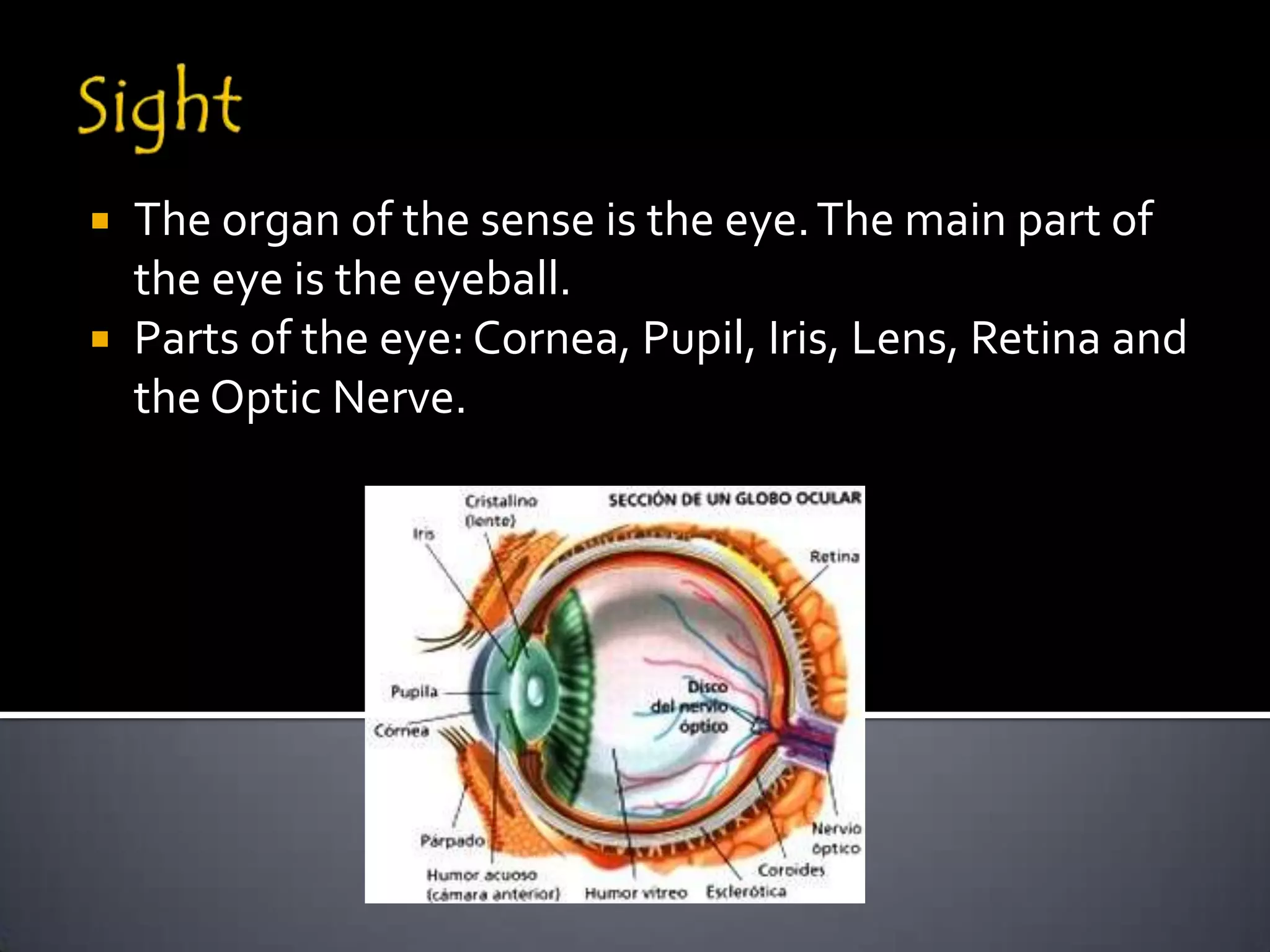
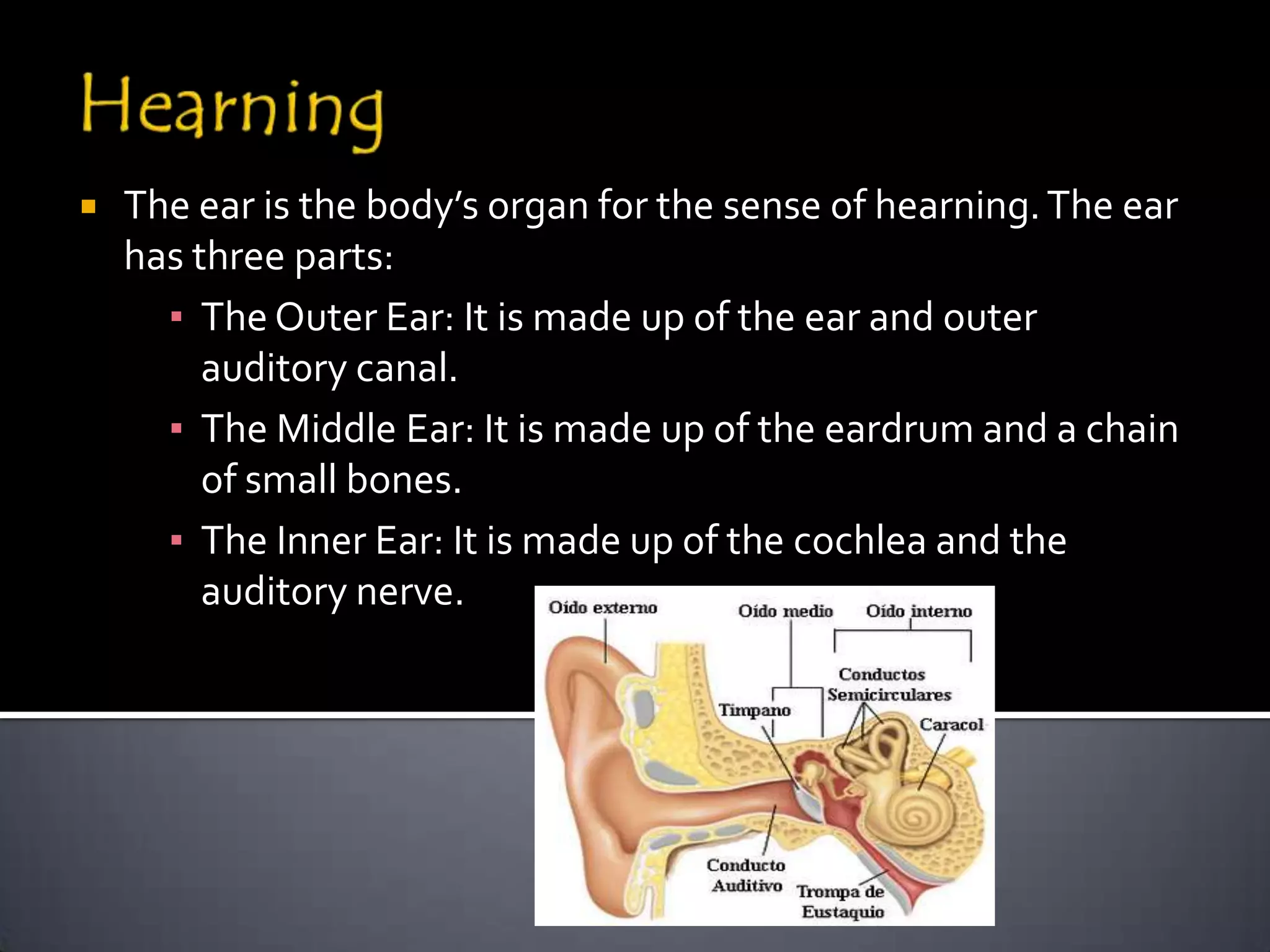
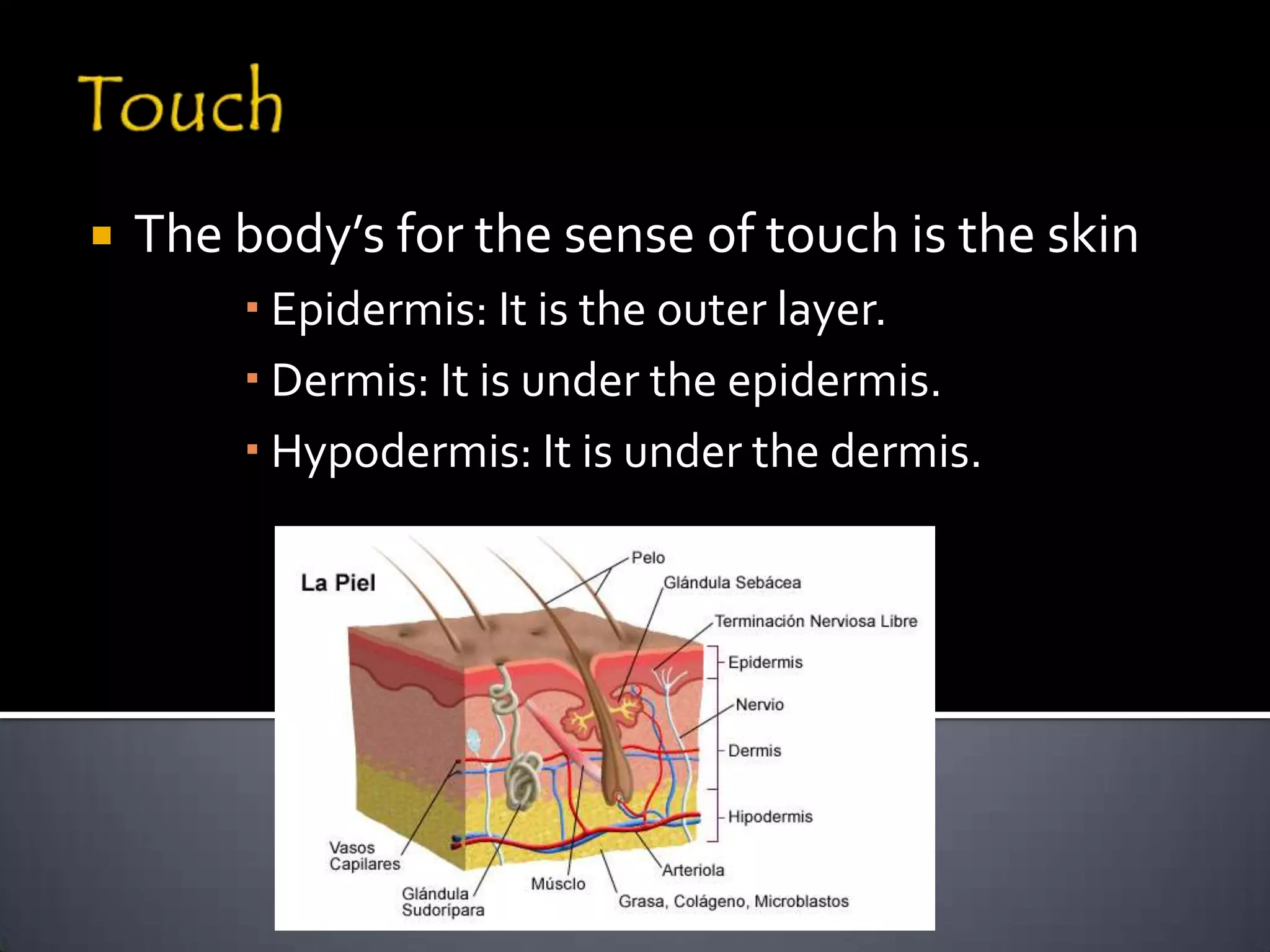
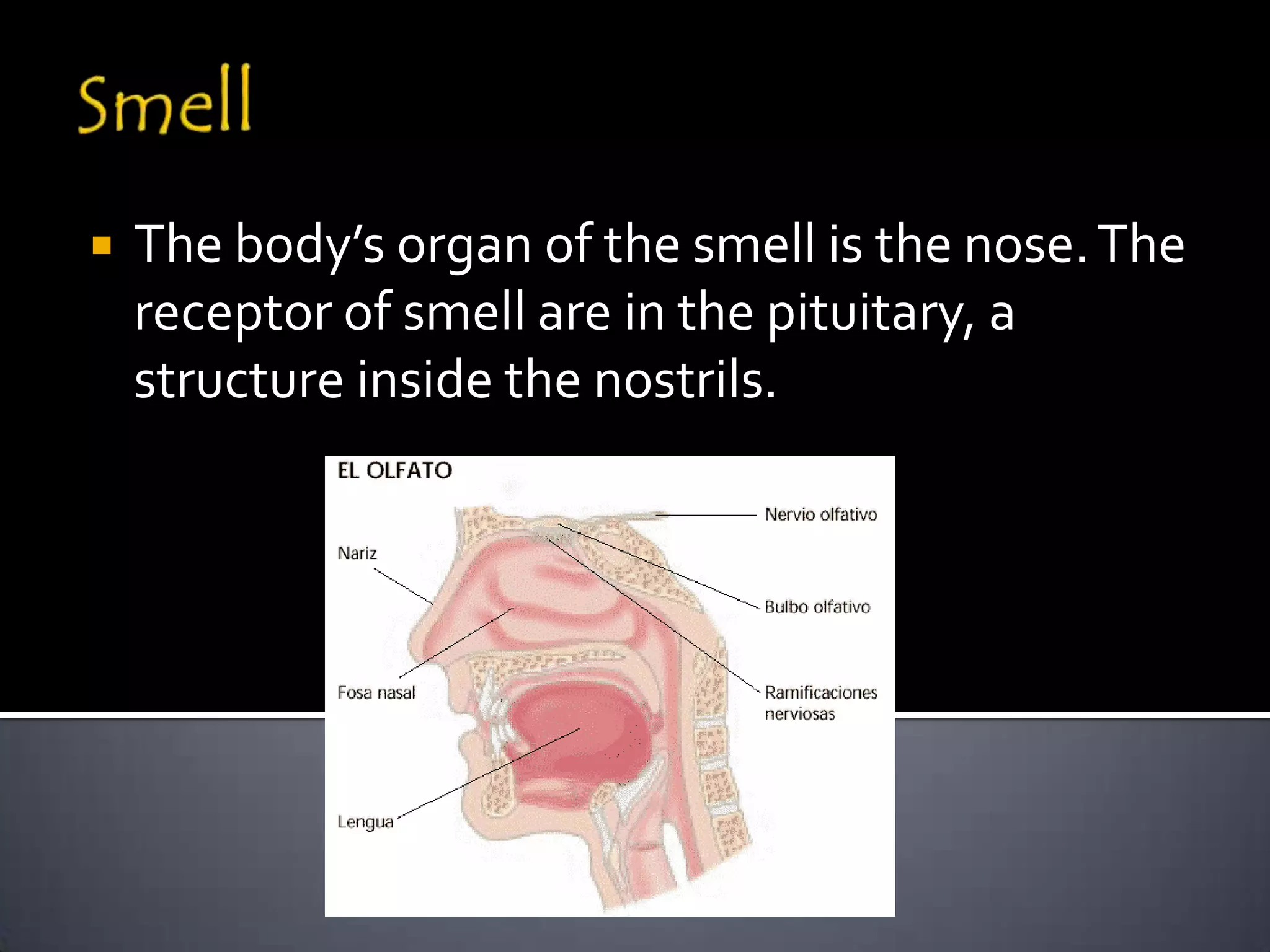
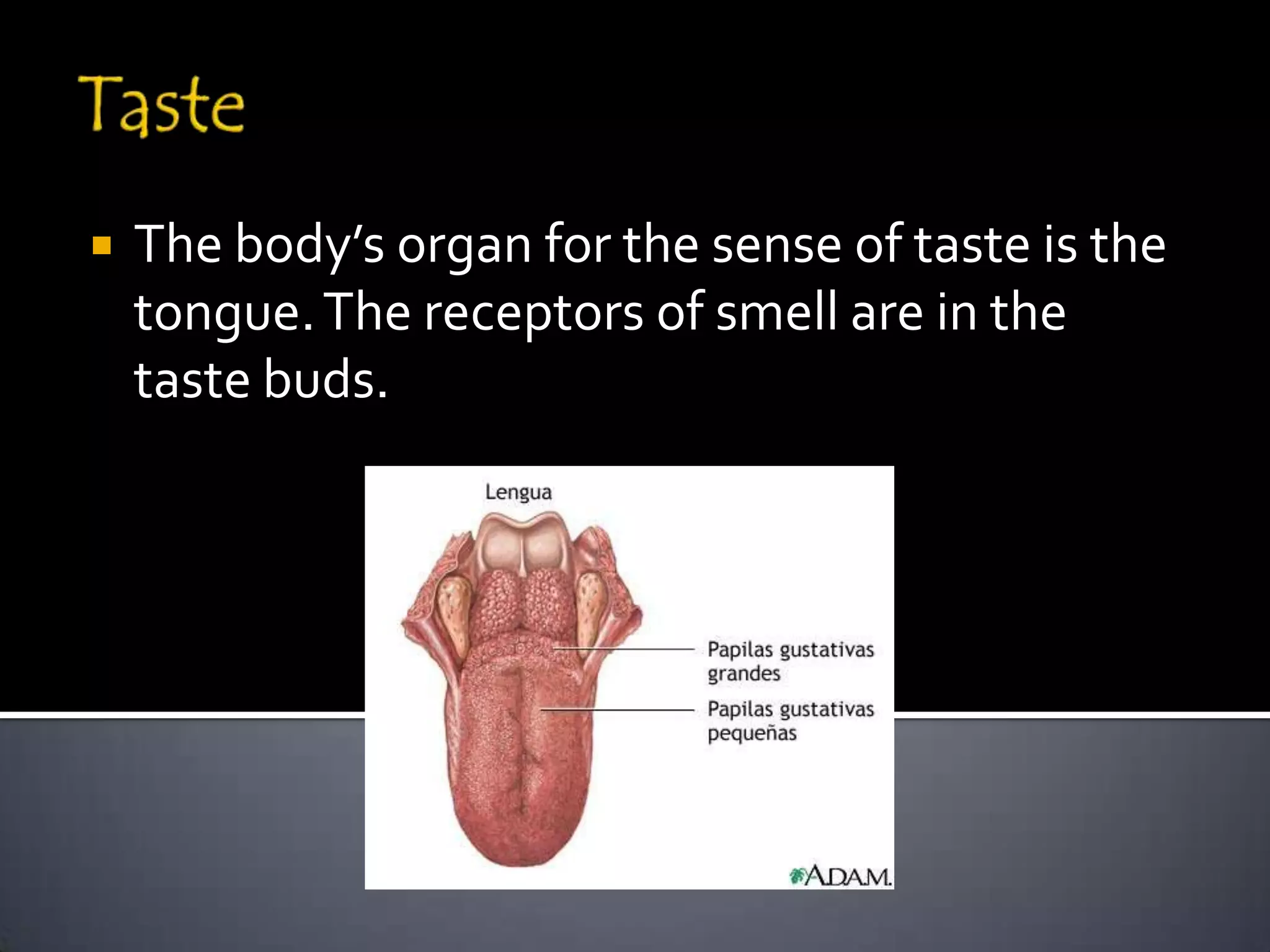
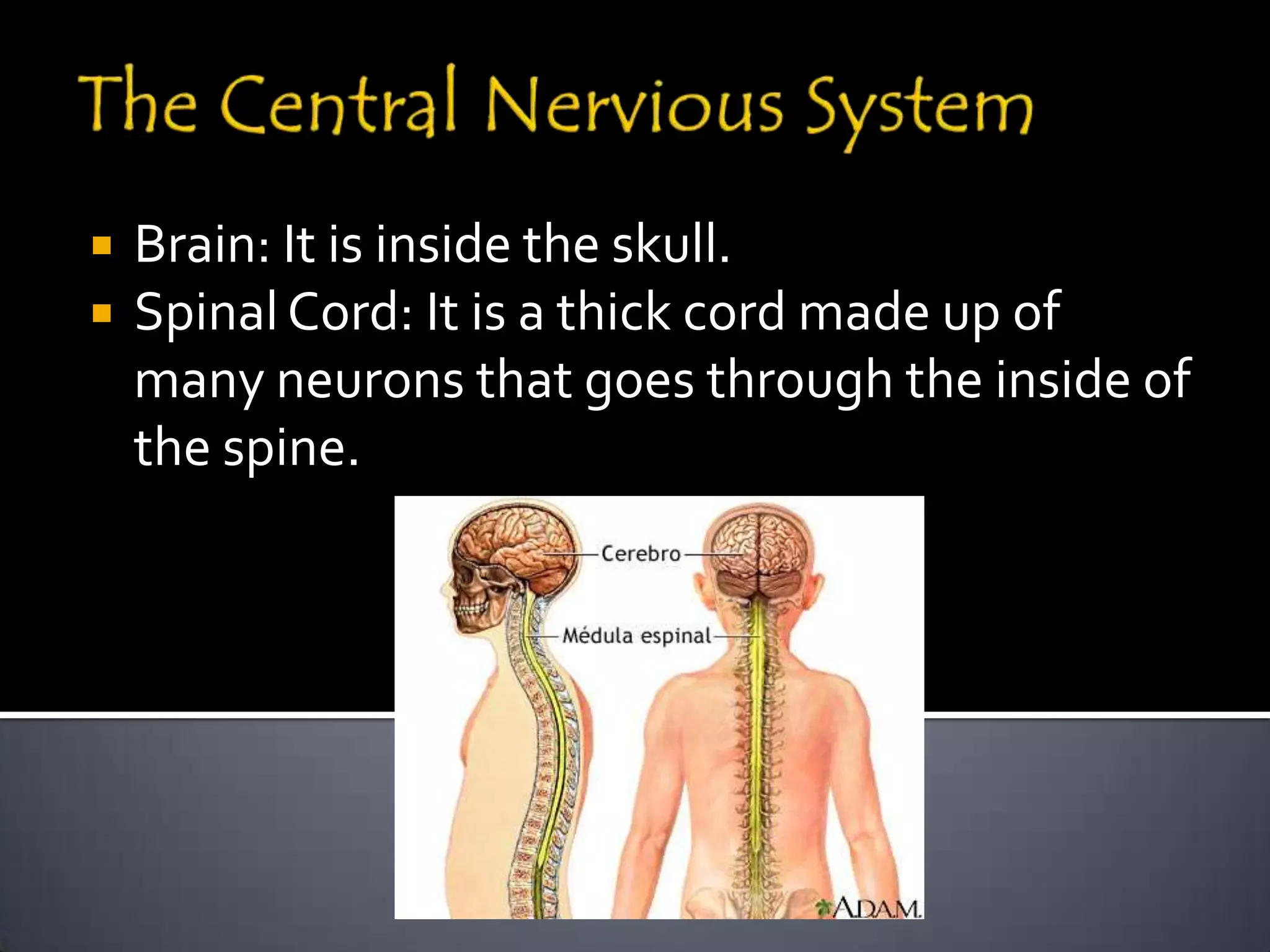
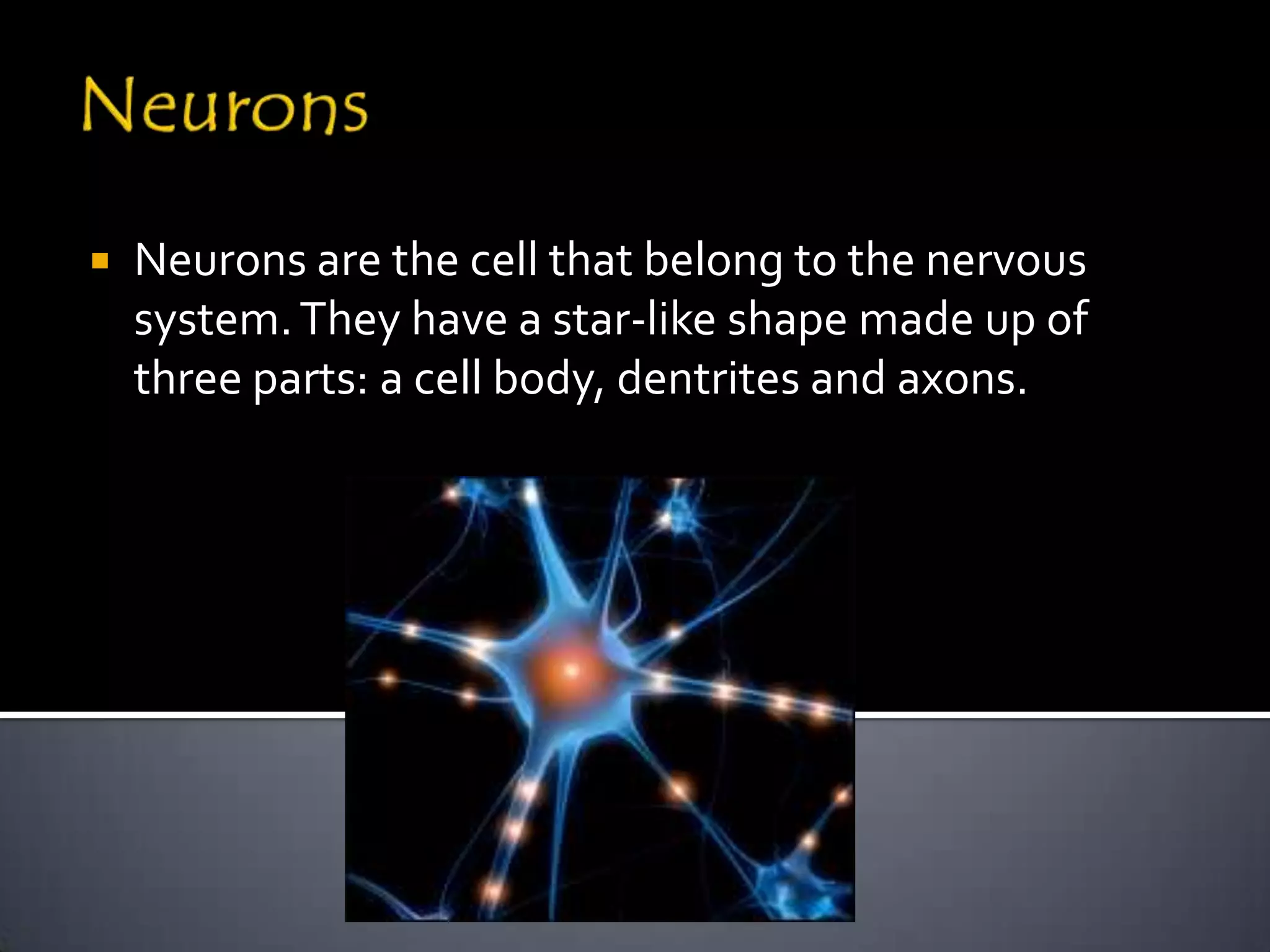
The document discusses the human body's sensory and response systems. It describes the different types of stimuli the body receives, both internal and external. It also outlines the main sensory organs - eyes, ears, skin, nose, tongue - and how each receives different types of stimuli via specialized receptors. Finally, it provides an overview of the central nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, sensory and motor nerves, and neurons, and how these systems work together to coordinate the body's responses to stimuli.