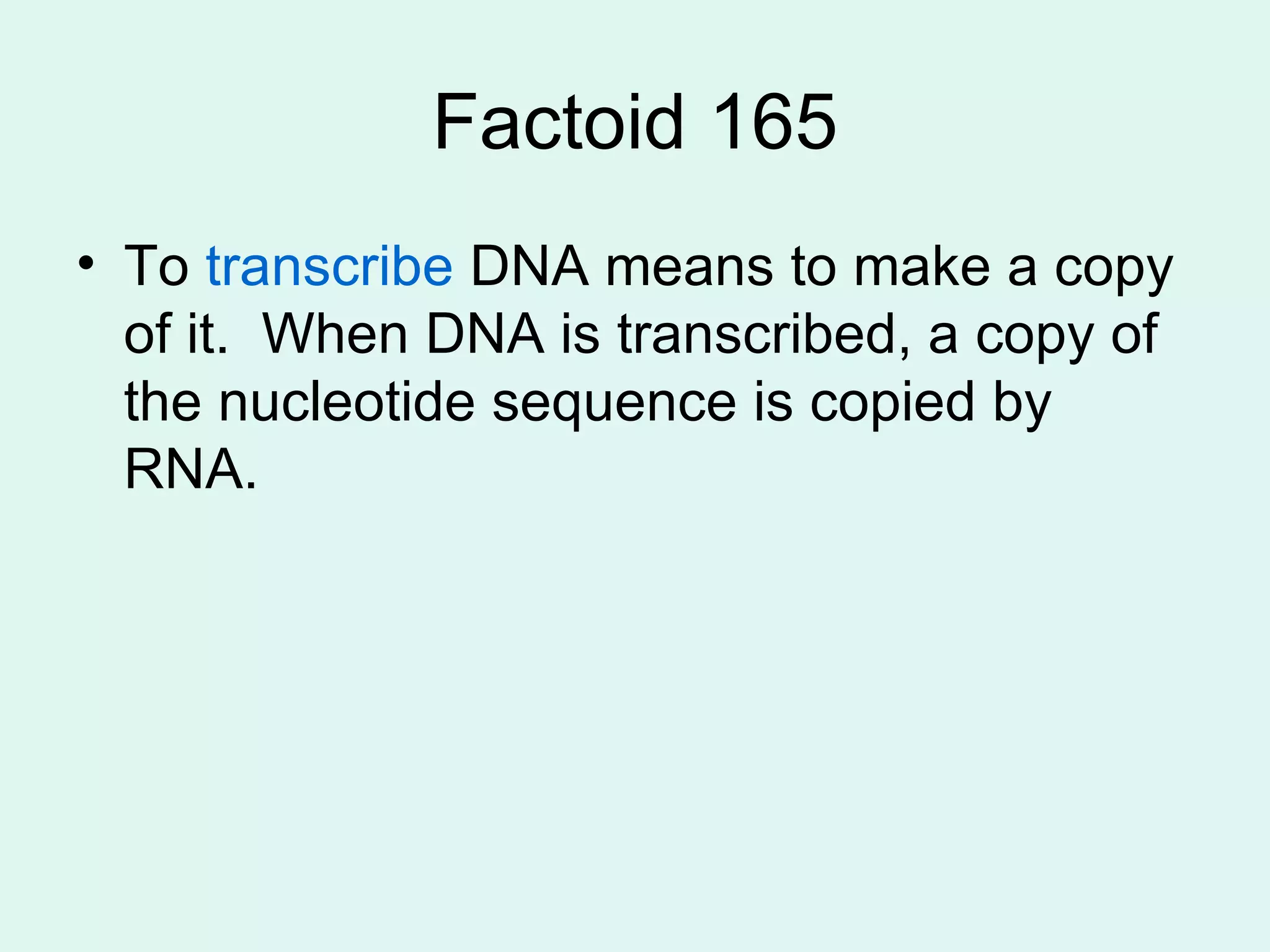
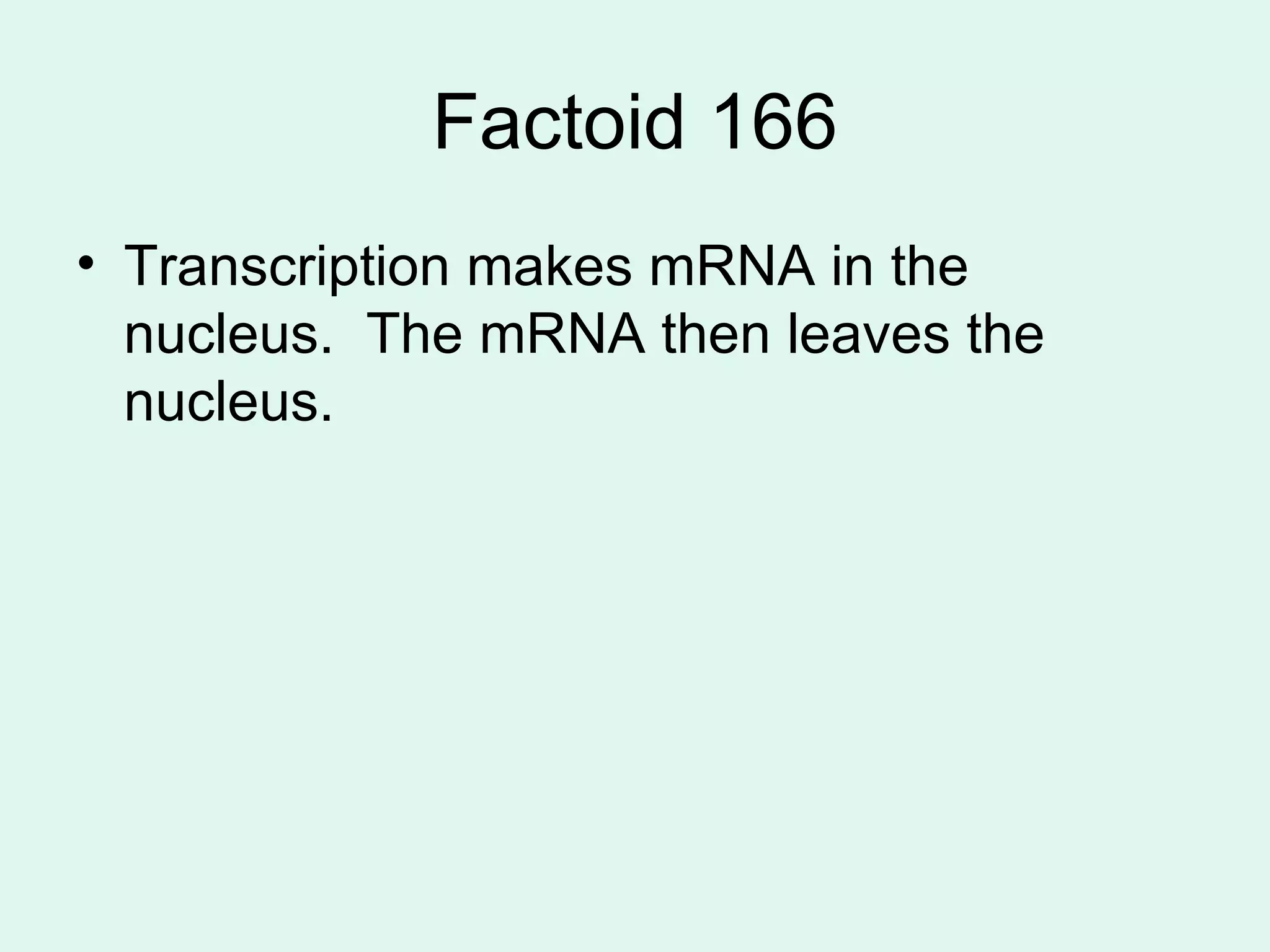
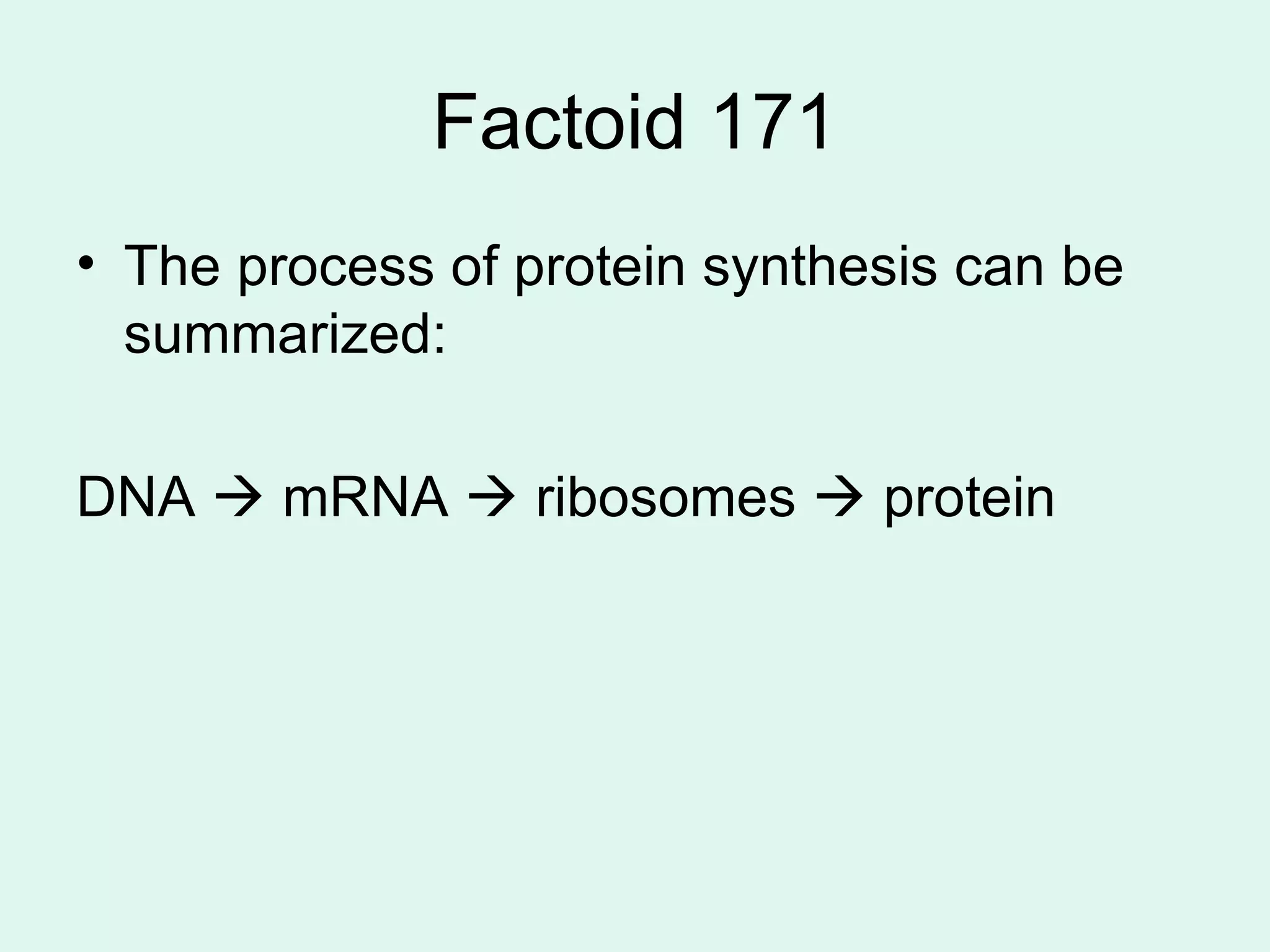
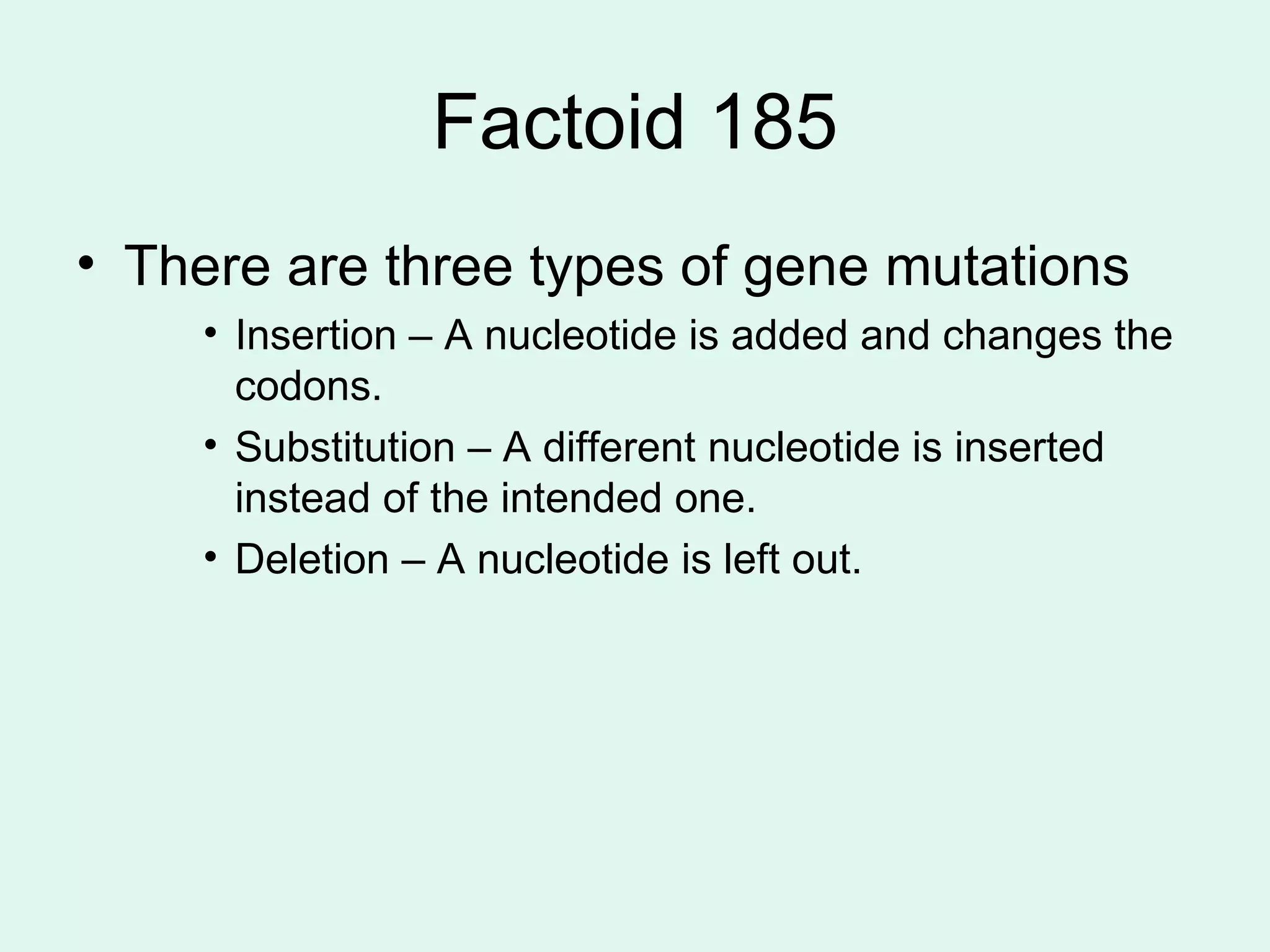
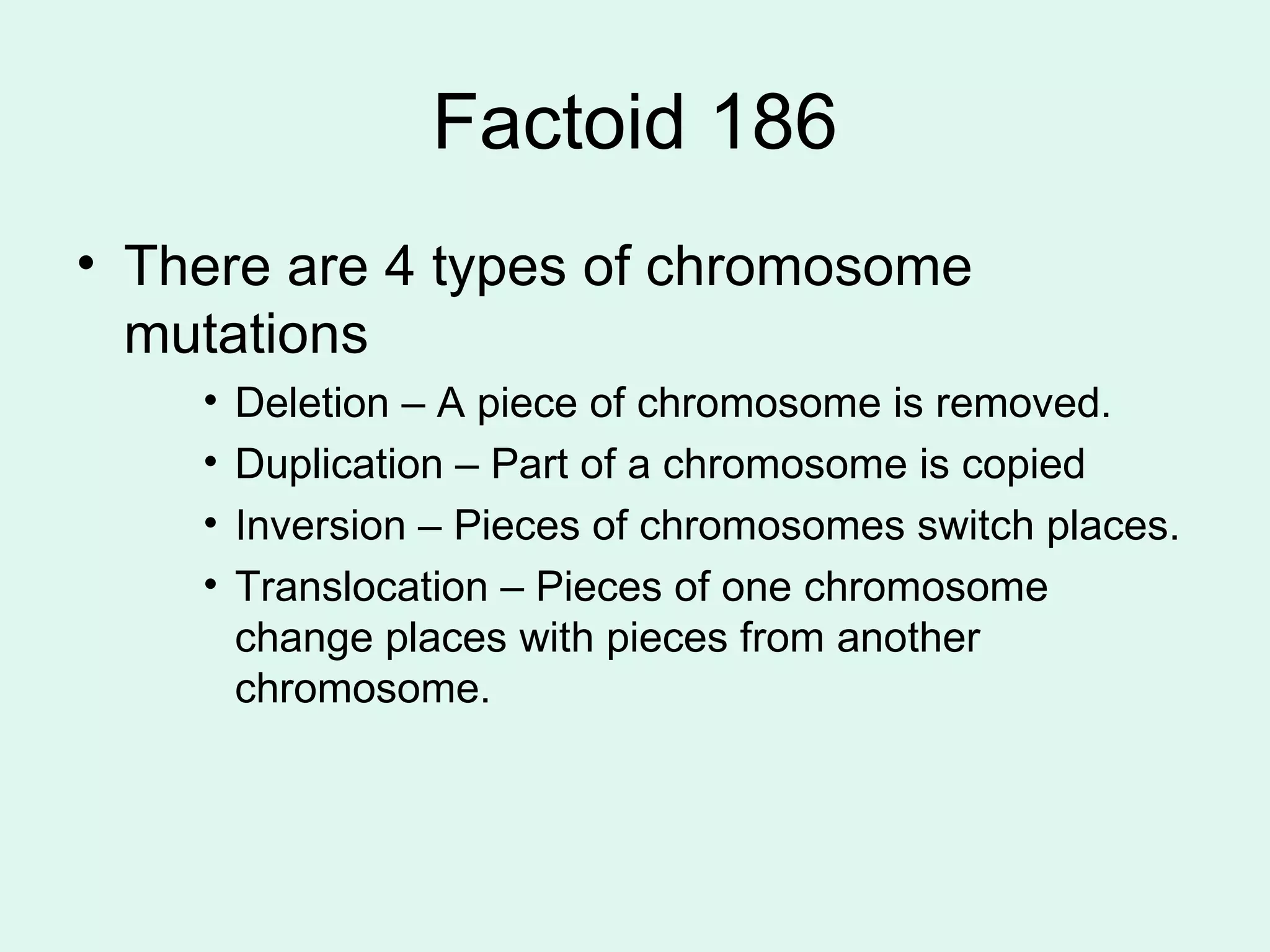
DNA controls the production of proteins in cells and contains the genetic instructions passed down from parents. It is made up of nucleotides that form the shape of a twisted ladder. In 1953, Watson and Crick determined that DNA has a double helix structure. Three types of RNA - mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA - help in the process of protein synthesis by transcribing DNA and transporting amino acids. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA is read in groups of three to determine which amino acid each codon codes for.