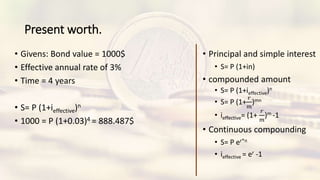1) The document discusses rules for calculating simple interest, compound interest, effective interest rates, and continuous compounding. It provides examples of calculating total amounts, interest rates, and present worth for various scenarios involving loans, bonds, and investments with different interest rates and time periods.
2) Questions are worked through calculating total amounts, interest rates, and present worth for investments with monthly, daily, semiannual compounding and continuous compounding over periods of 2, 4, 10, and 12 years.
3) Formulas used include simple interest, compound interest, effective interest rates, continuous compounding, and present worth. Results are calculated and explained for each question.



![The total amount of principal plus simple interest due
after 2 years if no intermediate payments are made.
• Givens: monthly interest rate = 2%, p=1000$
• Simple interest , 2 years = 24 months
• S= P (1+in)
• = 1000 (1+ [0.02*12]*2)=1480$
• Principal and simple interest
• S= P (1+in)
• compounded amount
• S= P (1+ieffective)n
• S= P (1+
𝑟
𝑚
)mn
• ieffective= (1+
𝑟
𝑚
)m -1
• Continuous compounding
• S= P er*n
• ieffective = er -1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/section2-230101090432-ec743b42/85/Section-2-pptx-4-320.jpg)