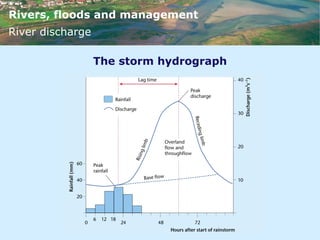
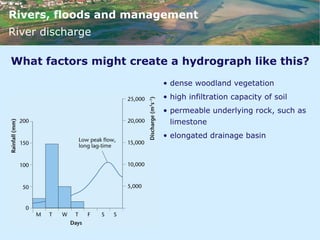
This document discusses rivers, floods, and flood management. It describes the hydrological cycle and factors that influence river discharge patterns. It also examines river landforms and processes such as waterfalls, meanders, and deltas. The document then discusses flooding, including causes, areas at high risk, and short-term and long-term responses. It provides examples of both hard and soft engineering techniques used for flood management.