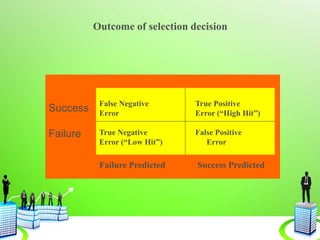
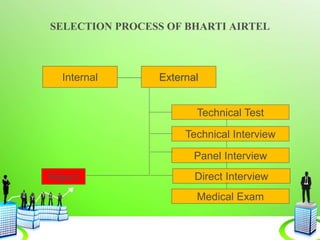
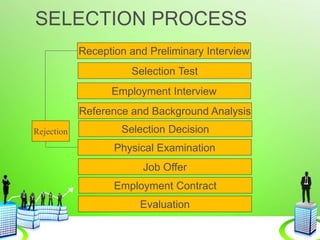
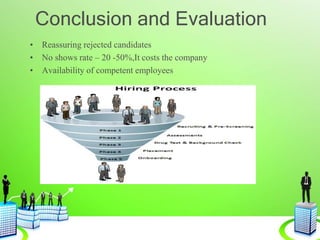
This document discusses the recruitment and selection process. It begins by defining recruitment and outlining its purpose and importance. It then describes the factors that influence recruitment, both internal and external. The recruitment process is explained as having 5 stages: planning, strategy development, searching, screening, and evaluation/control. Various recruitment sources, both internal and external, are listed. The selection process is then defined and explained as involving reception/interview, testing, employment interview, referencing, selection decision, medical exam, offer, and evaluation. Common selection tests, interviews, reference checks, employment contracts, and induction/orientation programs are also outlined.