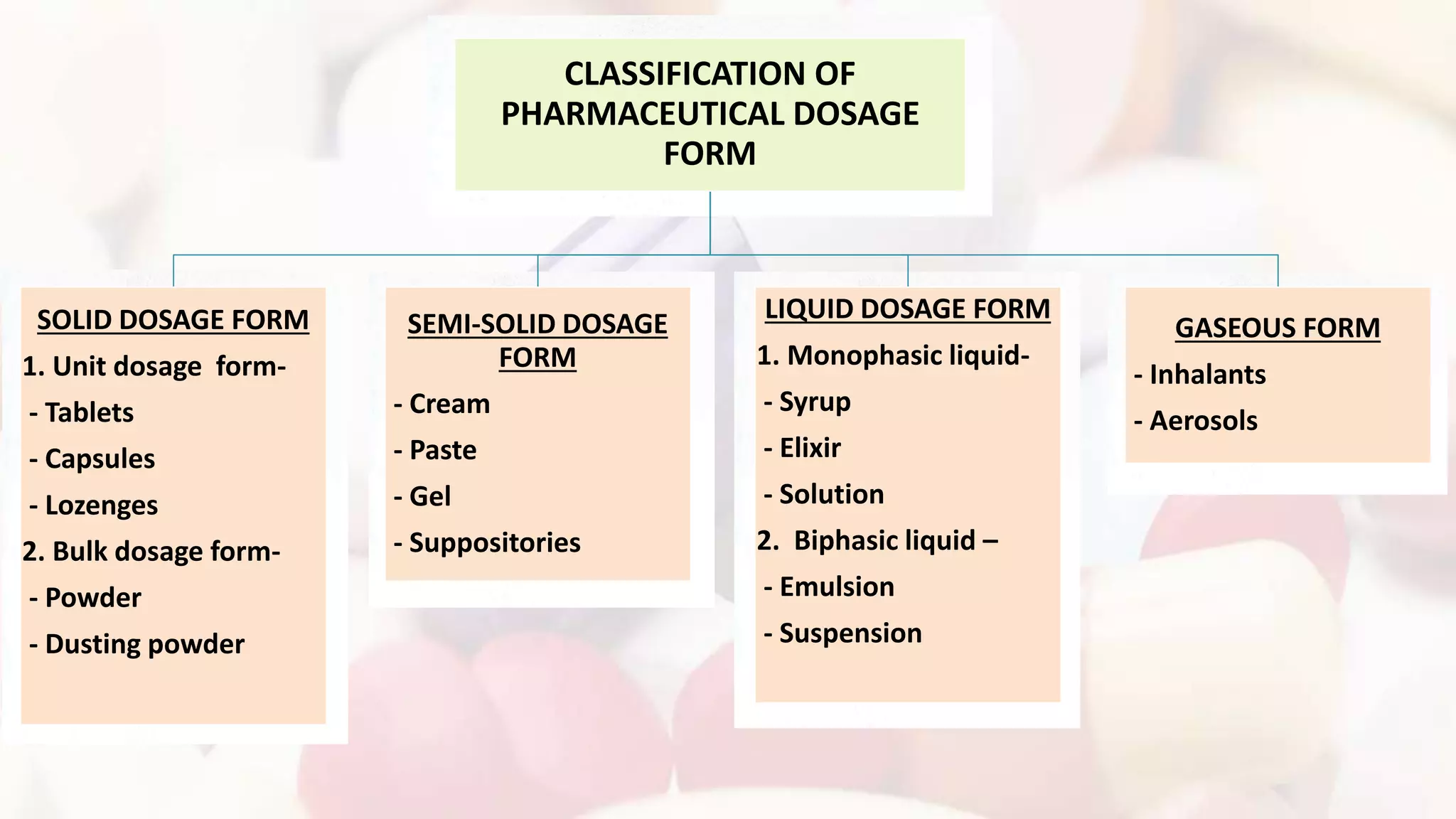
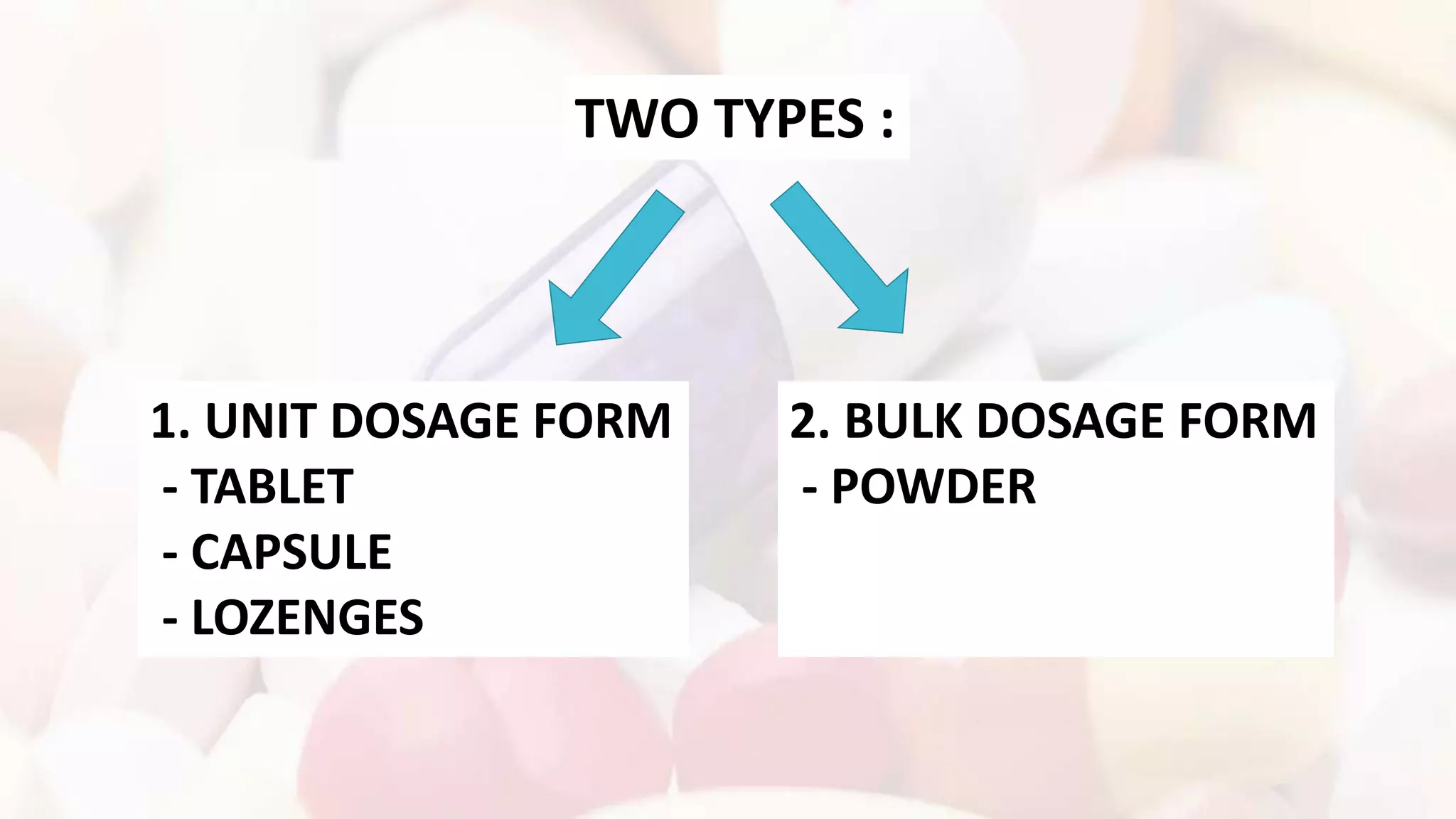
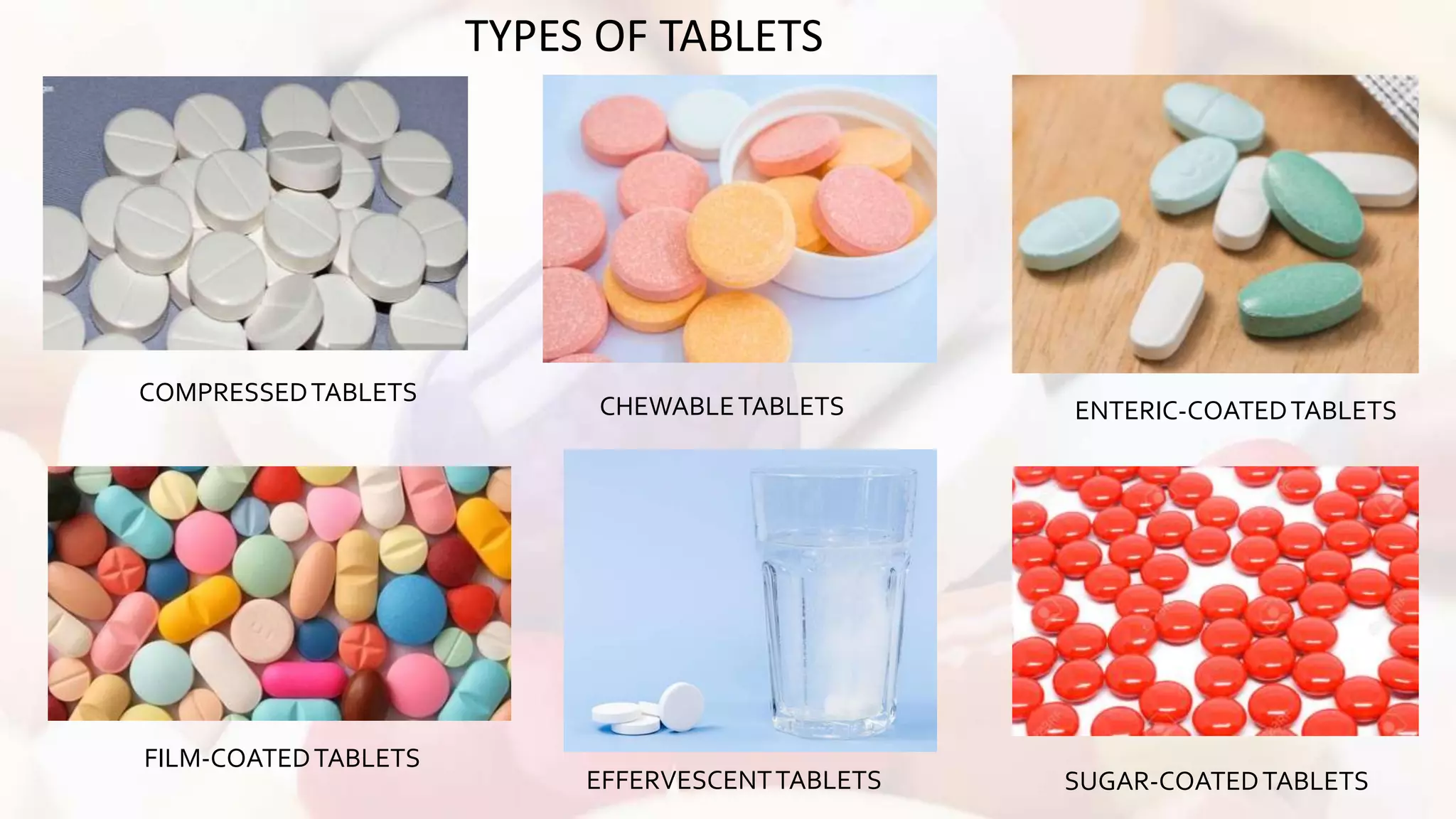
This document defines and classifies pharmaceutical dosage forms. It discusses that dosage forms contain active pharmaceutical ingredients and excipients formulated into solid, semi-solid, liquid or gaseous forms for administration. Solid dosage forms are classified as unit (e.g. tablets, capsules) or bulk (e.g. powders). Semi-solid forms include creams, ointments, and gels for topical use. Liquid forms comprise solutions, syrups, elixirs, emulsions and suspensions for oral or other internal use. Gaseous forms like inhalants and aerosols are administered via respiratory routes. Various types of these dosage forms are described based on their formulations and routes of administration.