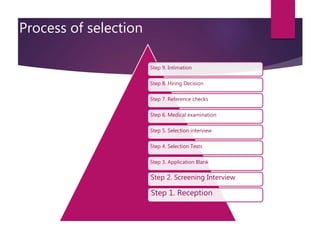
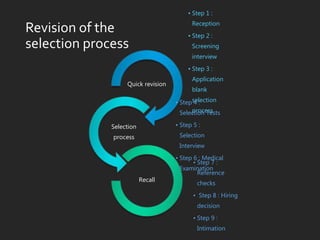
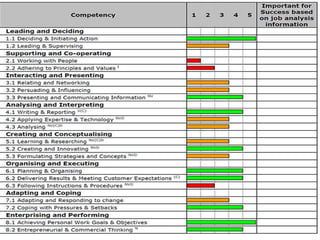
The document outlines the selection process in recruitment, emphasizing its importance in identifying suitable candidates and avoiding costly mismatches. It details the steps involved in selection, including screening interviews, application blanks, tests, medical examinations, reference checks, and hiring decisions. The document also highlights issues like credential fraud and provides case studies illustrating negative outcomes due to negligent hiring practices.





























![Sources
Personnel and human Resource management – P Subbarao
(5th Edition)
http://hrtrendinstitute.com/2015/08/13/trends-in-
recruitment-and-selection-new-
infographic/#prettyPhoto[galname]/0/
Slide Share Articles.
Online research Articles.
D. Callahan, “Resume Padding”, in www.cheatingculture.com
www.cnn.com
www.backgroundchecking.co.un](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/selection1-160801145655/85/Selection-process-features-and-examples-33-320.jpg)
