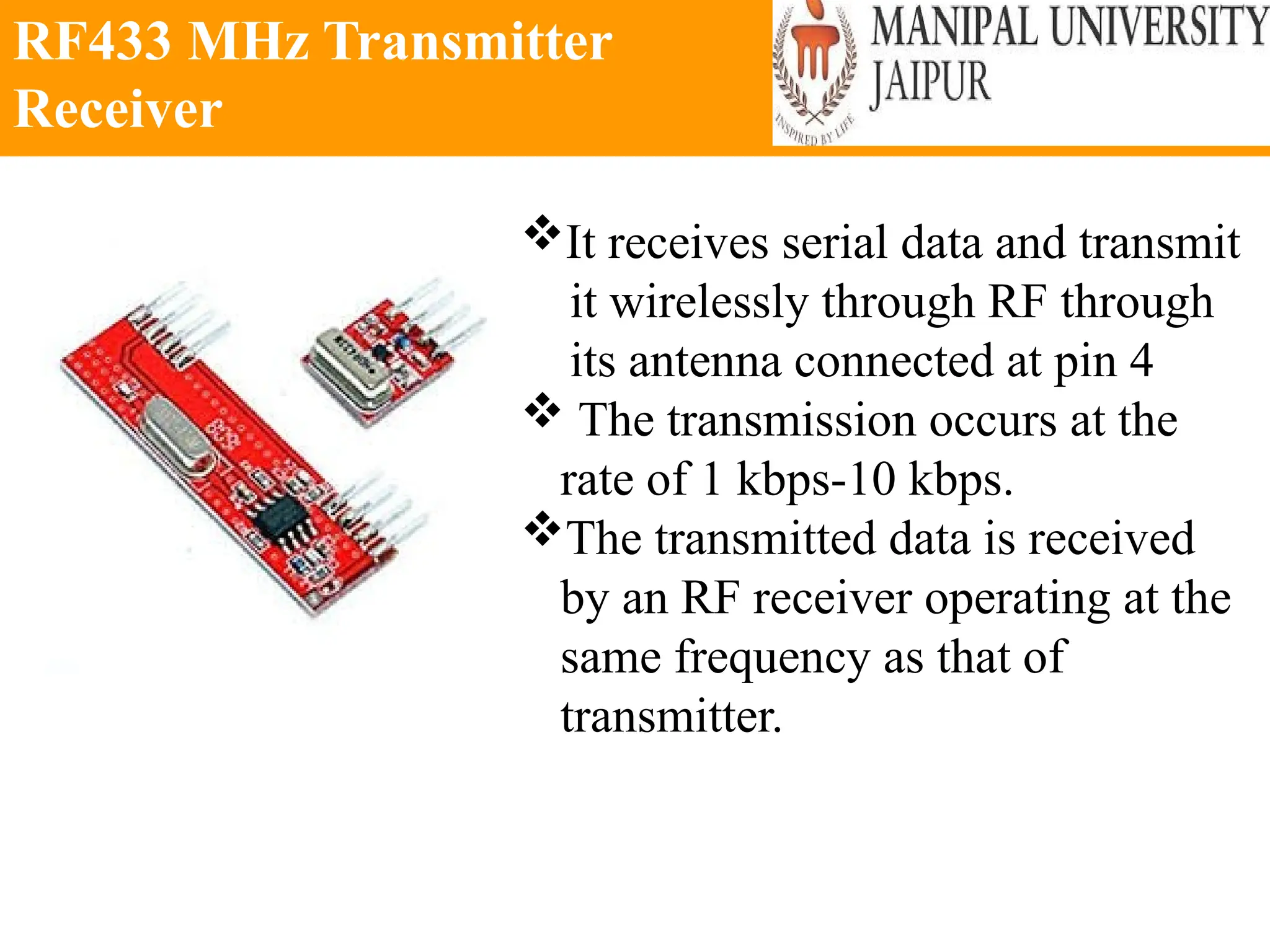
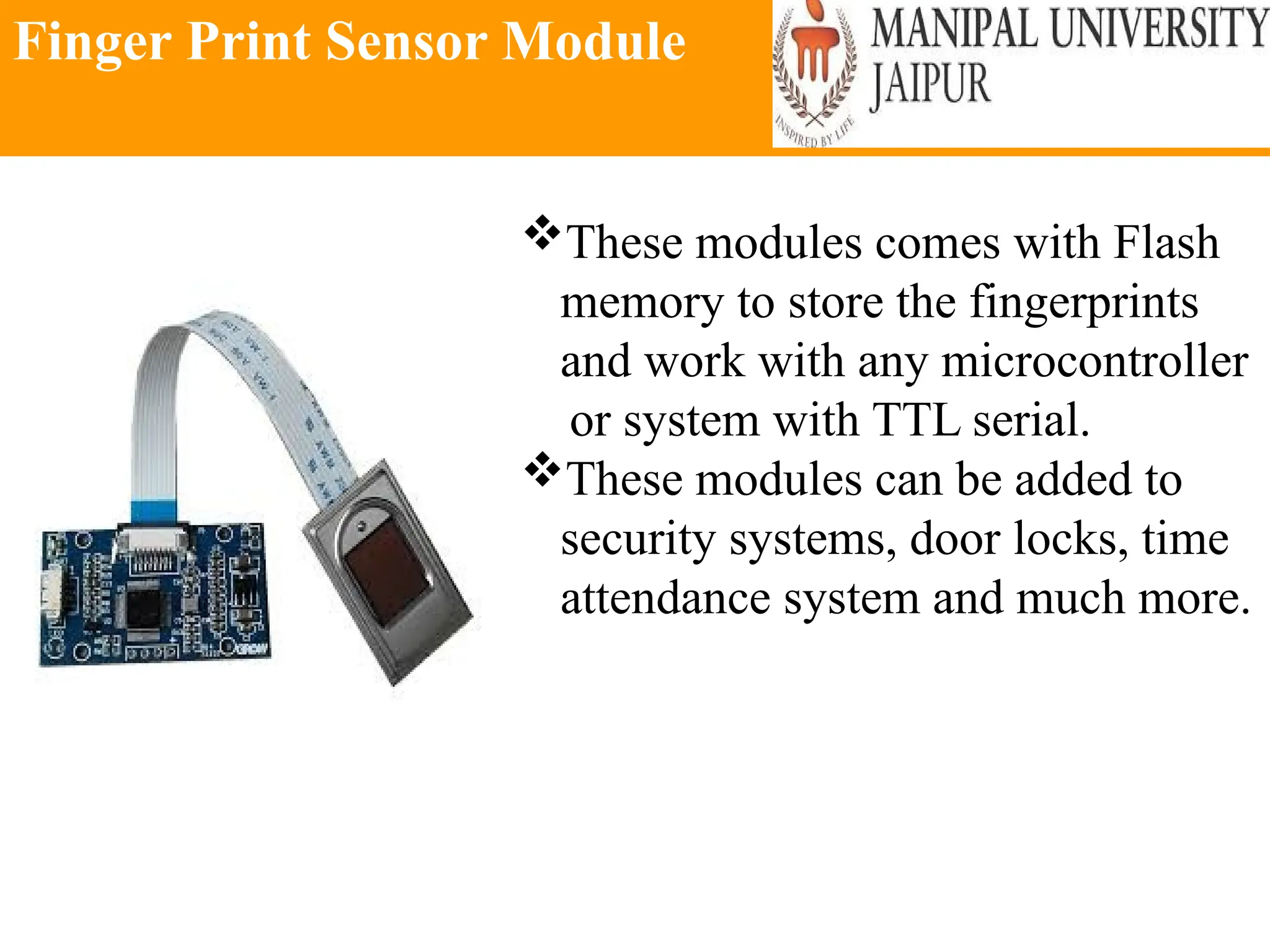
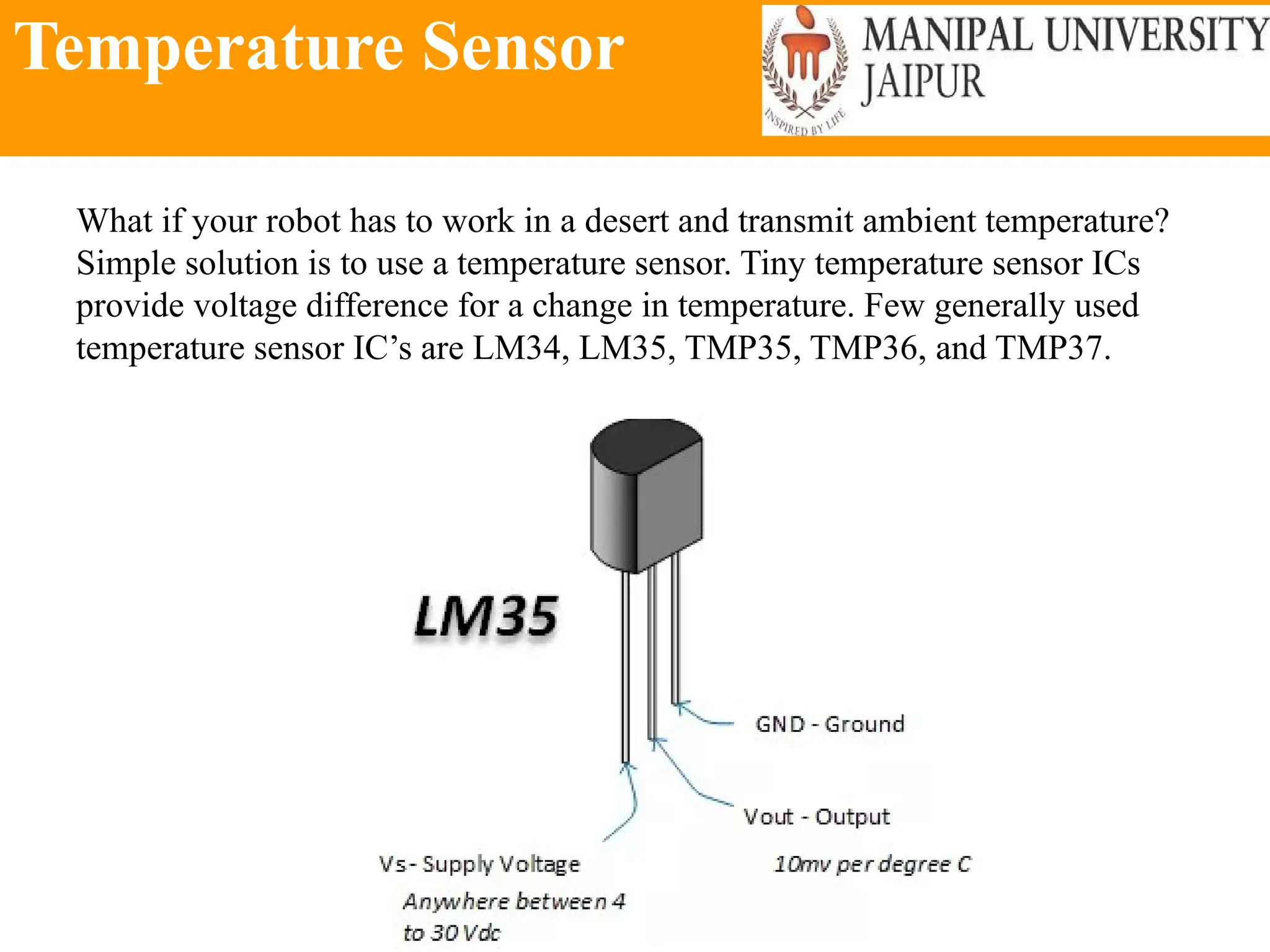
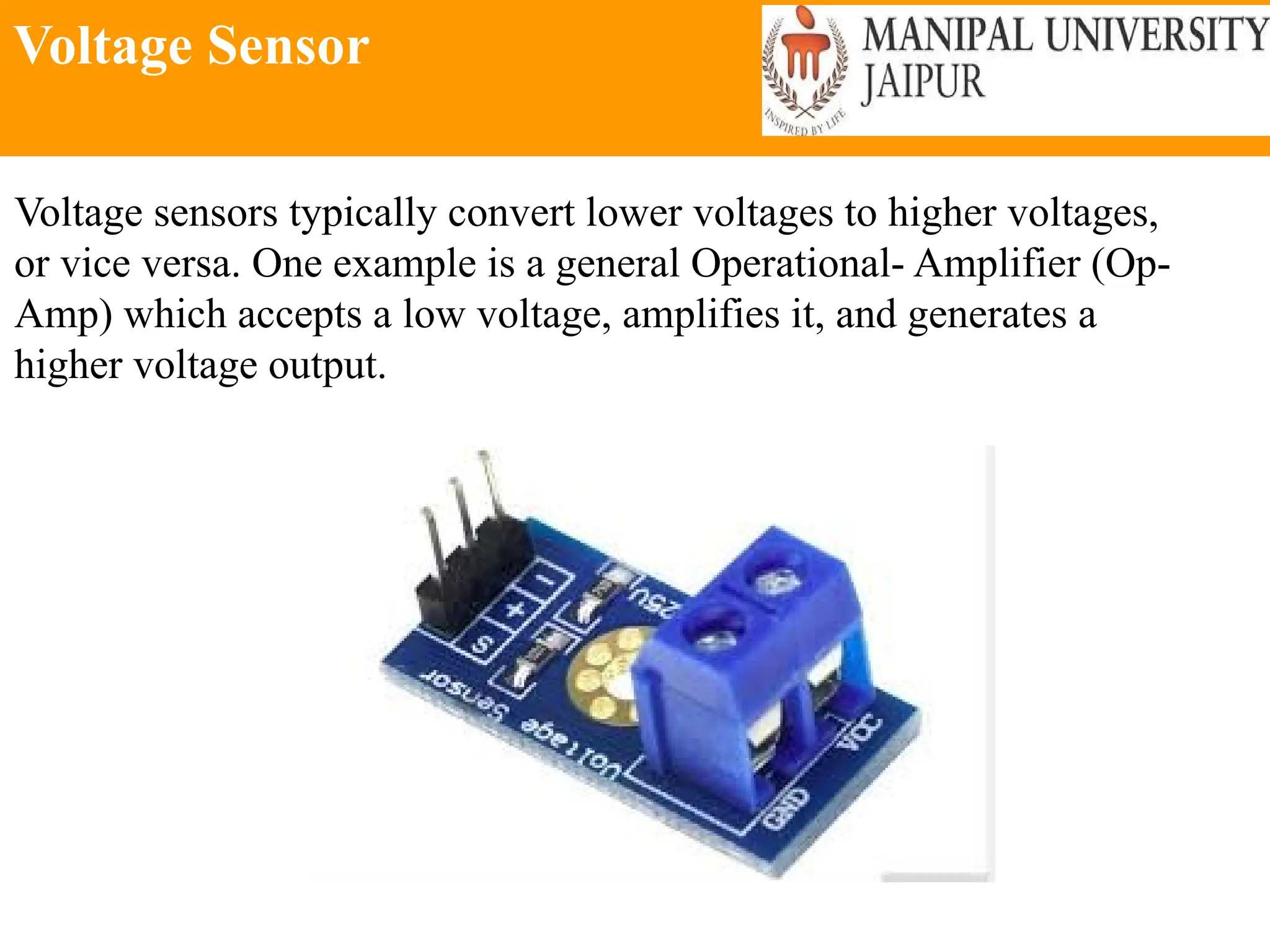
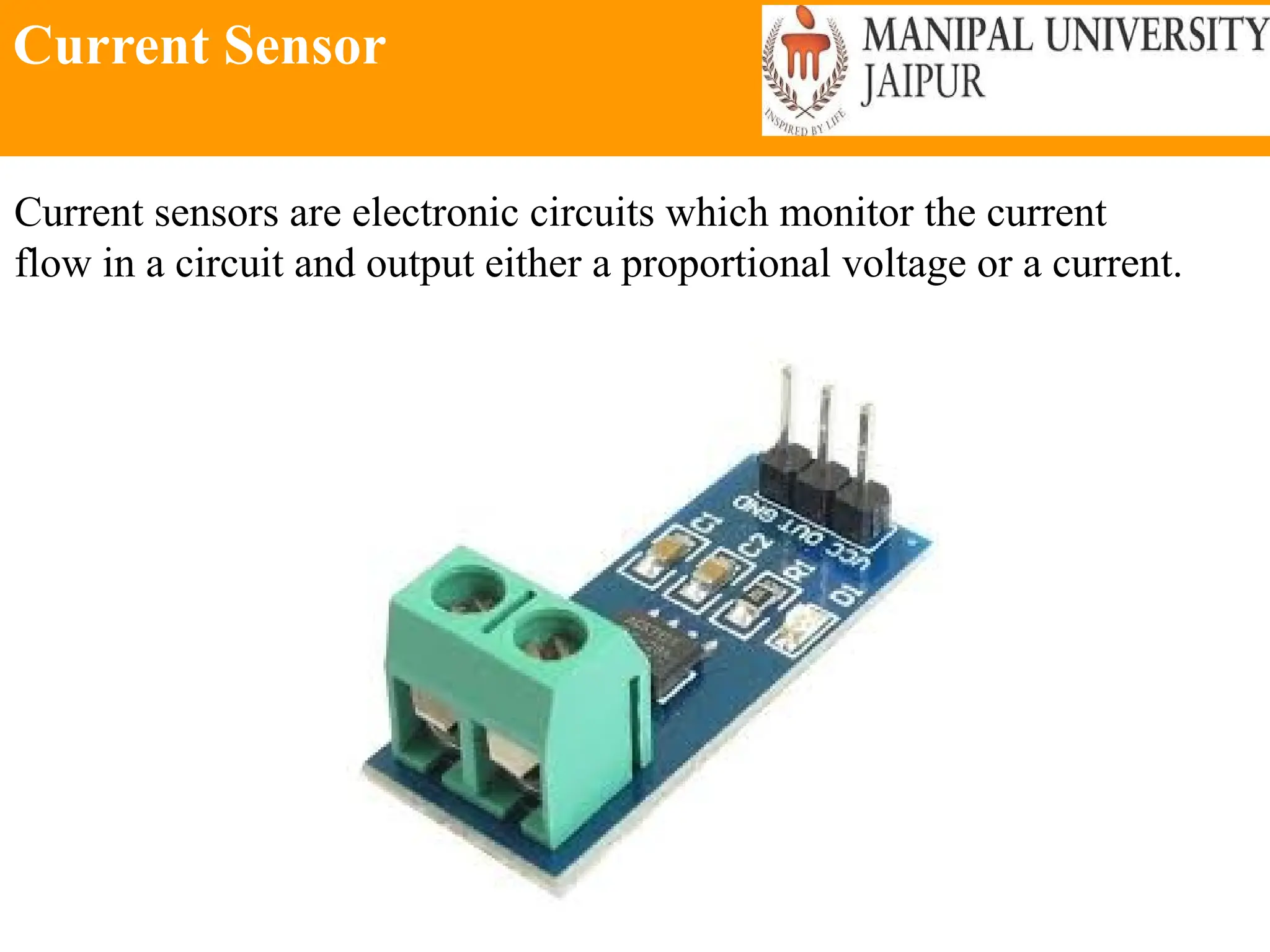
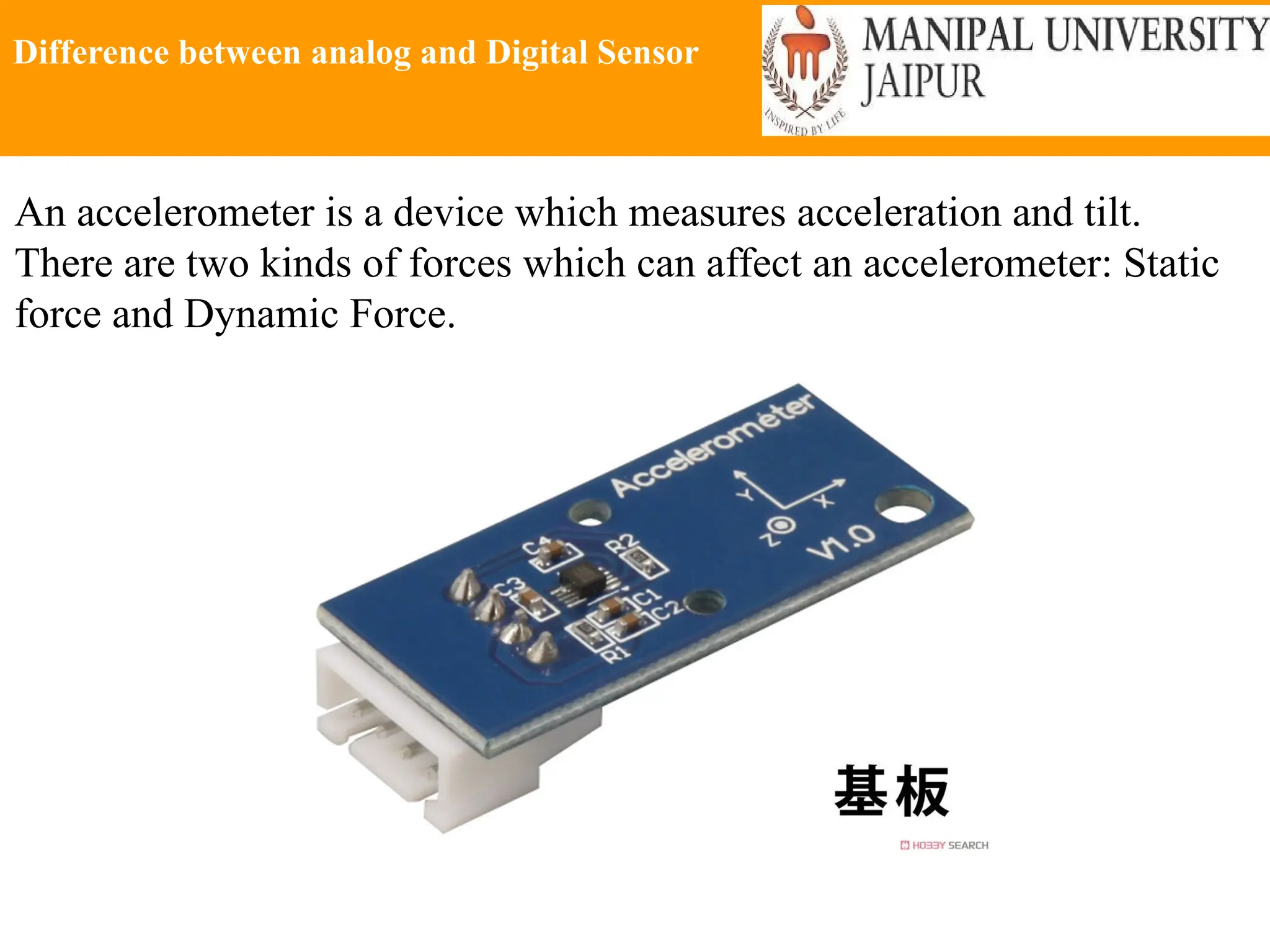
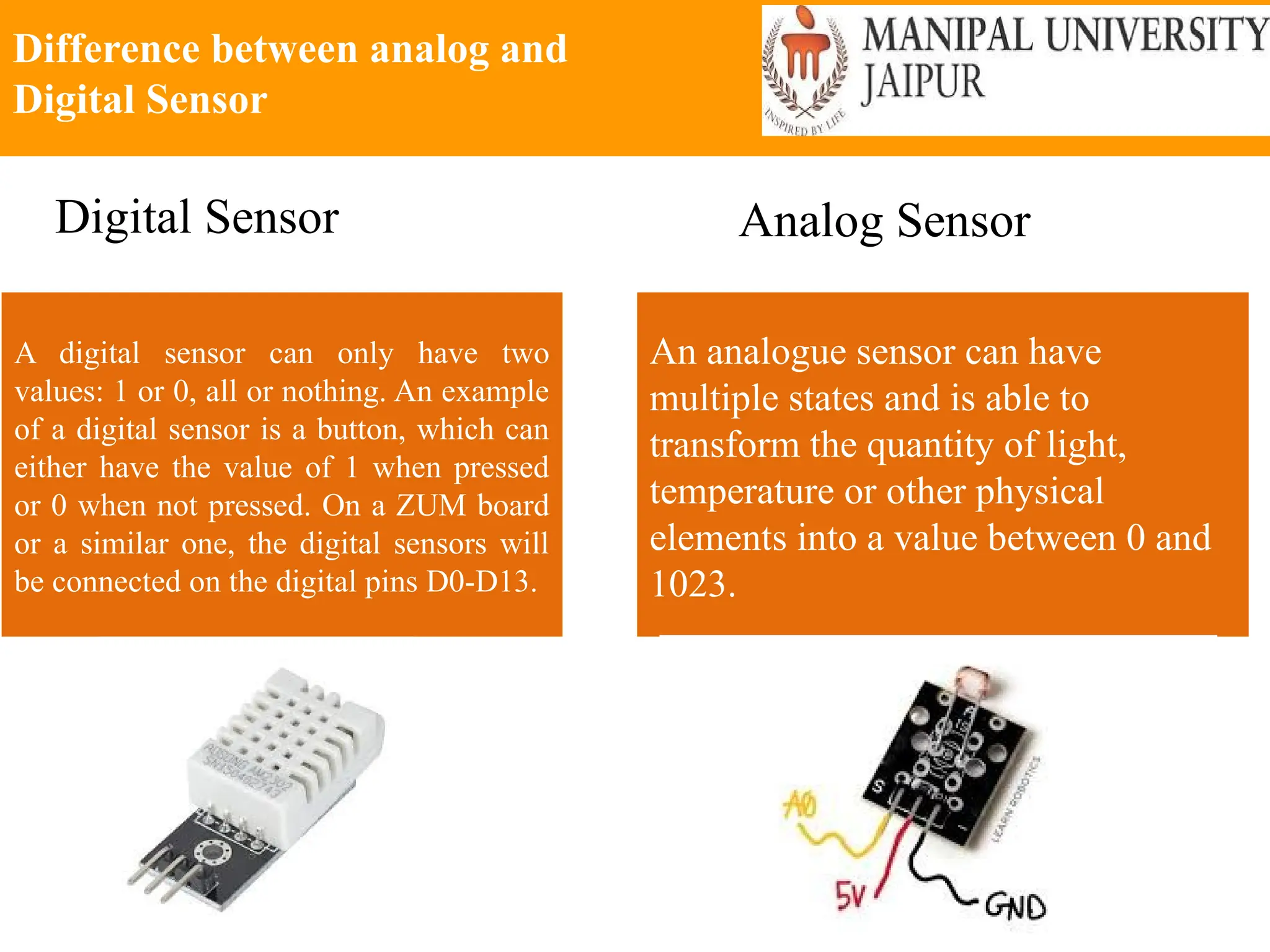
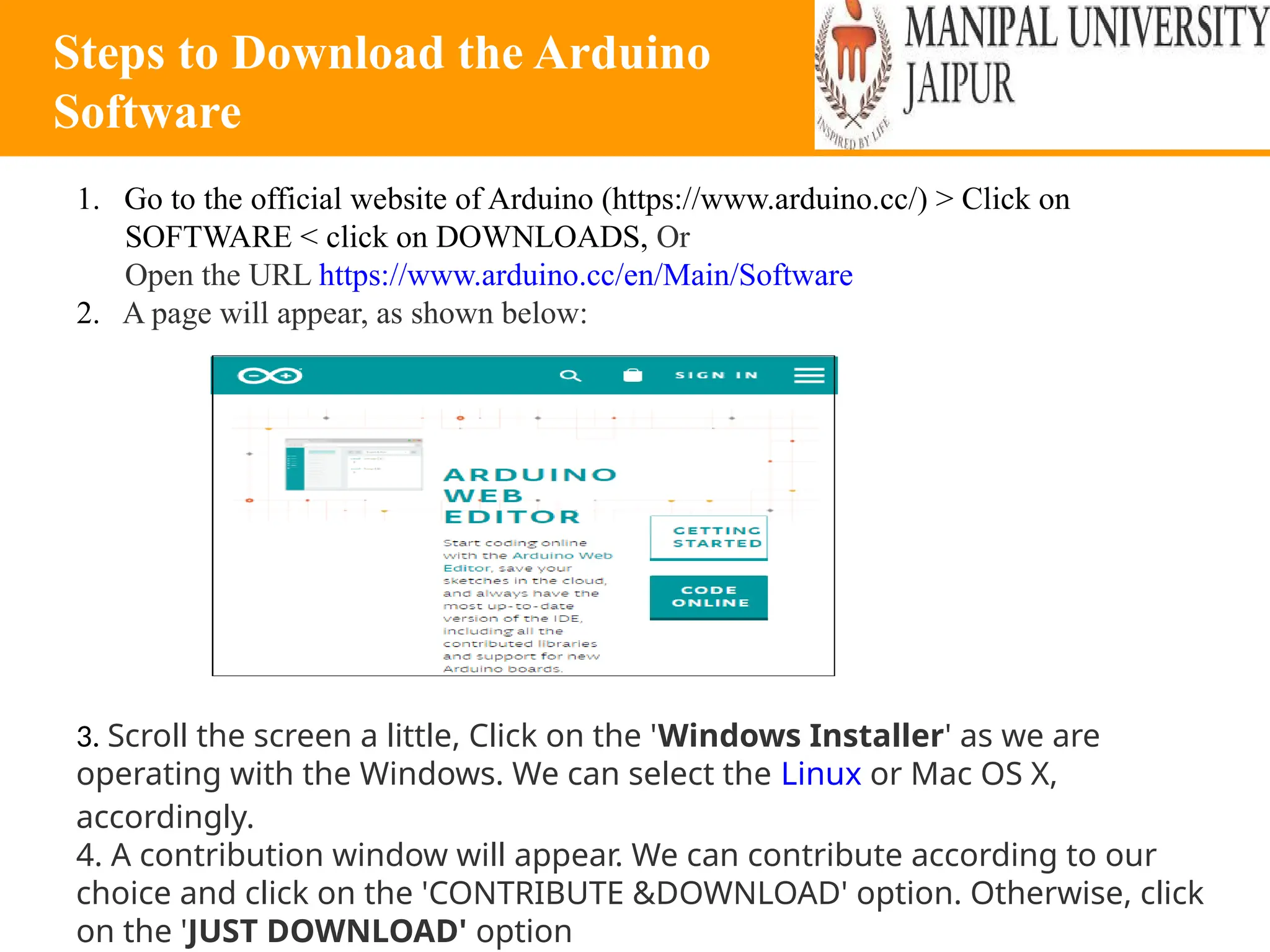
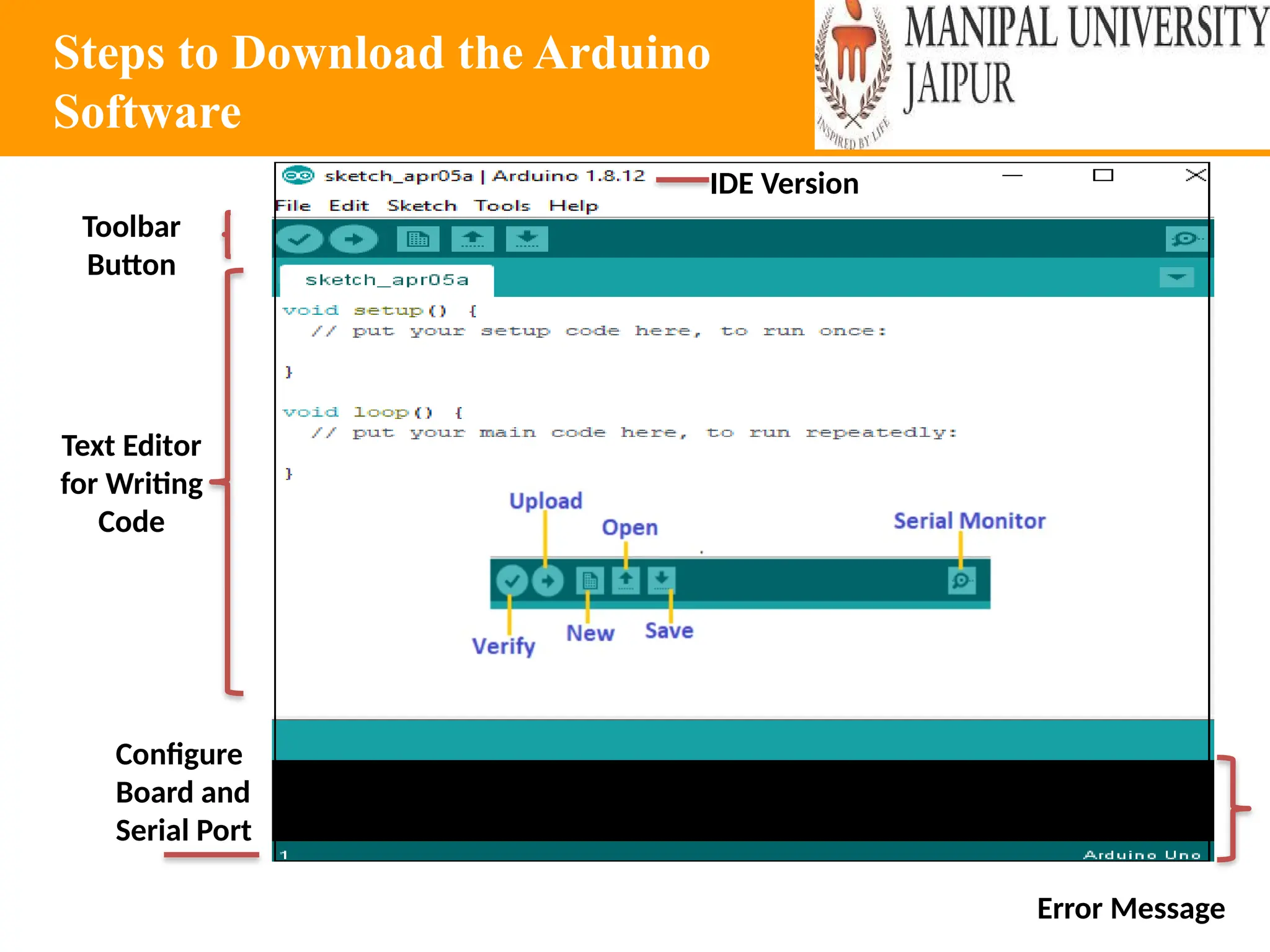
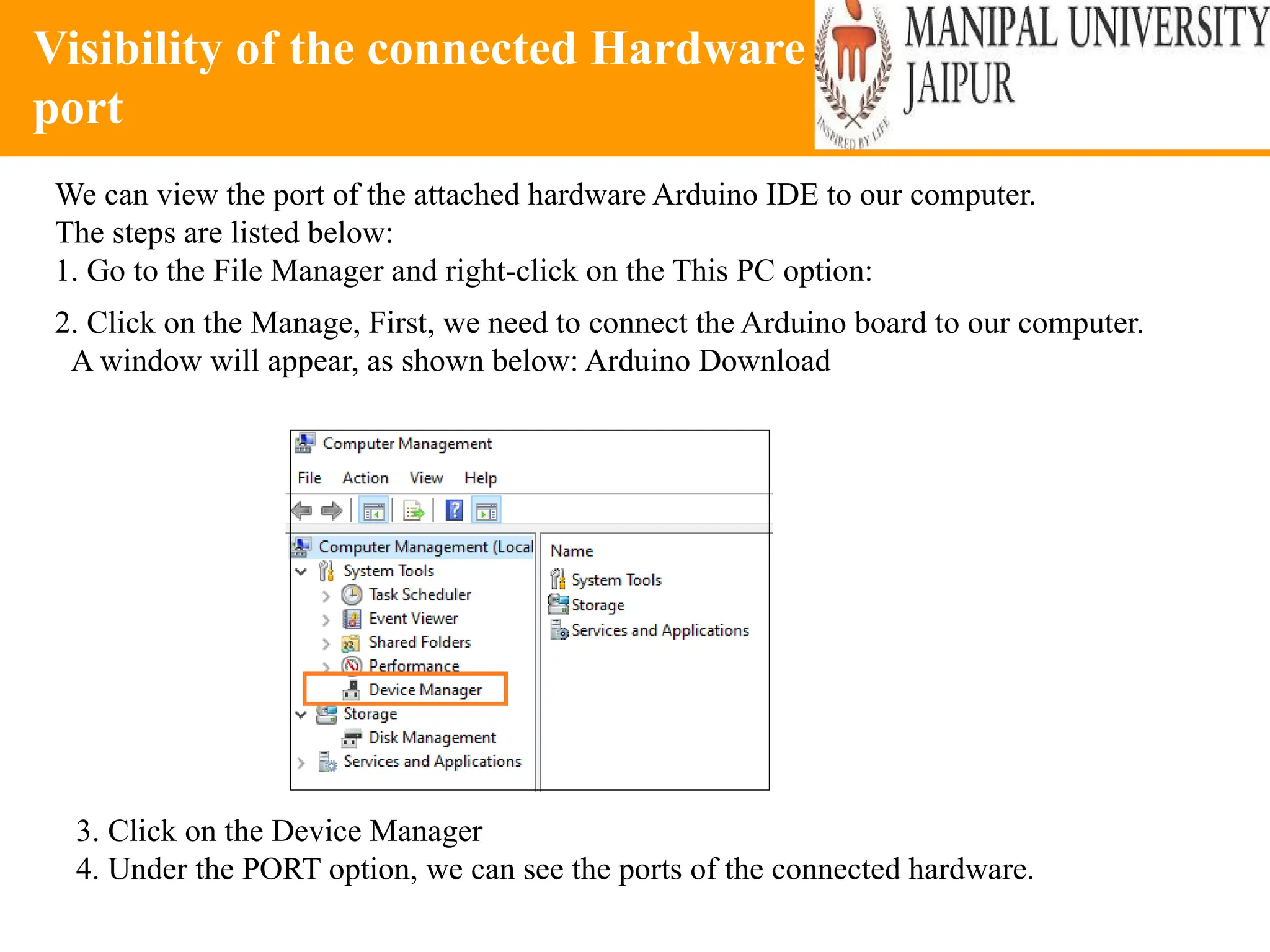
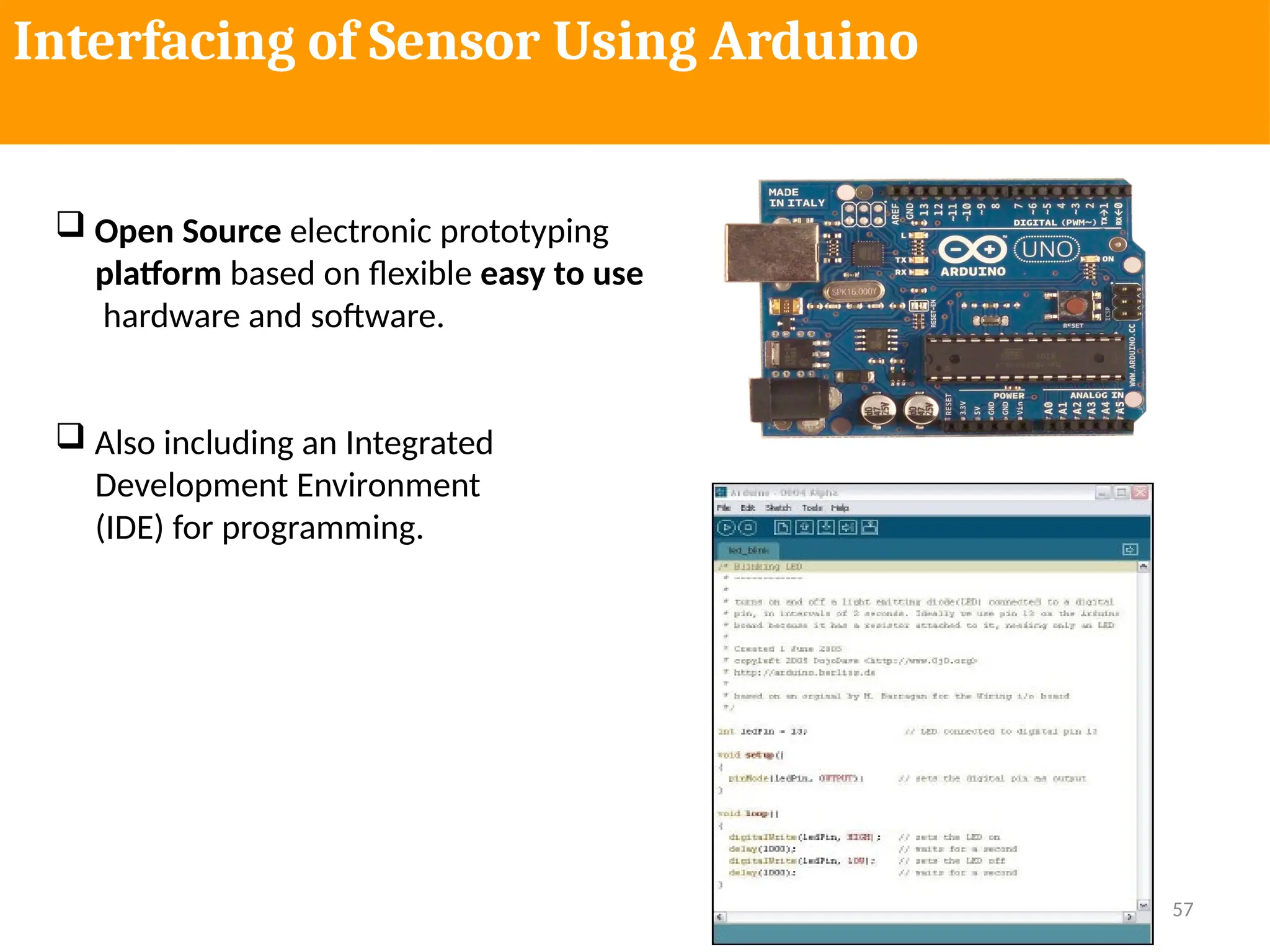
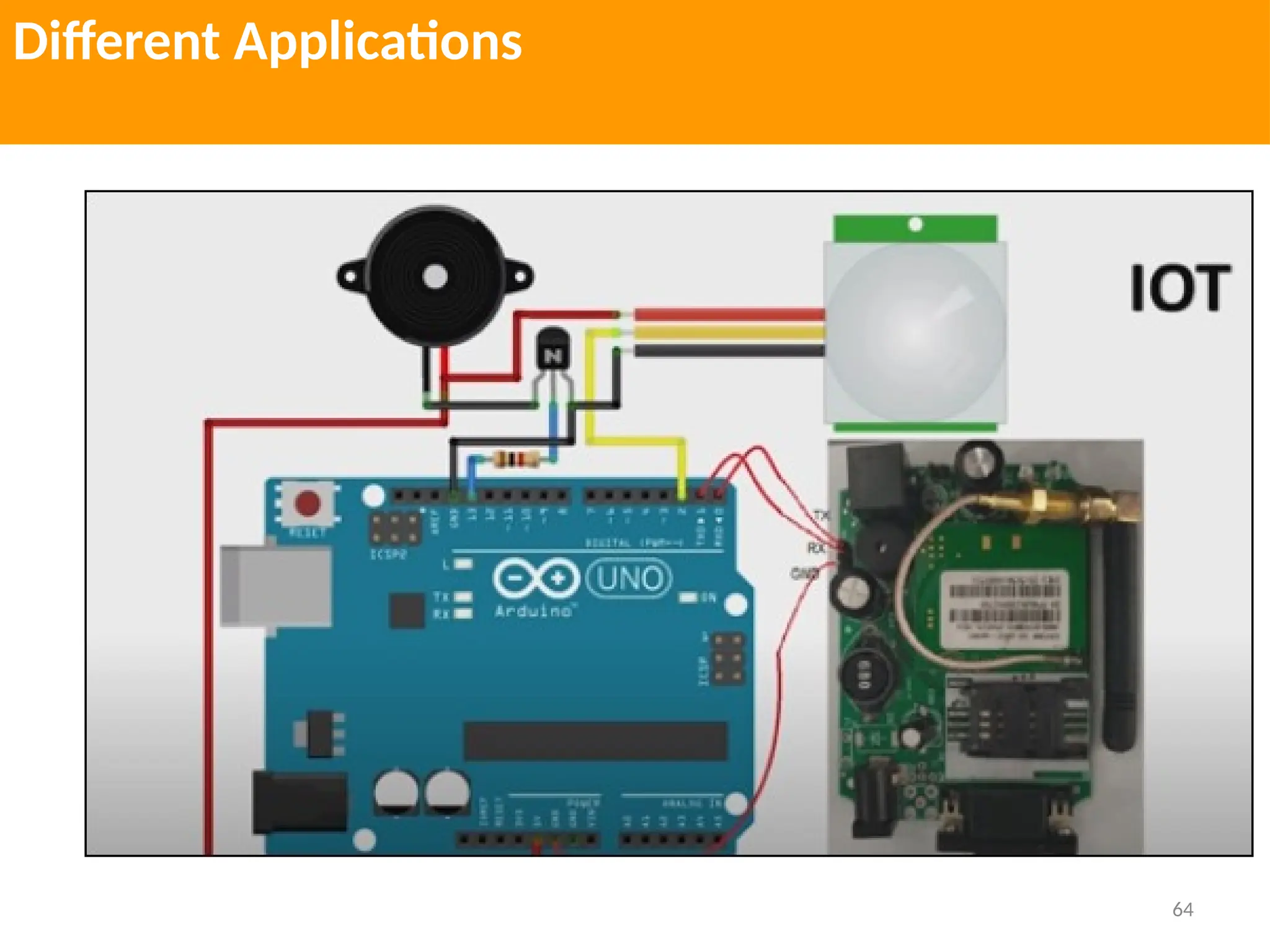
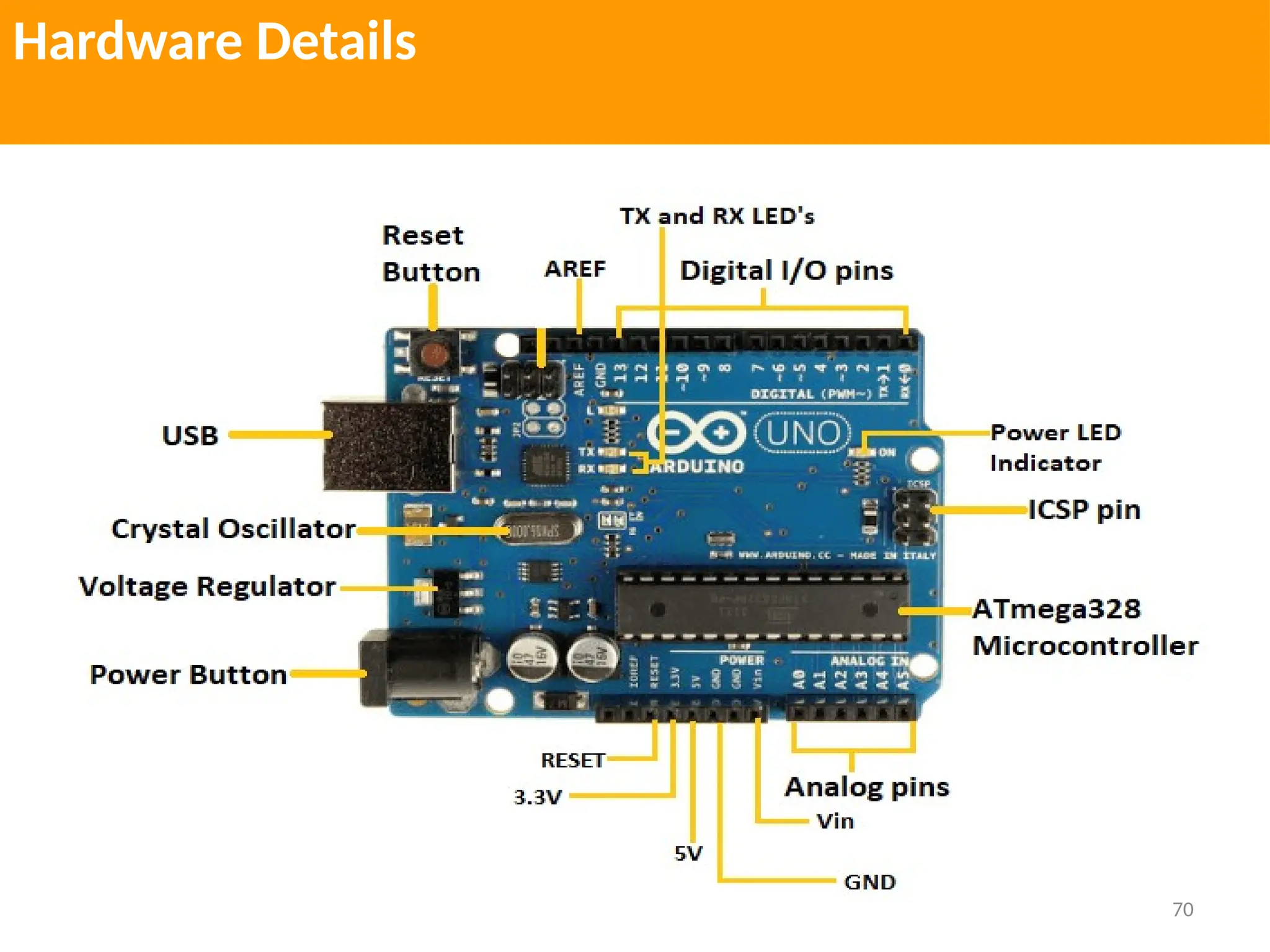
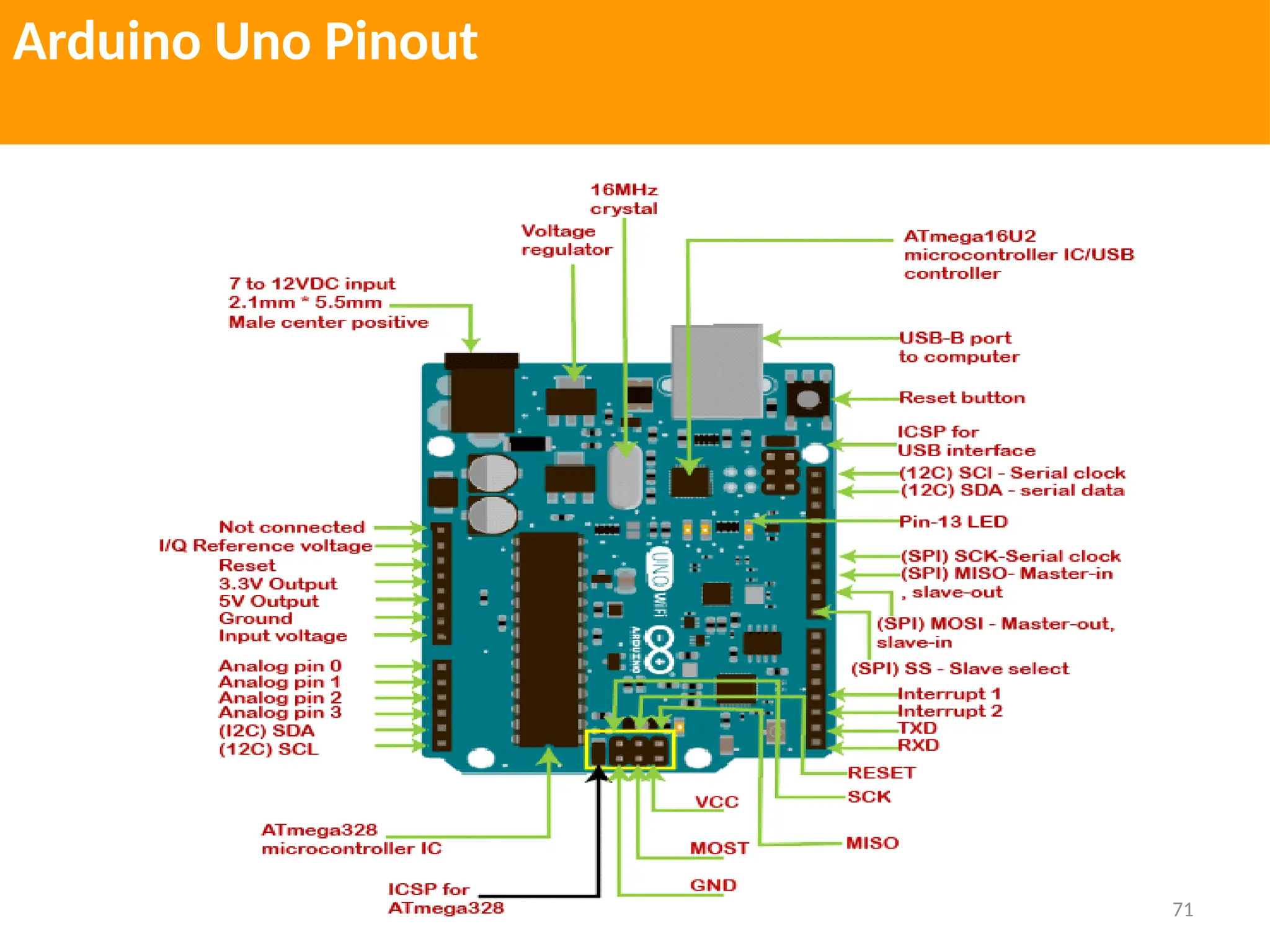
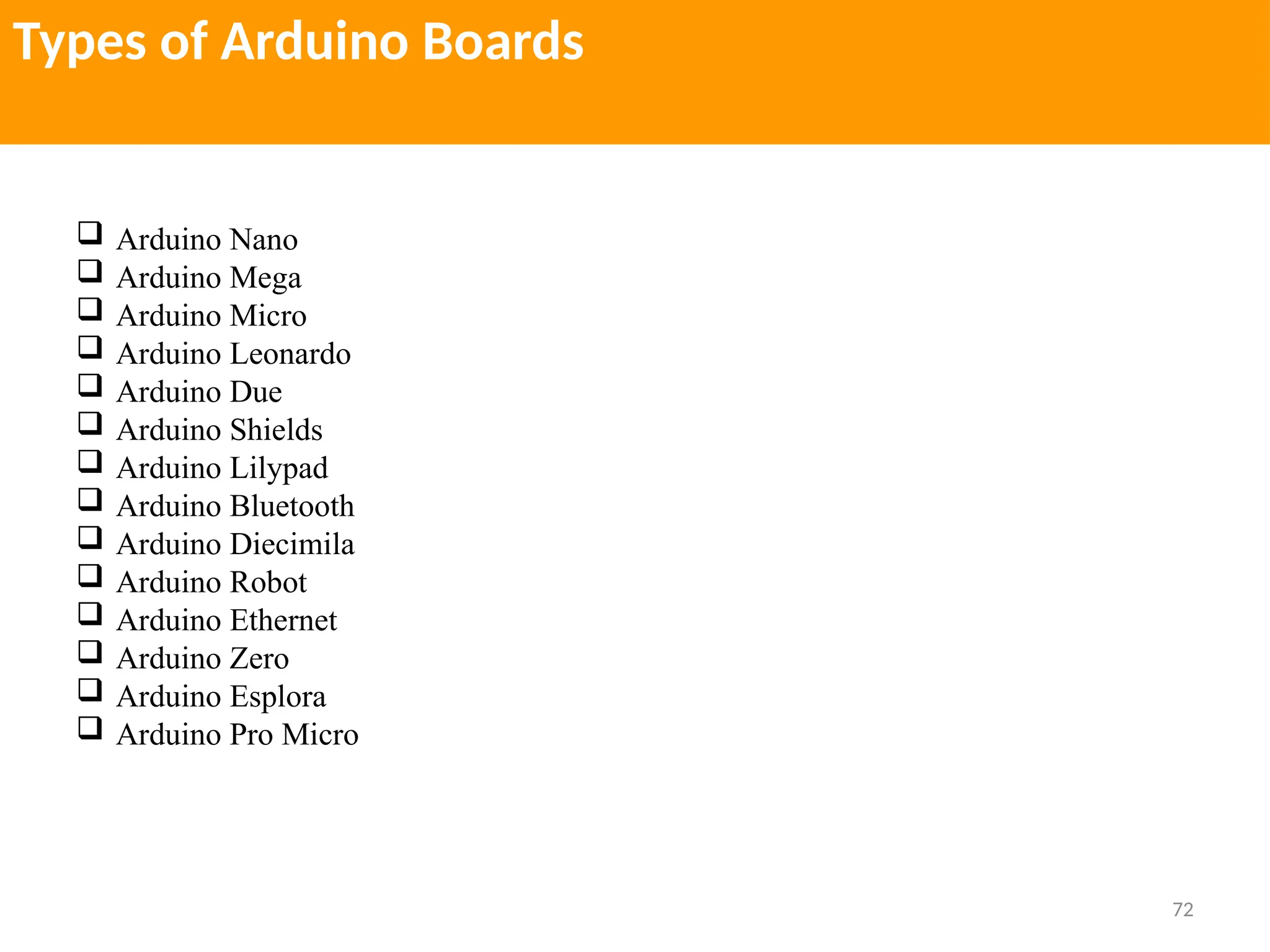
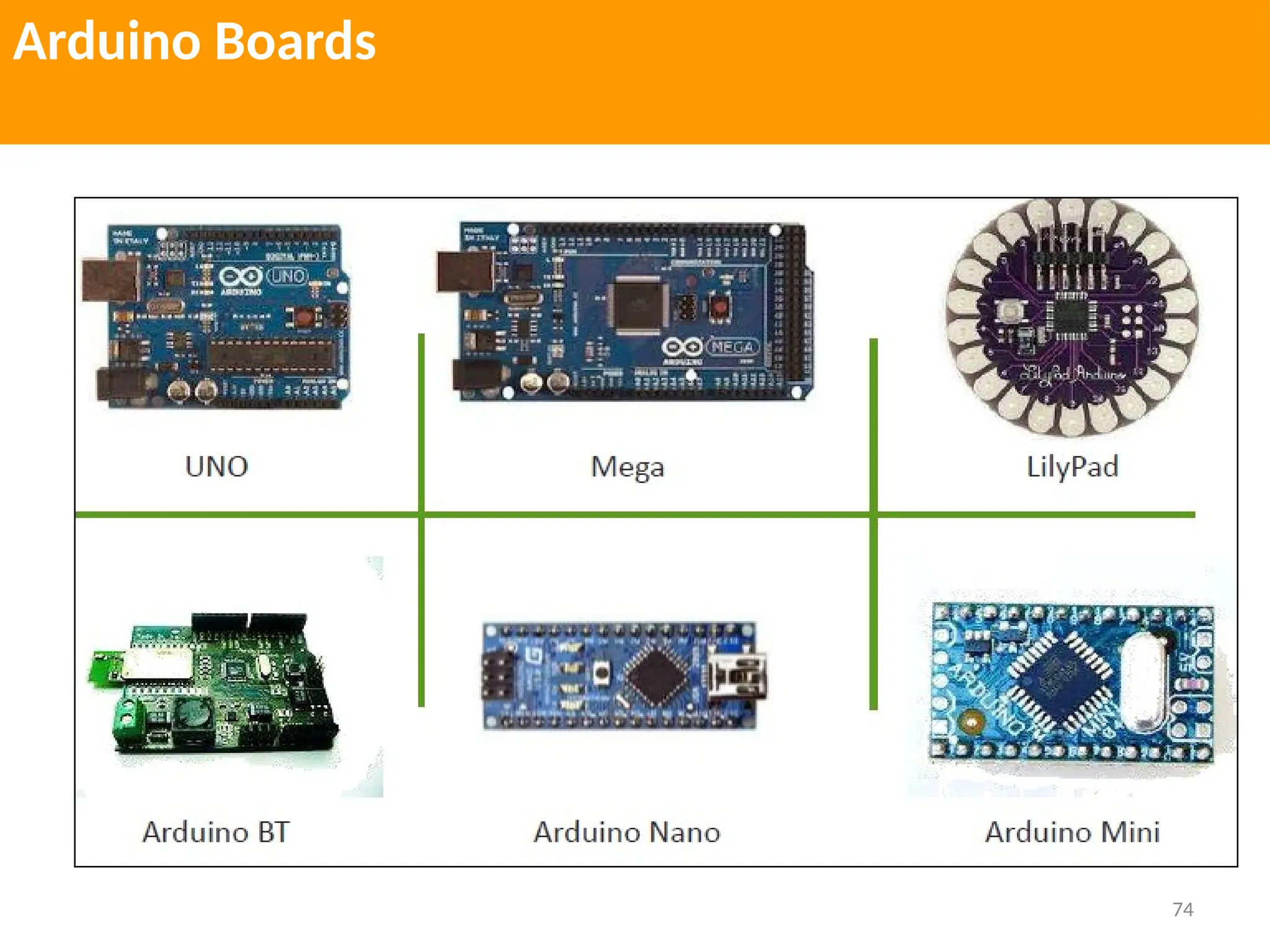
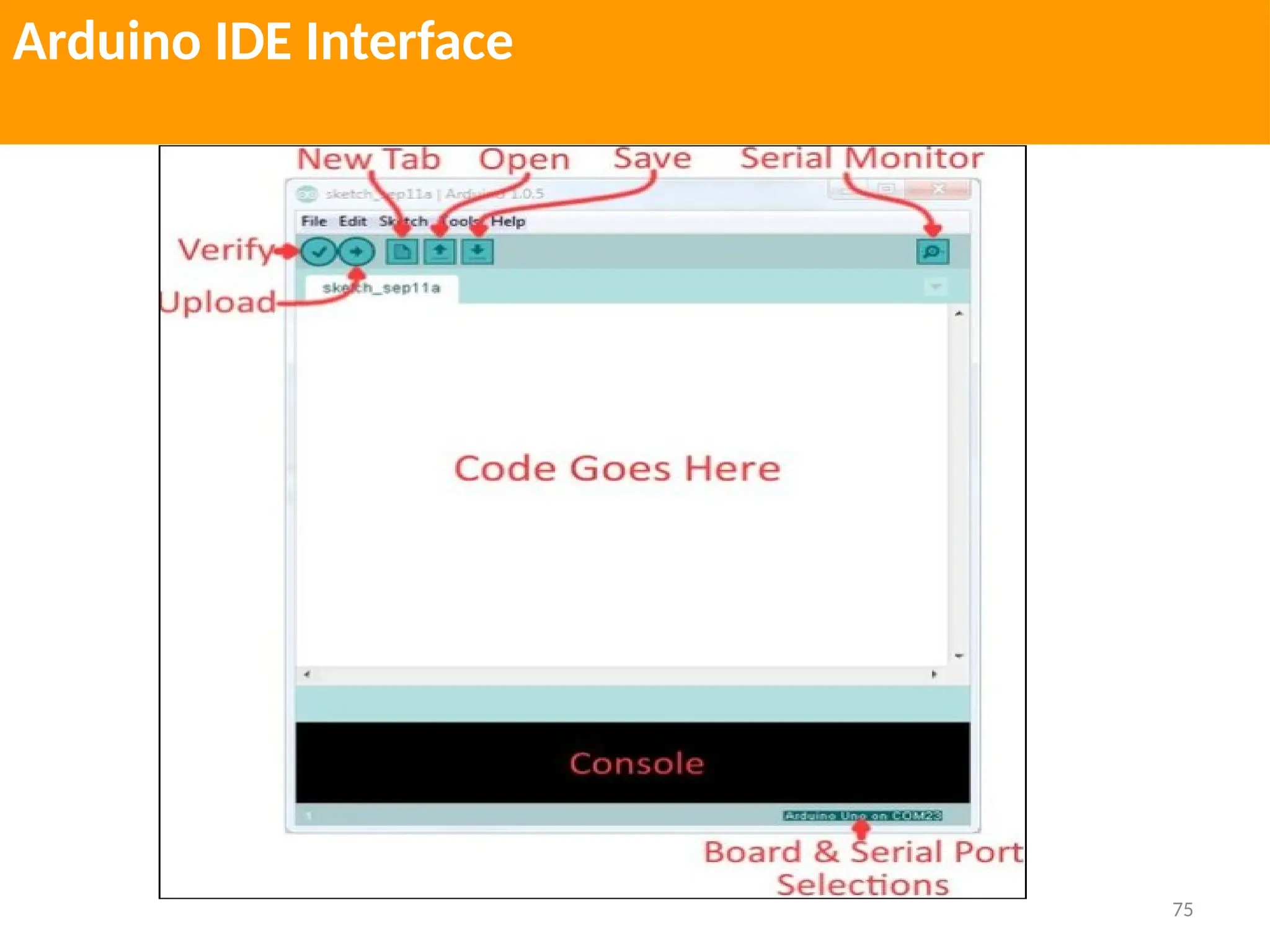
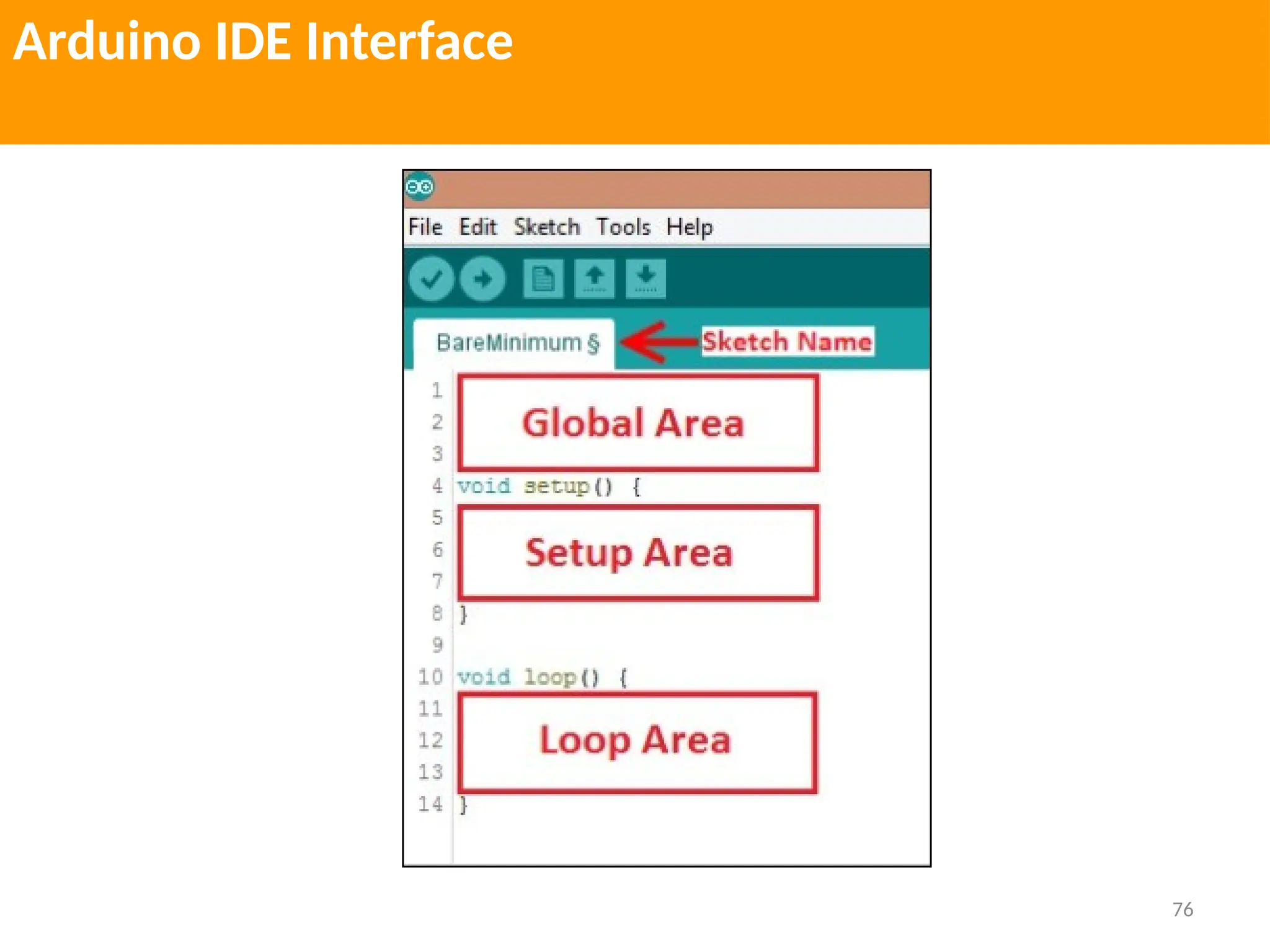
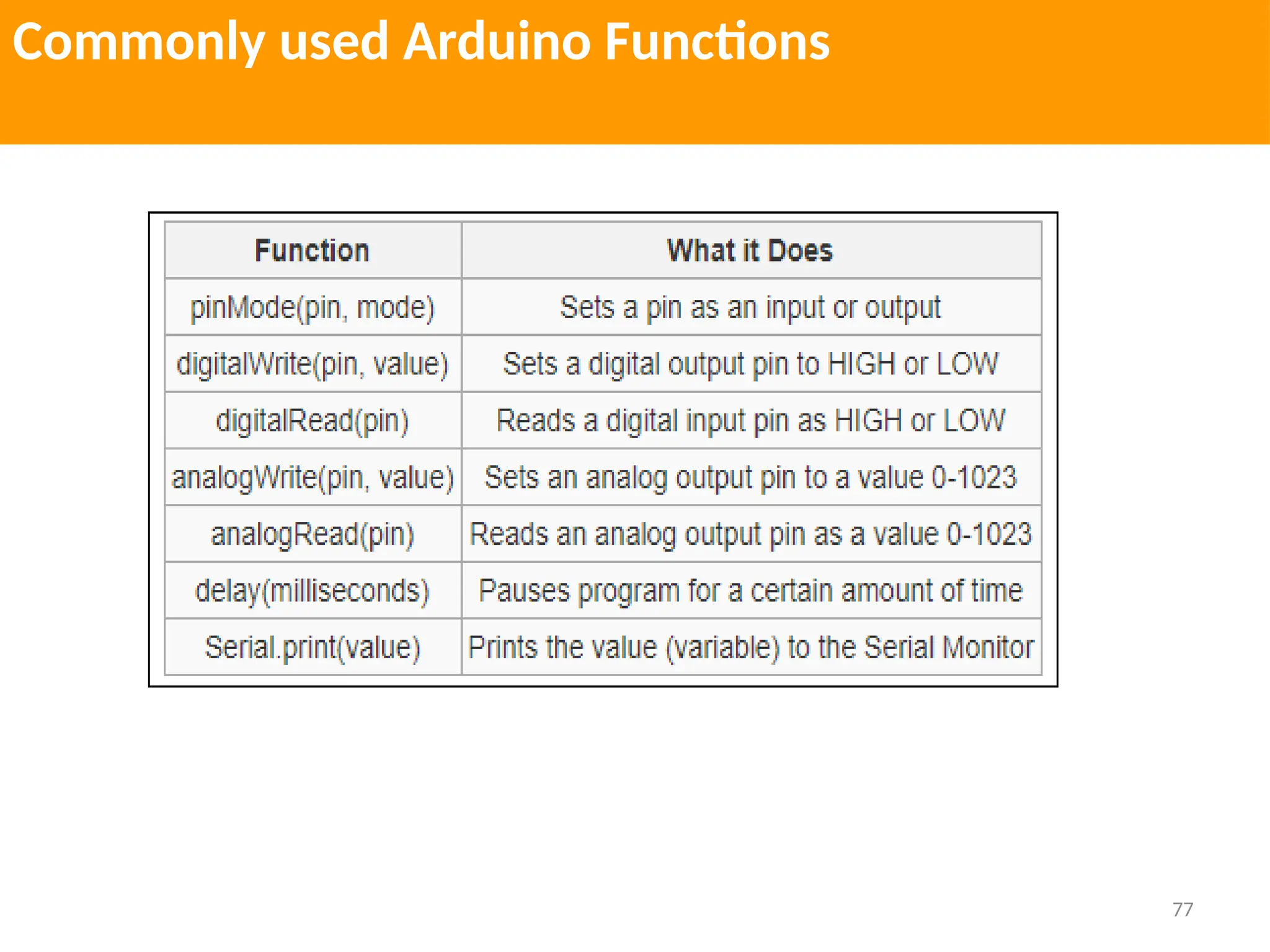
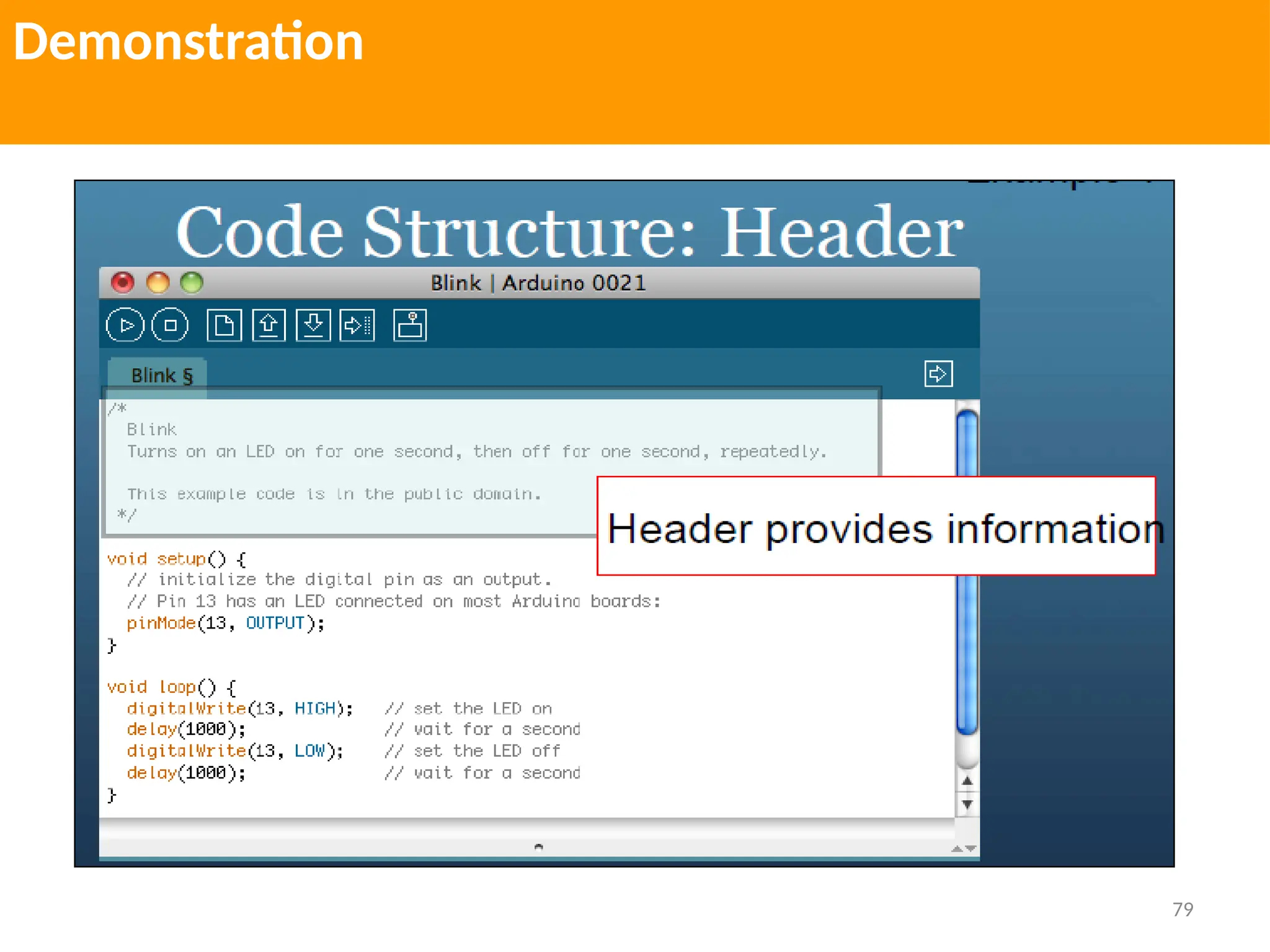
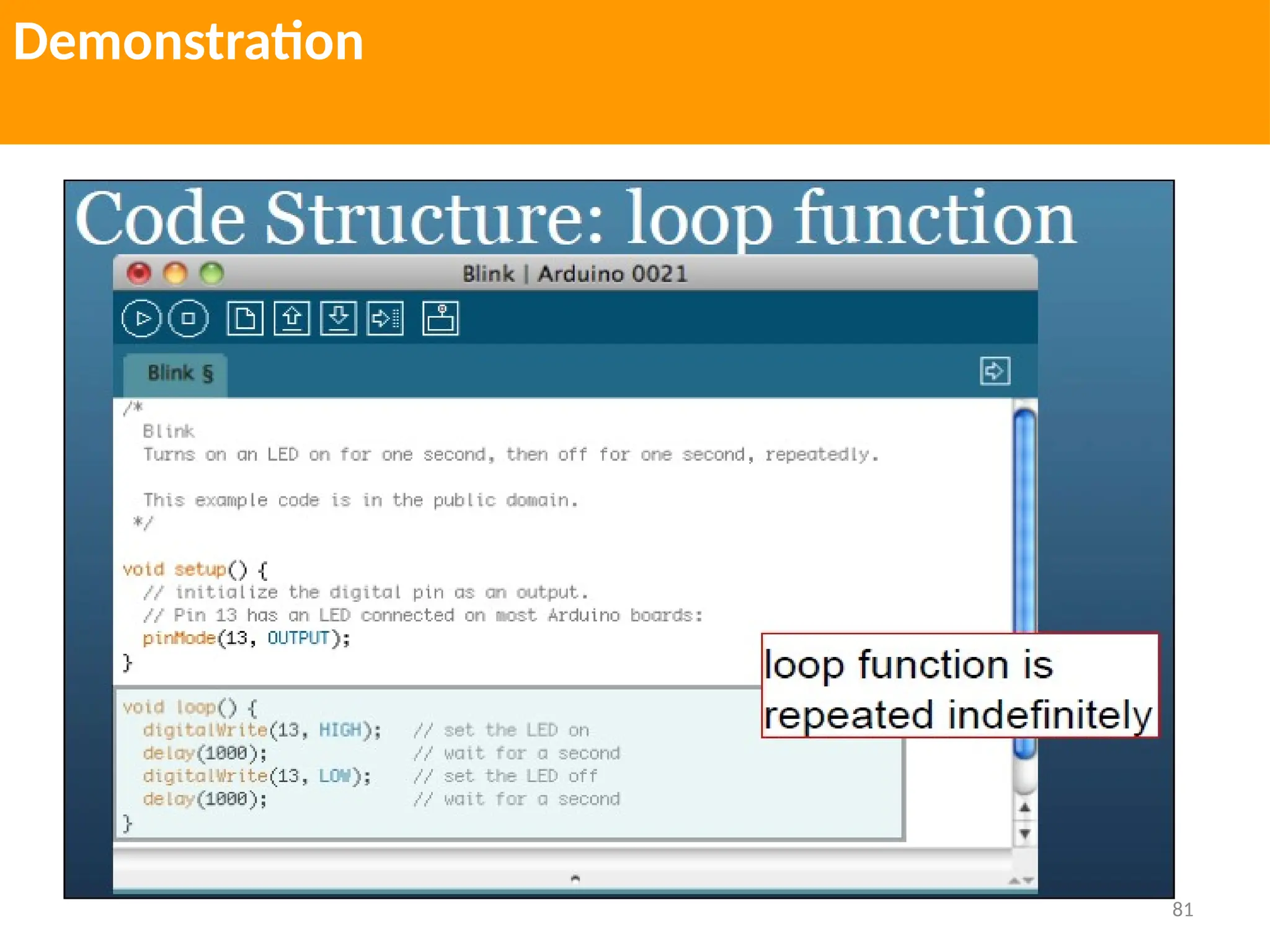
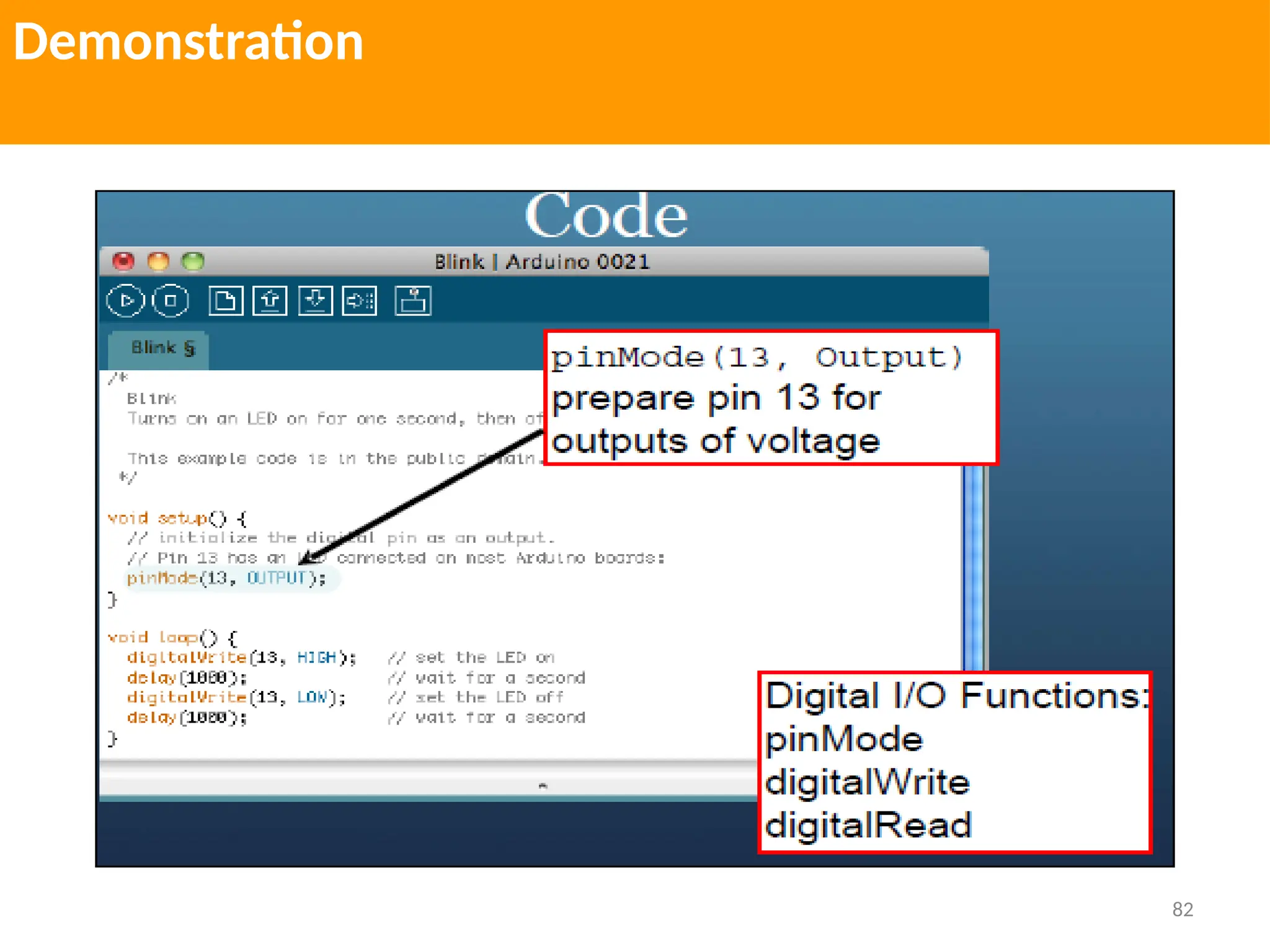
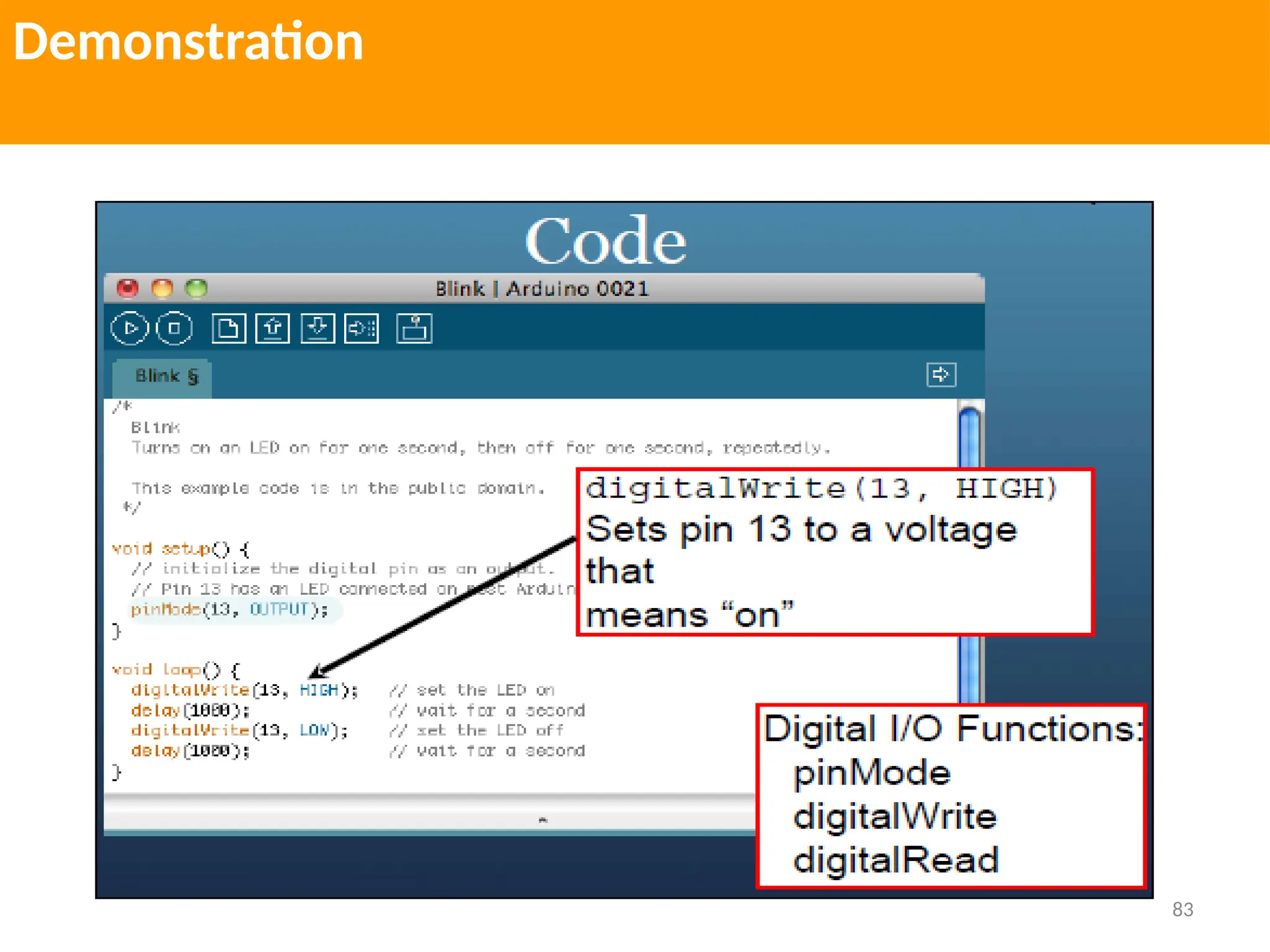
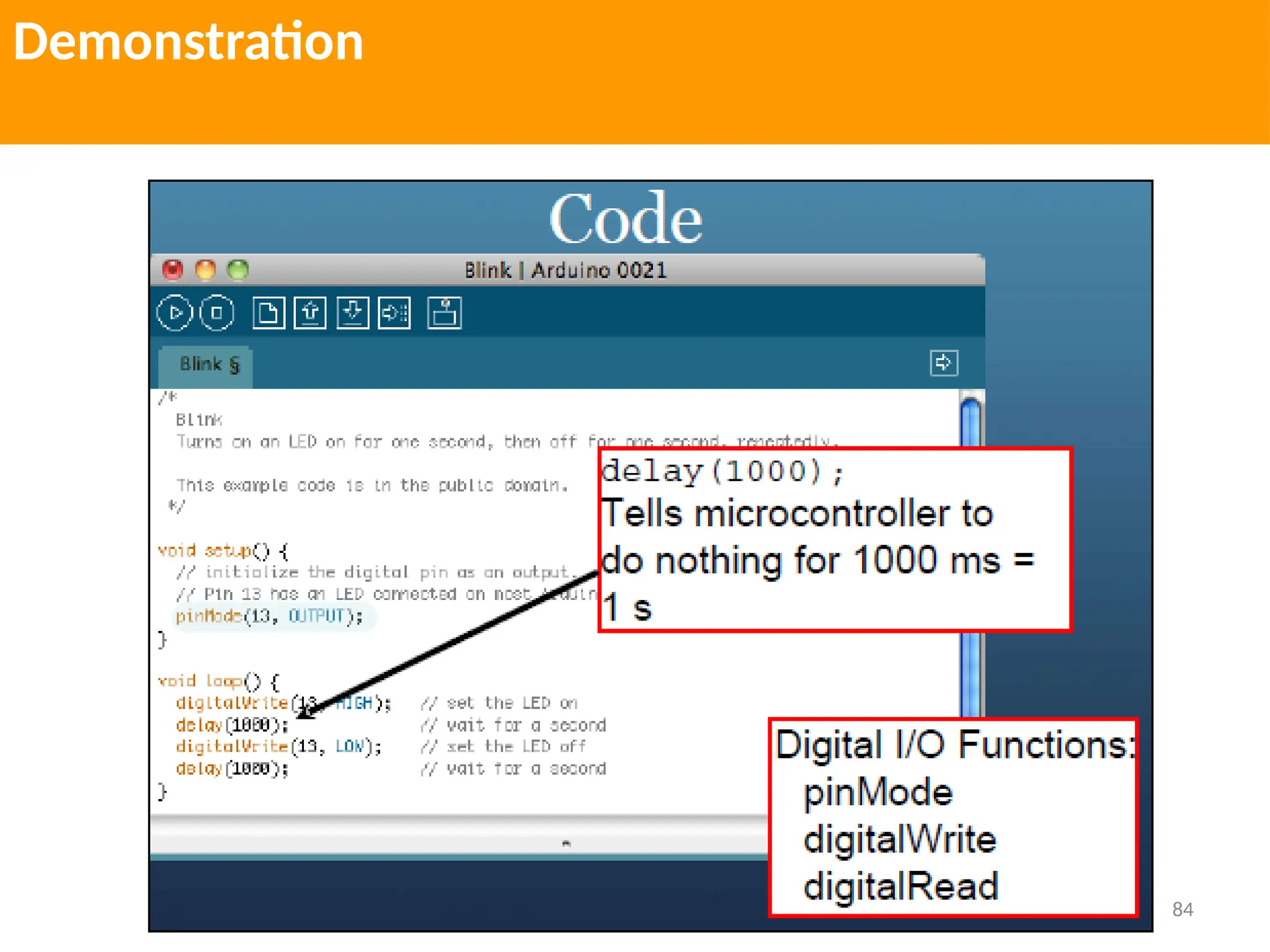
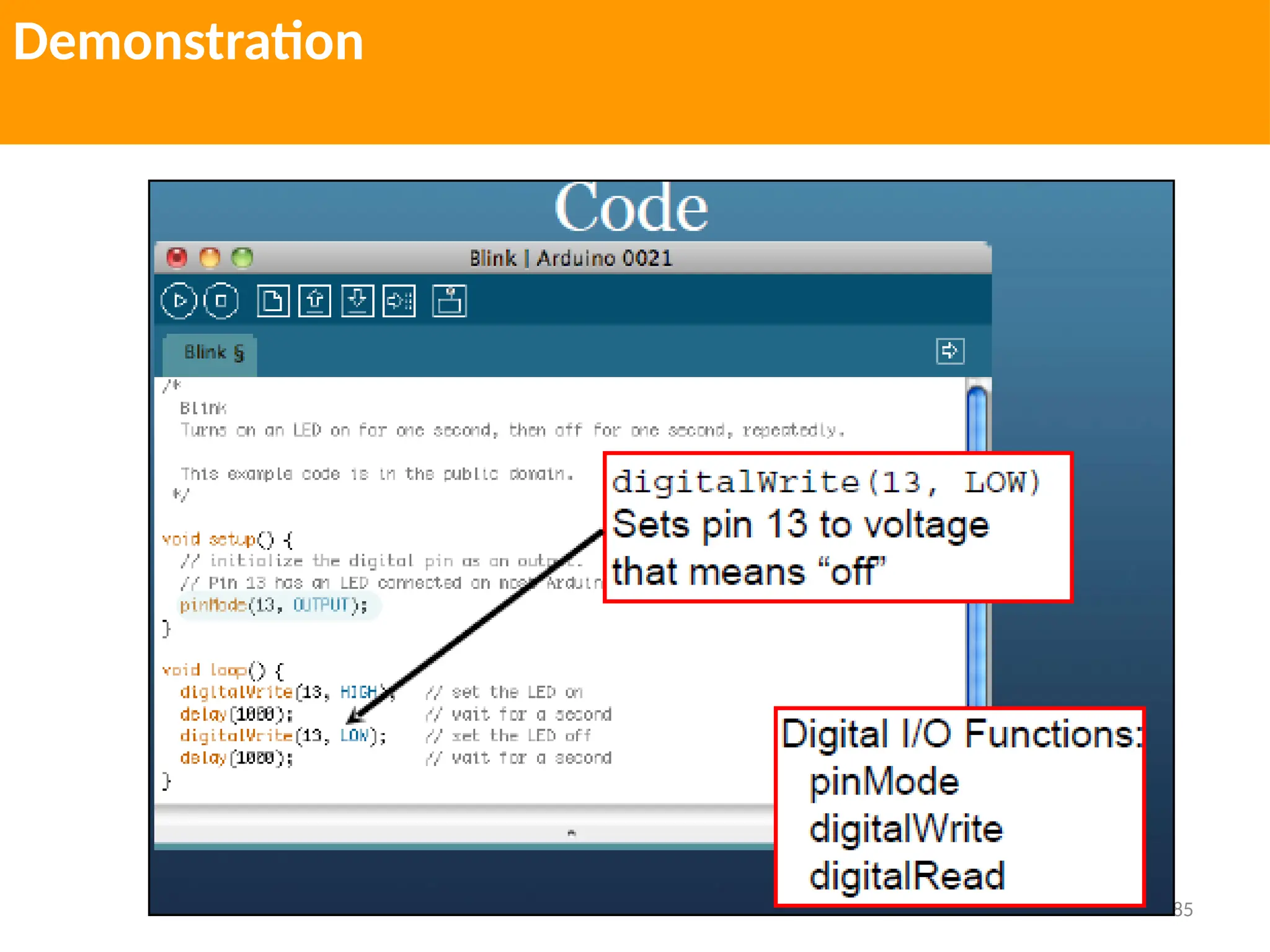
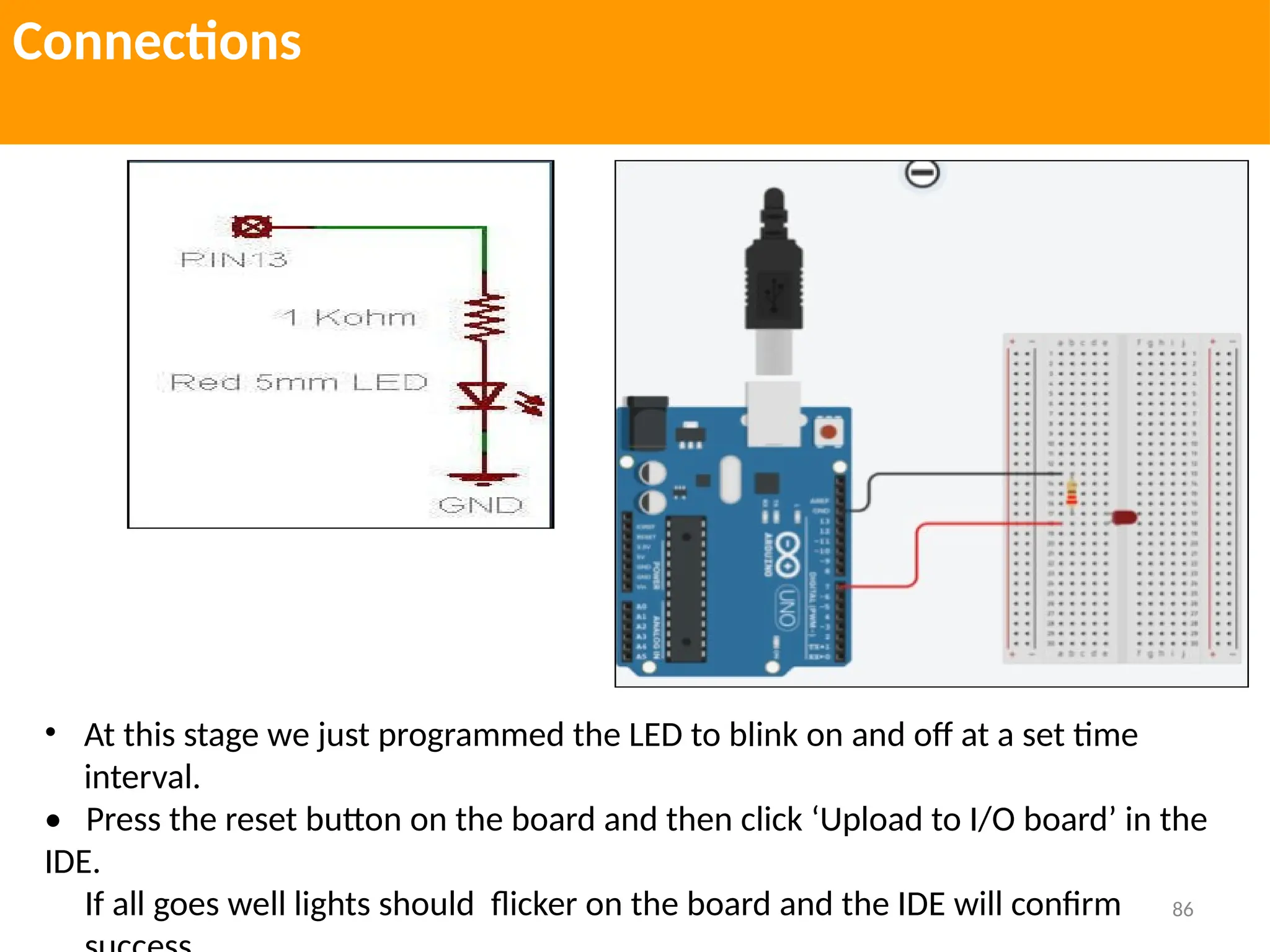
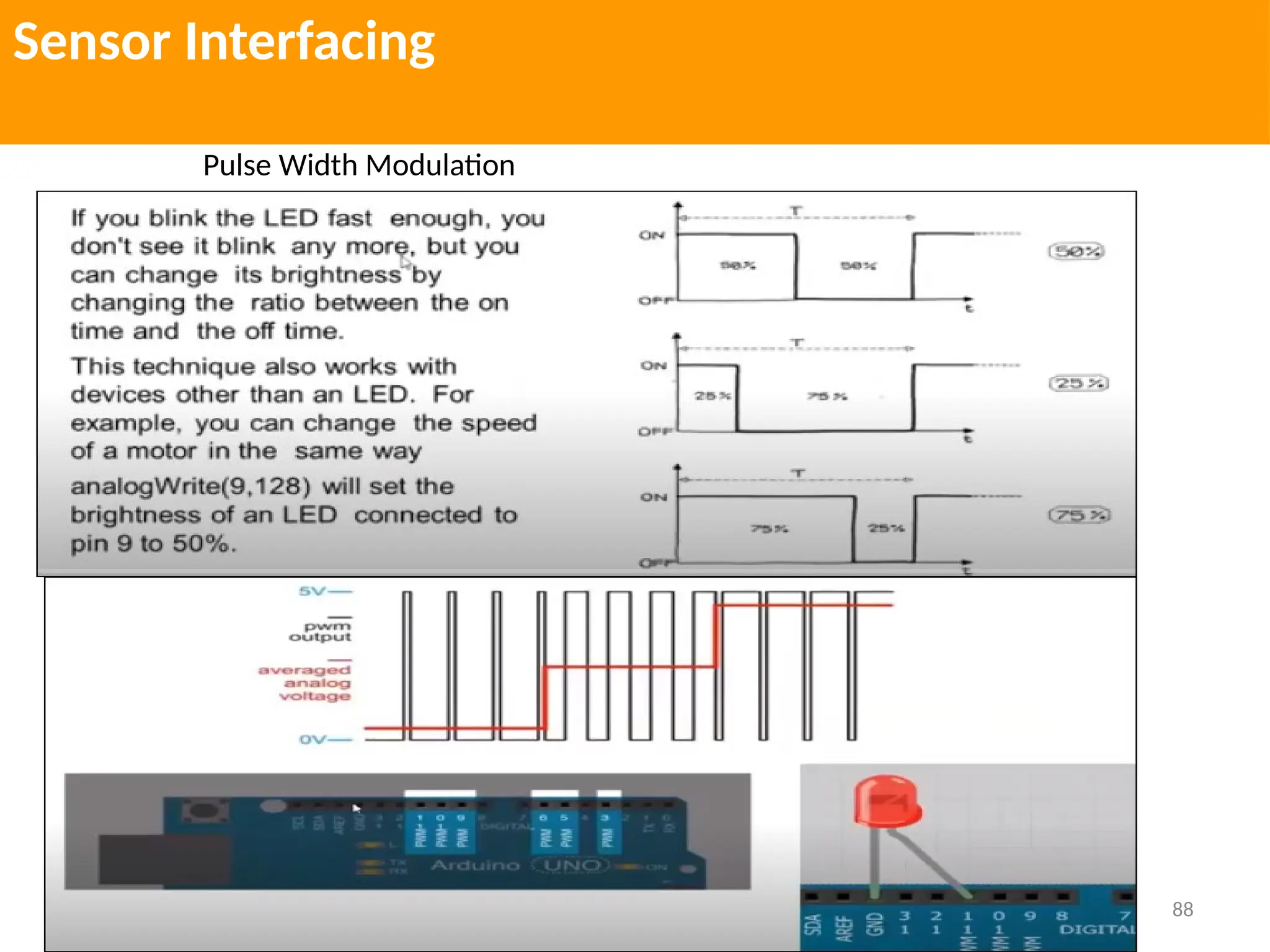
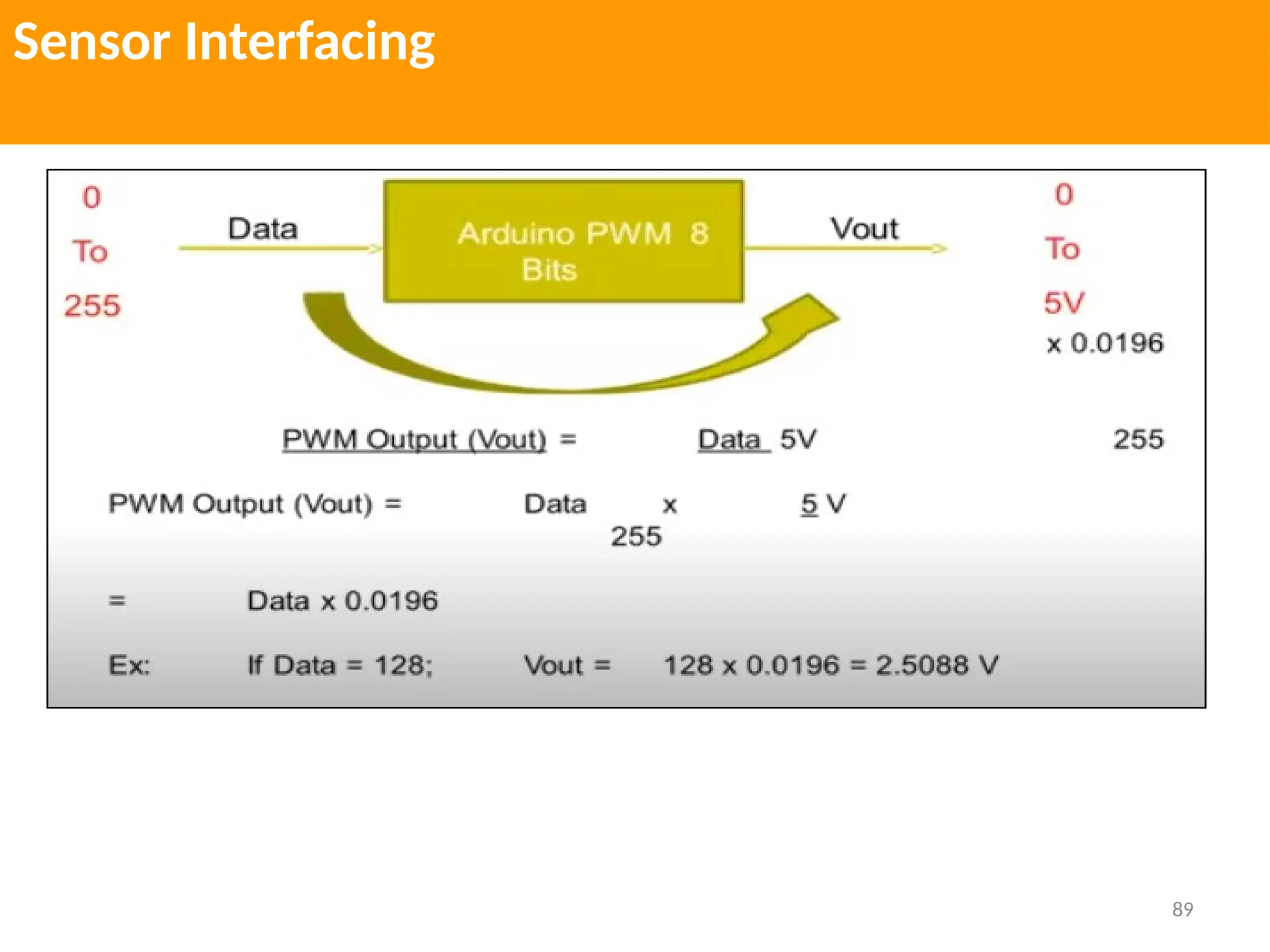
The document provides an extensive overview of various types of sensors used in robotics and automation, detailing their functions, classifications, and applications. It includes information on internal and external sensors, contact and non-contact sensors, as well as specialized modules like ultrasonic and humidity sensors, emphasizing their importance in building intelligent systems. Additionally, it covers steps for downloading and working with the Arduino software for interfacing sensors and actuators.