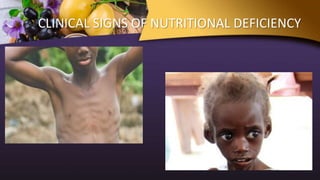
This document discusses nutrition and nutritional needs. It defines nutrition as the science of food and its components in the body. Nutrients are classified as macro or micronutrients and provide energy, build tissues, and regulate functions. Nutritional needs are affected by biological, environmental, religious, economic, social, educational, health, psychological factors. Nutritional needs are assessed using direct methods like measurements, tests, and dietary surveys or indirect methods like vital statistics. Meeting nutritional needs requires a diet planned for an individual's culture and conditions that is introduced gradually and in variety. Nurses play a role in ensuring therapeutic diets are taken and providing home care instruction.