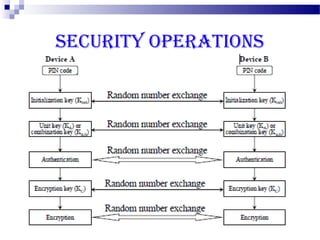
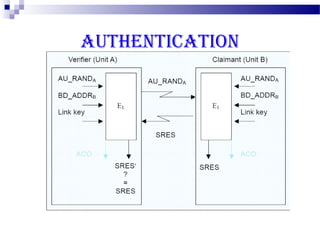
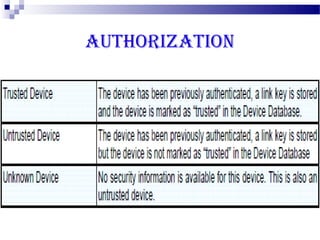
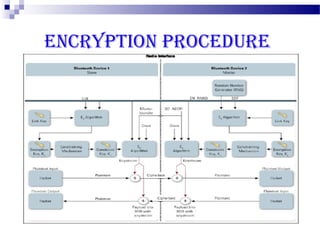
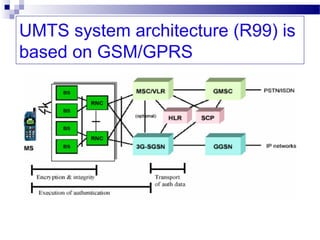
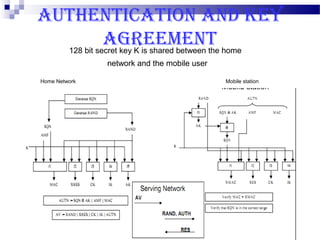
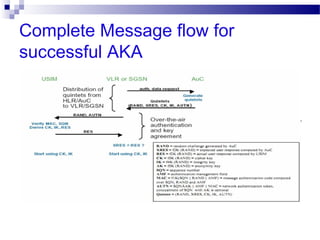
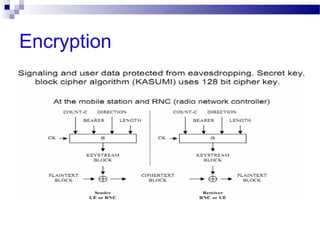
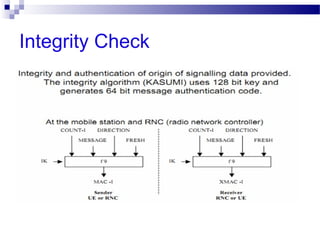
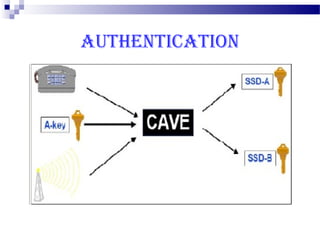
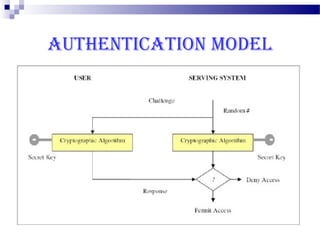
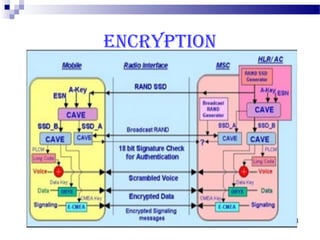
This document discusses security in Bluetooth, CDMA, and UMTS wireless technologies. It describes security threats like disclosure and integrity threats in Bluetooth. It outlines Bluetooth security levels, modes, and techniques like authentication, authorization, and encryption. It also discusses known vulnerabilities like spoofing and denial of service attacks against Bluetooth. The document then covers 3G security features in UMTS like mutual authentication and data integrity. Finally, it provides an overview of CDMA technology and security through encryption and authentication.