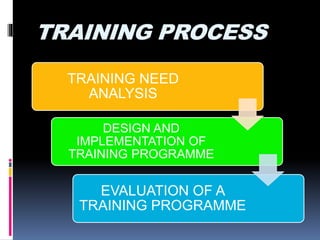
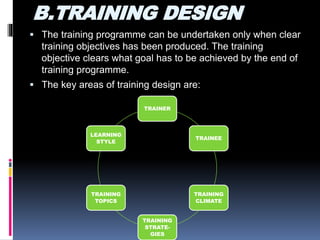
The document discusses training and development for a sales force. It defines training as increasing employees' knowledge and skills for their current job, while development prepares them for future jobs and brings their performance to a higher level. Training focuses on technical skills for current roles and is short-term, while development is long-term and involves managerial skills. Effective sales training is important for optimizing the sales force, improving employee skills and productivity, building team spirit, and reducing turnover. However, training also has limitations like retaining trained employees and being time-consuming. The training process involves analyzing needs, designing and implementing programs, and evaluating the results. Various cognitive, behavioral, on-the-job, and off-the-job training methods