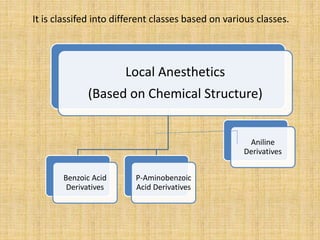
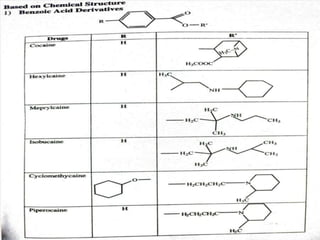
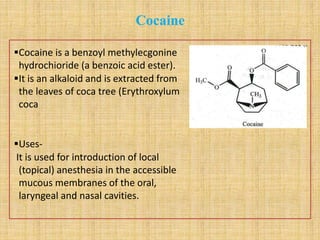
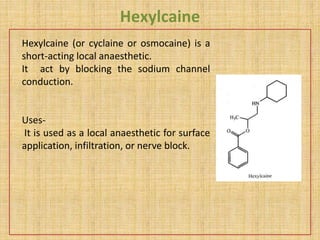
The document discusses various benzoic acid derivative local anesthetics, including cocaine, hexylcaine, meprylcaine, cyclomethycaine, and piperocaine. It describes the chemical structure and mechanisms of action of each drug. Cocaine is extracted from coca leaves and acts by blocking sodium channels and inhibiting neurotransmitter reuptake. Hexylcaine and meprylcaine also block sodium channels to produce local anesthesia, while meprylcaine has additional stimulant properties through monoamine transporter inhibition. Cyclomethycaine and piperocaine are benzoate esters used for surface anesthesia and nerve blocks through undefined mechanisms.