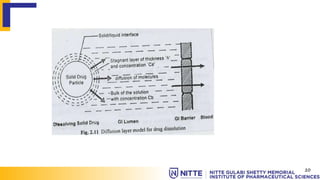
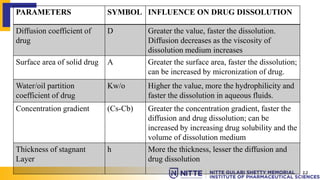
This document summarizes key concepts related to diffusion, dissolution, and pharmacokinetic parameters. It defines diffusion as the spontaneous migration of molecules from high to low concentration regions driven by Brownian motion. Fick's laws describe the rate of diffusion being proportional to the concentration gradient. Dissolution is defined as a solid solute dissolving in a solvent to form a solution. Several parameters influence dissolution rate including surface area, diffusion coefficient, and concentration gradient. Pharmacokinetics describes the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of drugs and key parameters include Cmax, Tmax, and AUC which describe the concentration of drugs in plasma over time.