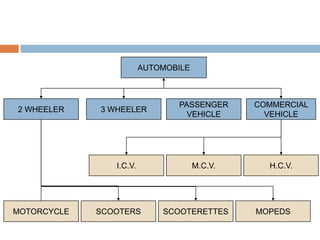
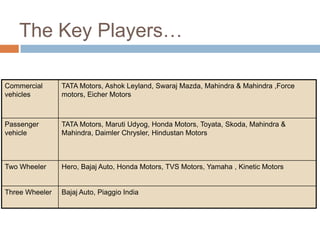
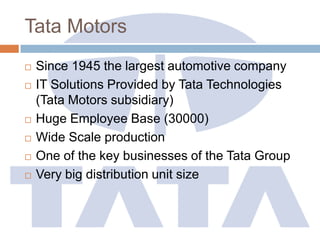
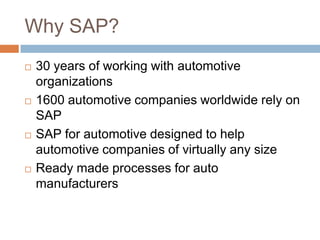
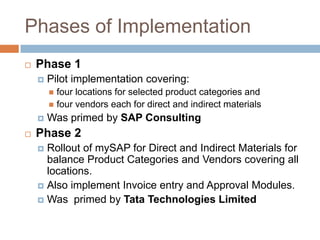
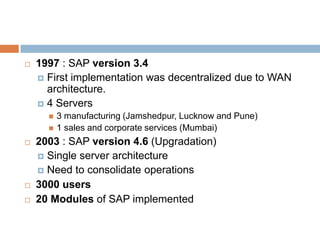
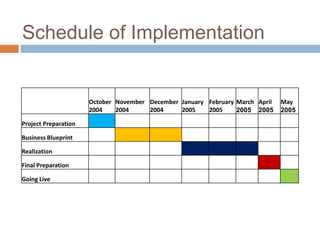
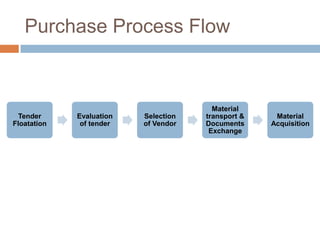
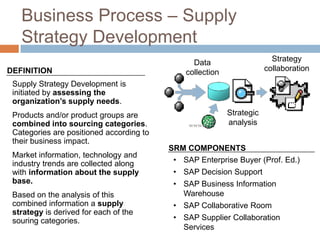
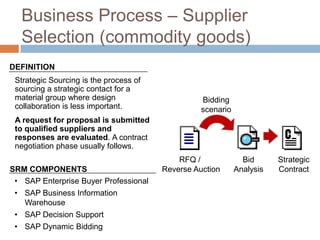
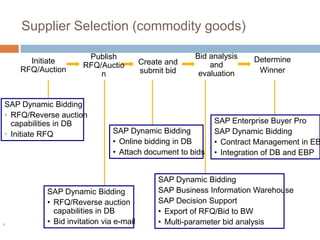
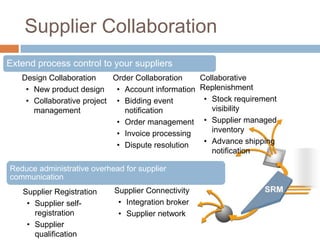
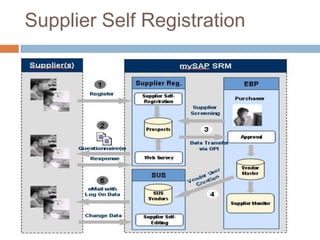
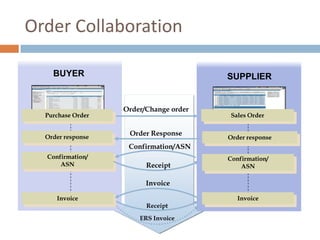
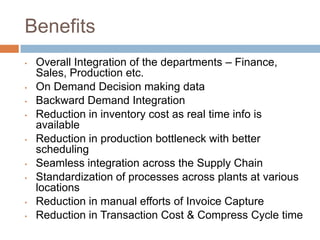
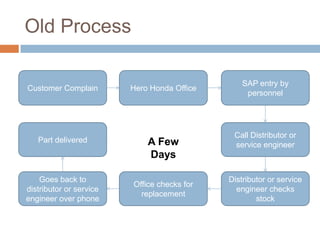
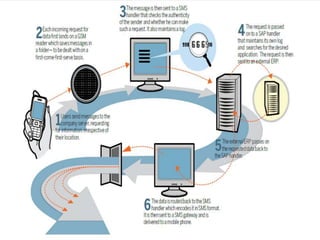
The document discusses the implementation of ERP systems in the Indian automotive industry. It provides background on the size and growth of the industry. It then describes some key needs of the automotive industry that ERP systems can address, such as full traceability, quality management, inventory optimization, and integrated financials. Two company case studies are presented: Tata Motor's implementation of SAP, and Hero Honda's implementation of an SMS-based solution to provide real-time information to field staff. Both implementations helped improve operations and customer service.