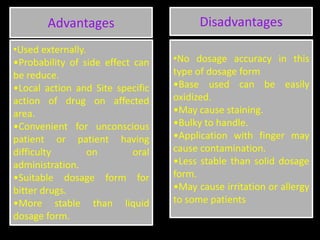
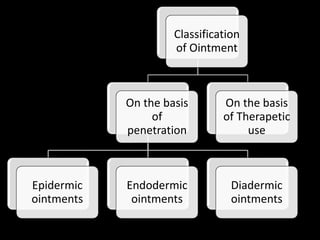
This document defines and describes semisolid dosage forms, which are dermatological preparations intended for external application on the skin. It discusses their ideal properties, sites of application, classification based on formulation type (ointments, creams, jellies, pastes, suppositories), advantages and disadvantages. Ointments are homogeneous, viscous preparations classified based on penetration (epidermic, endodermic, diadermic) and therapeutic use. Creams are emulsions consisting of an opaque internal phase within a lipophilic external phase. Jellies contain sufficient gelling agent to impart a polymeric matrix. Pastes are thick ointments with high amounts of insoluble solids. Suppositories are intended for insertion