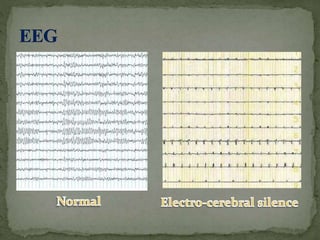
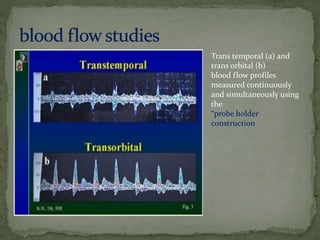
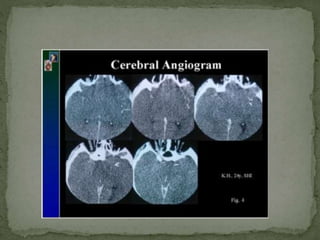
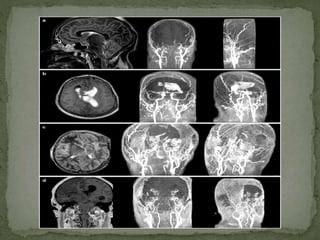
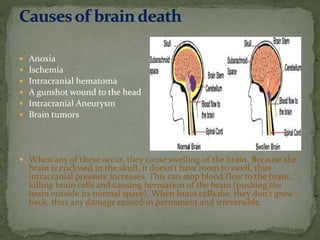
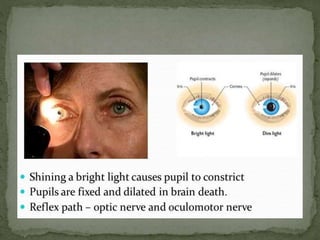
Brain death is defined as the complete and irreversible cessation of all brain functions, including the brain stem. It can be determined by the absence of electrical activity in the brain via EEG, lack of blood flow to the brain, and the absence of all clinical brain functions upon examination. Some causes that can lead to brain death include anoxia, ischemia, intracranial hemorrhage, brain tumors, and head injuries. Proper certification of brain death requires examination by a board of doctors at least three times over a period of hours to confirm the irreversible loss of all brain functions. Recovery from brain death is not possible, as it indicates misdiagnosis, while patients in comas or vegetative states still