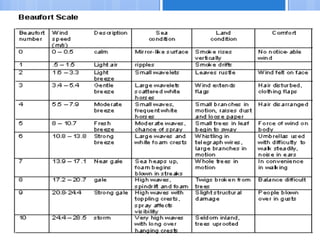
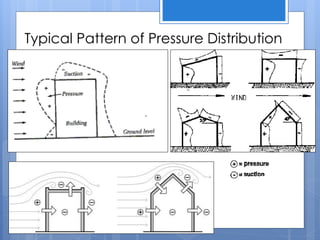
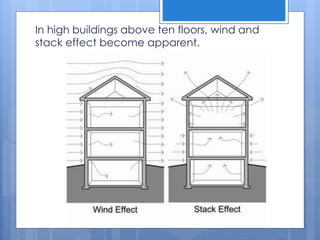
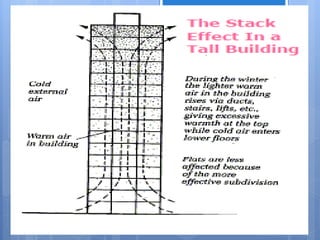
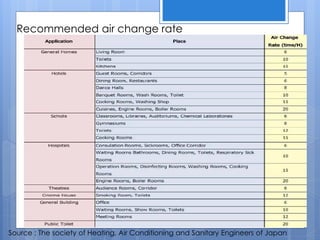
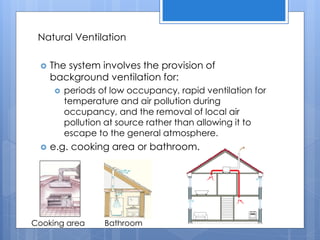
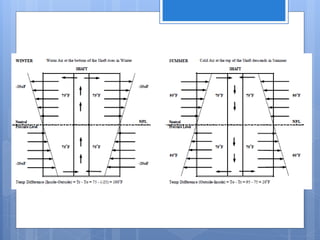
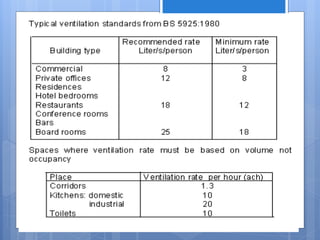
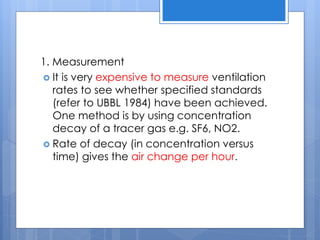
Ventilation is the process of changing or replacing air in an enclosed space to control air quality by removing contaminants and introducing outside fresh air. It is needed to maintain oxygen levels, remove carbon dioxide, control humidity, prevent heat buildup, and dilute odors and other contaminants. Ventilation can be natural through wind and stack effects, or mechanical using fans. Standards recommend minimum air change rates to ensure adequate indoor air quality and occupant comfort. Factors like air temperature, humidity, airflow patterns, and rates must be properly controlled.