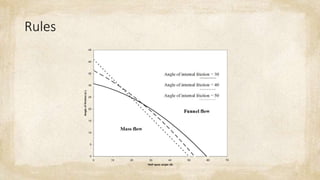
This document provides rules and examples for calculating mechanical operations related to bulk solids storage and transport. It includes formulas for calculating volume and mass flow rate of cones, as well as vertical and lateral pressures at the bottom of a bin. An example calculates these pressures for a given bin geometry. It also discusses belt conveyor design, including belt and idler specifications and formulas for power calculations. The final example uses these formulas to calculate the motor power and storage bin dimensions needed for a given solid transportation rate and production period.






![Belt conveyor- no of rollers
• Idlers spacing
• If 2000 kg/m3 1100 mm to 1500 mm
• If heavier 1000, 1300 mm
• No of idler rollers on one side= [length of belt/spacing]-1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/section5-230101085933-71b99ee5/85/section-5-pptx-8-320.jpg)






