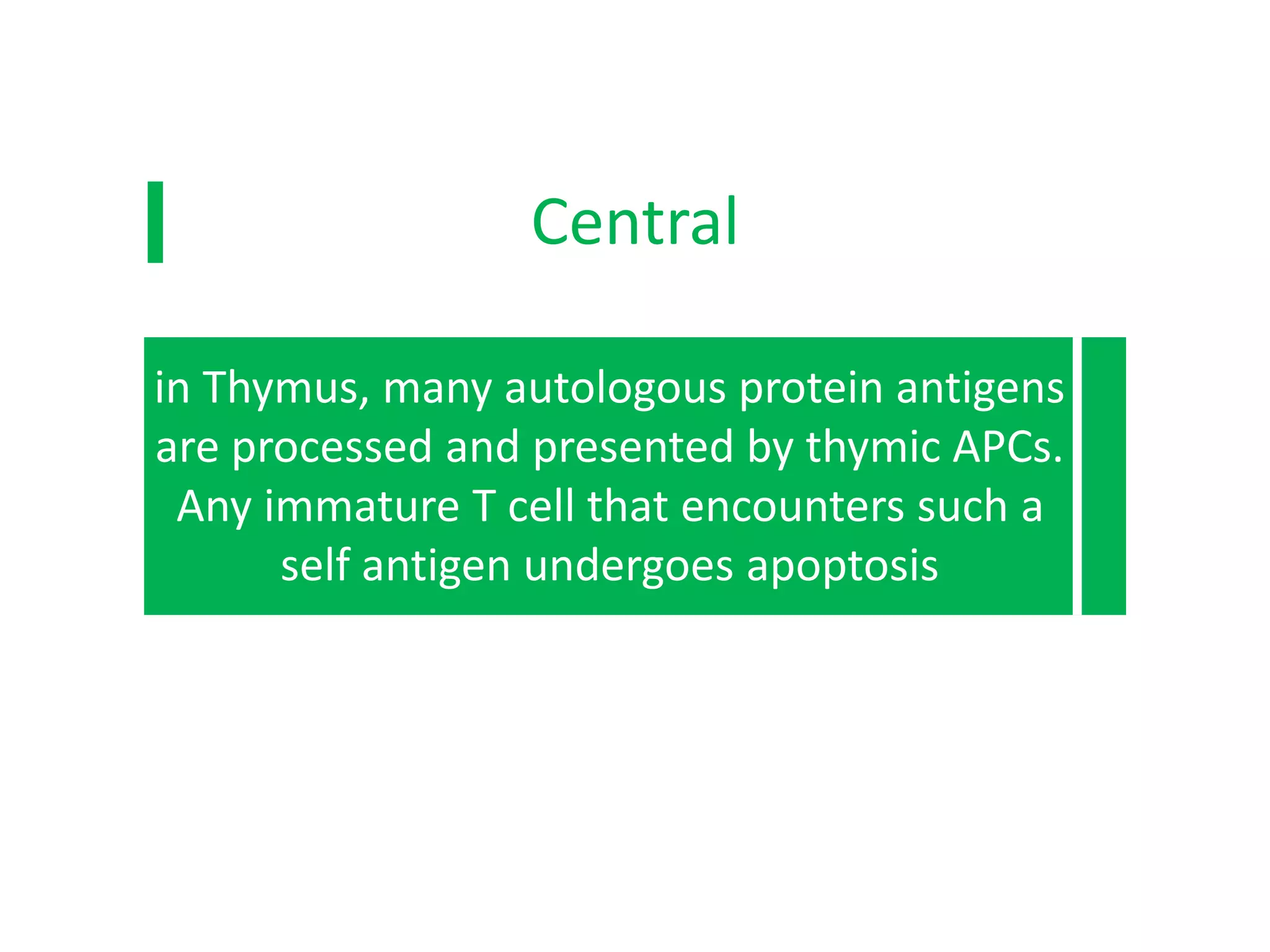
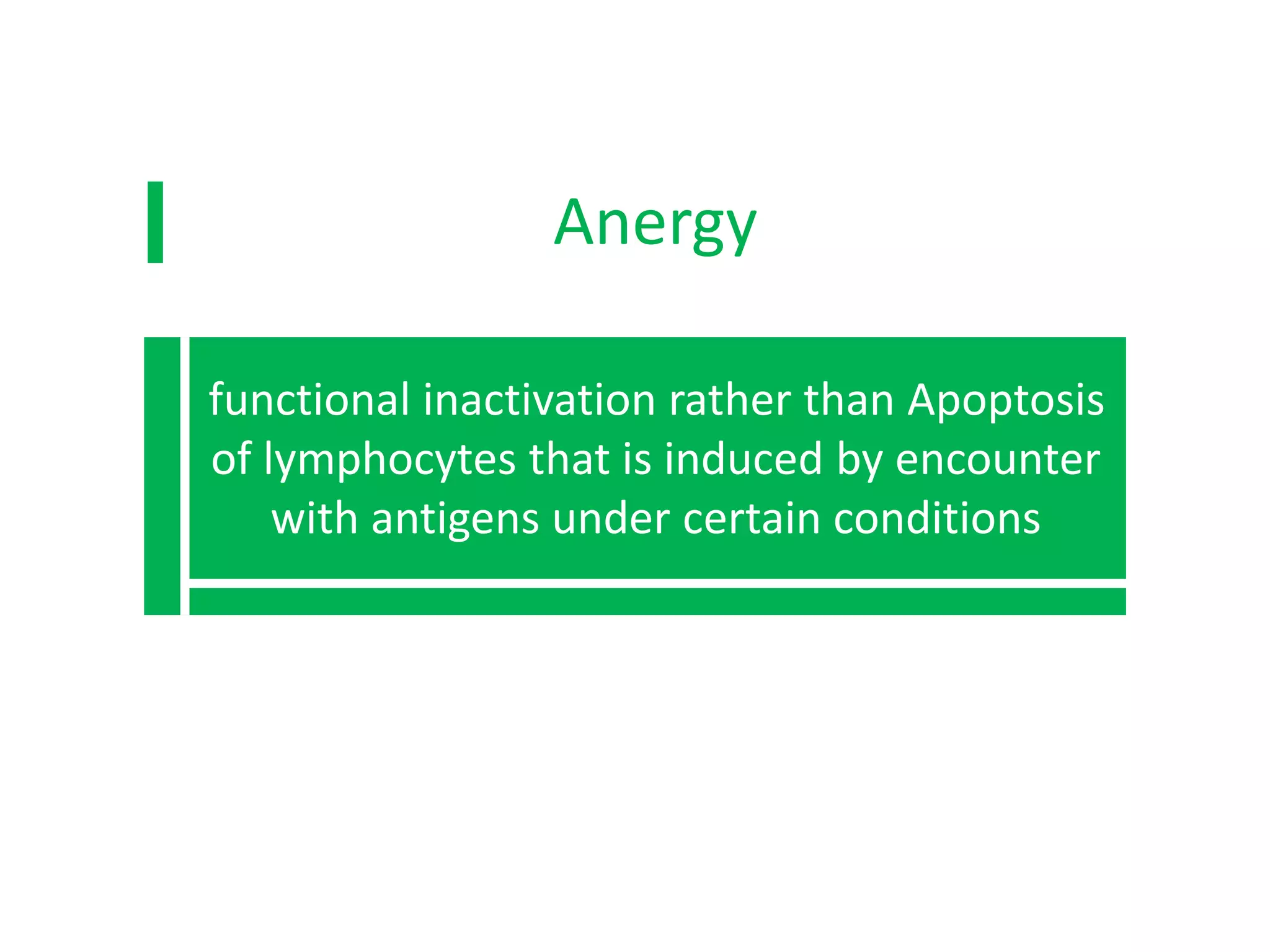
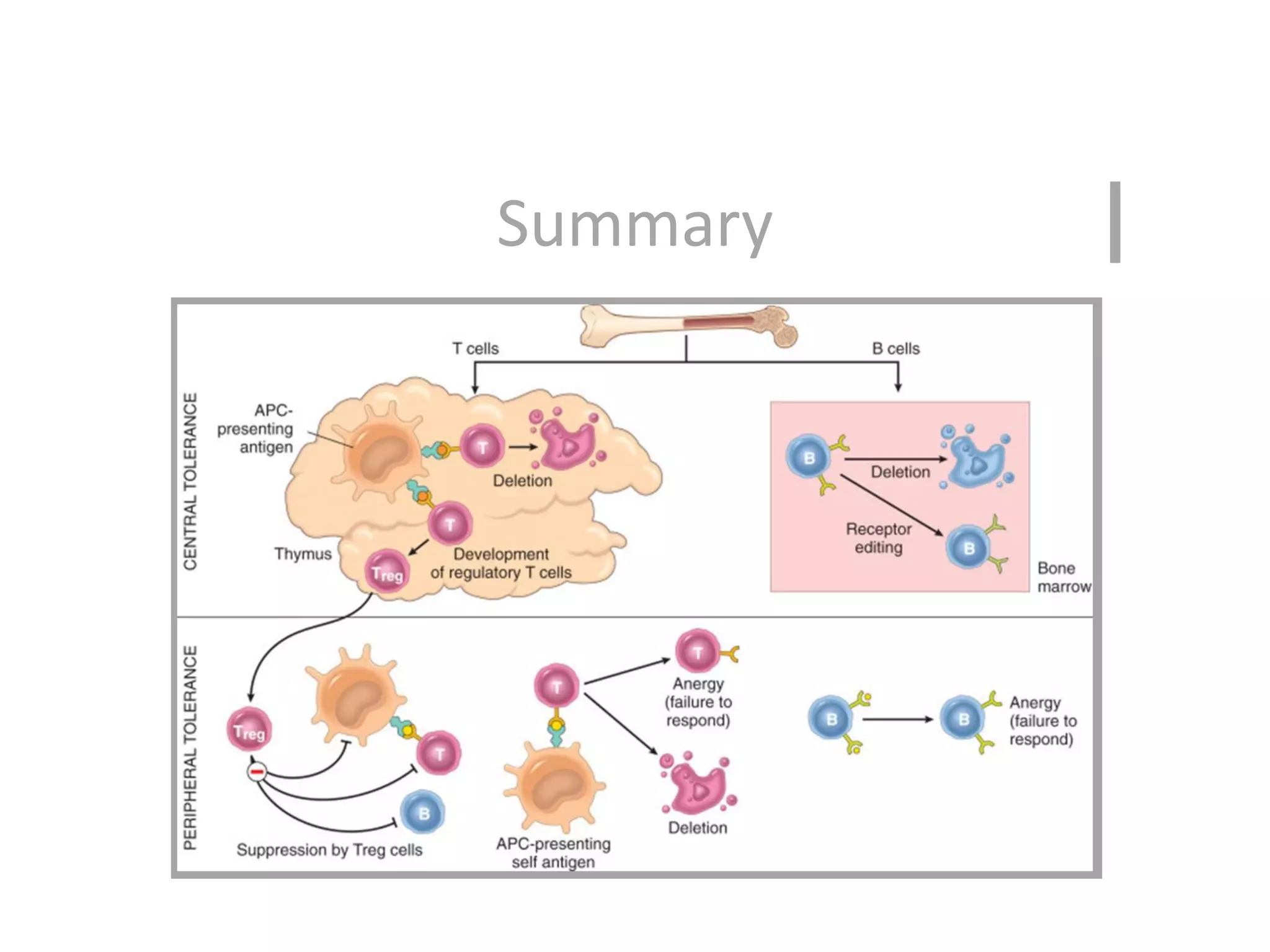
Self-tolerance is maintained through central and peripheral mechanisms in the immune system. In the central mechanism, immature T and B cells that recognize self-antigens in the thymus and bone marrow undergo apoptosis or receptor editing. In the peripheral mechanism, lymphocytes encountering self-antigens are anergized, suppressed by regulatory T cells, or deleted through apoptosis to prevent autoimmune responses.