The document provides an overview of the Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) protocol. It discusses:
- SET is an open encryption standard designed to securely process credit card transactions over the internet. It uses digital certificates and signatures.
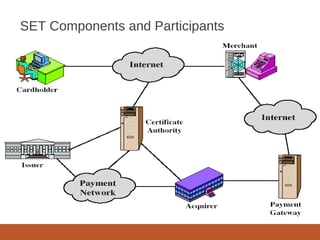
- Key components of SET include confidentiality of information, integrity of data, cardholder authentication, and merchant authentication.
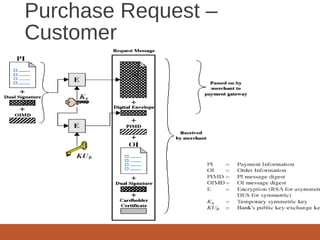
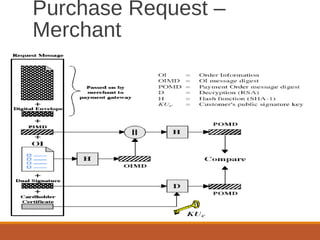
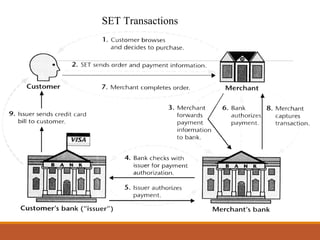
- A SET transaction involves a cardholder, merchant, issuer, acquirer, payment gateway, and certification authority going through an initiate request, initiate response, purchase request, and purchase response process.
- Payment authorization and capture are also part of the SET transaction flow. Digital signatures and certificates are used to authenticate parties and messages.















![Dual Signature
The operation for dual signature is as follows:
Take the hash (SHA-1) of the payment and order information.
These two hash values are concatenated [H(PI) || H(OI)] and then the result is hashed.
Customer encrypts the final hash with a private key creating the dual signature.
DS = EKRC [ H(H(PI) || H(OI)) ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/upload-150403113028-conversion-gate01/85/secure-electronics-transaction-18-320.jpg)
![DS Verification by Merchant
• The merchant has the public key of the customer obtained from the customer’s
certificate.
• Now, the merchant can compute two values:
H(PIMD || H(OI))
DKUC[DS]
• Should be equal!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/upload-150403113028-conversion-gate01/85/secure-electronics-transaction-19-320.jpg)
![DS Verification by Bank
• The bank is in possession of DS, PI, the message digest for OI (OIMD), and
the customer’s public key, then the bank can compute the following:
H(H(PI) || OIMD)
DKUC [ DS ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/upload-150403113028-conversion-gate01/85/secure-electronics-transaction-20-320.jpg)