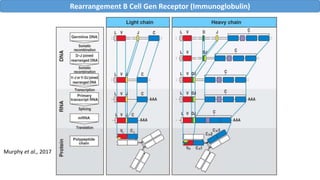
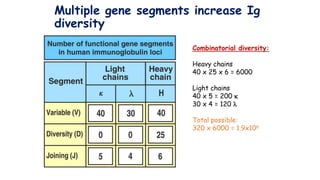
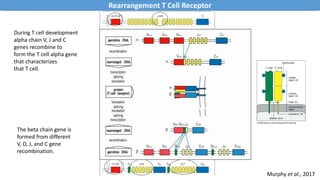
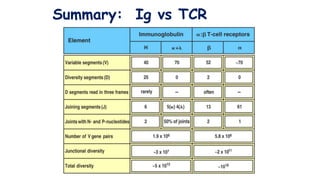
The document discusses immune tolerance and autoimmunity. It explains that the immune system normally distinguishes between self and non-self, but in autoimmune diseases this tolerance breaks down and the immune system attacks the body's own tissues and organs. The document outlines the mechanisms of central and peripheral tolerance that normally prevent this from occurring, including negative selection of autoreactive lymphocytes in the thymus and bone marrow. Factors like genetics and environment can disrupt tolerance and lead to autoimmunity.