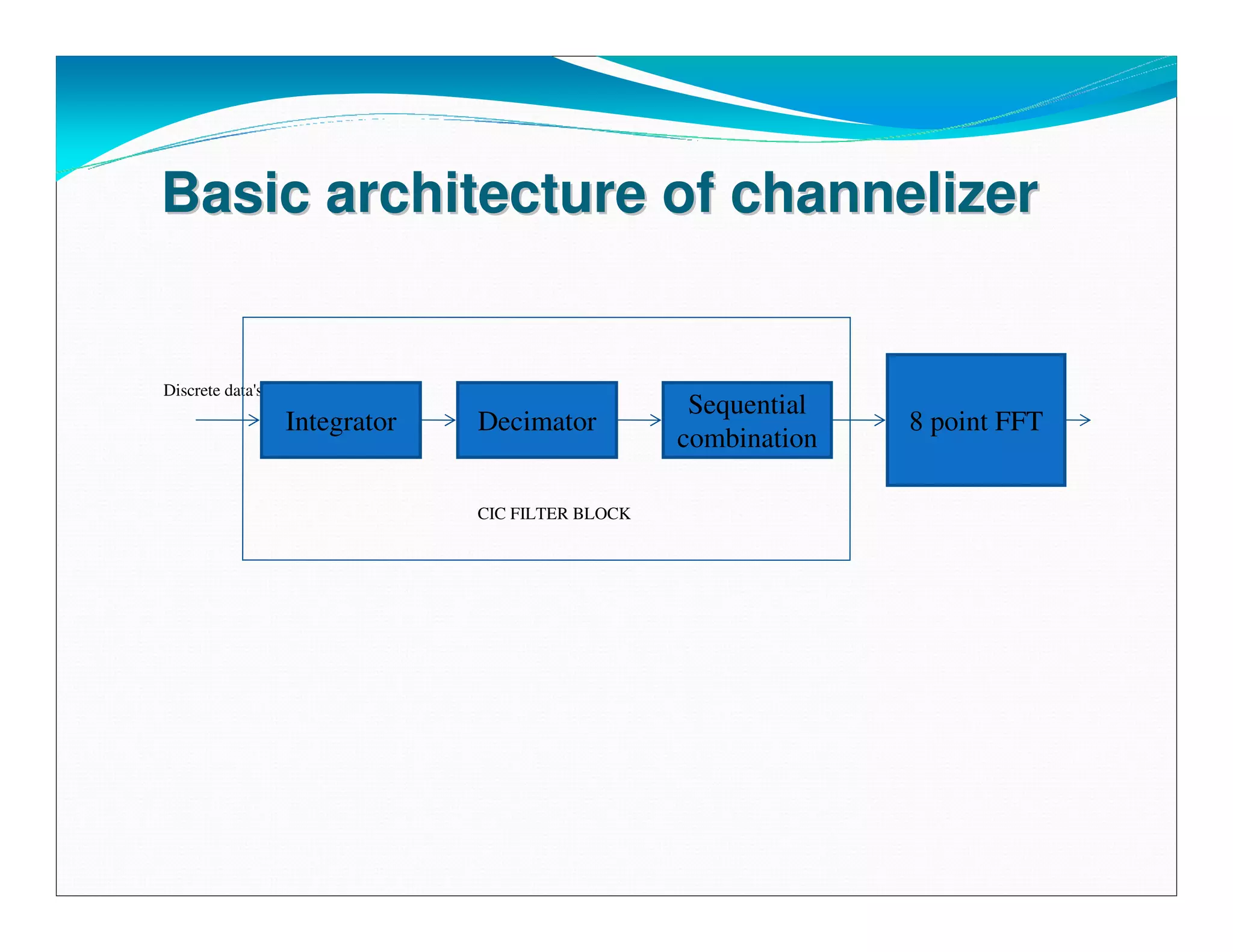
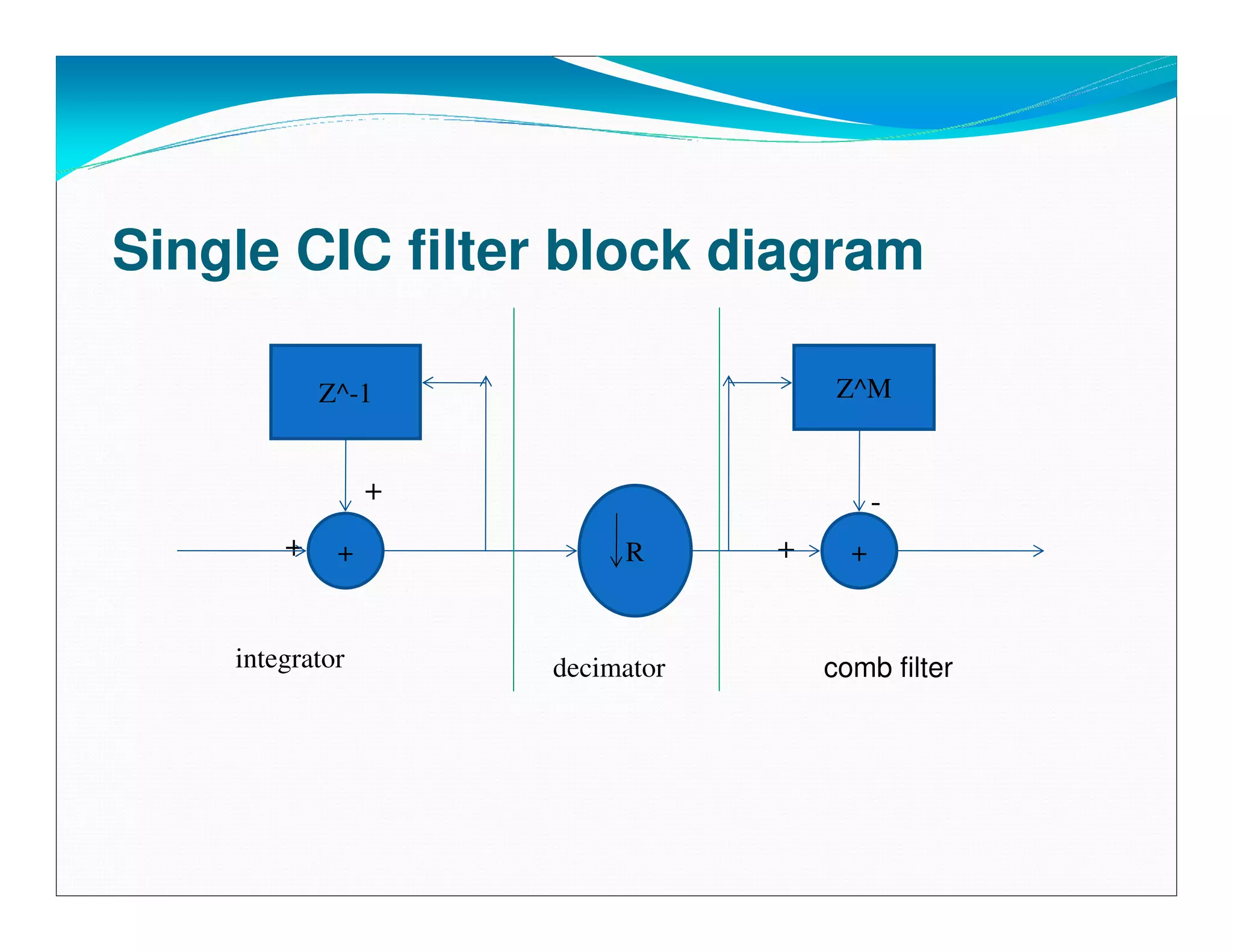
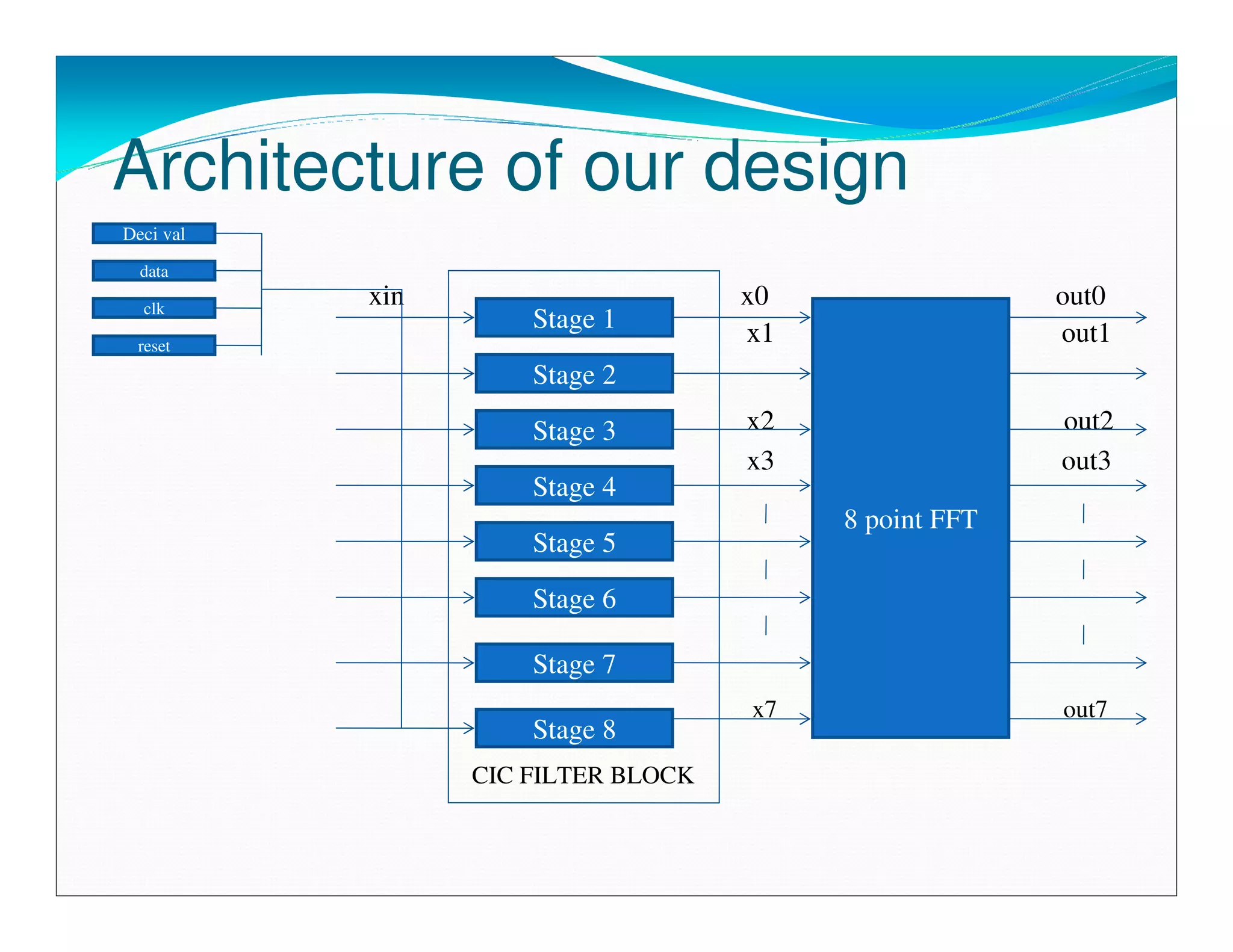
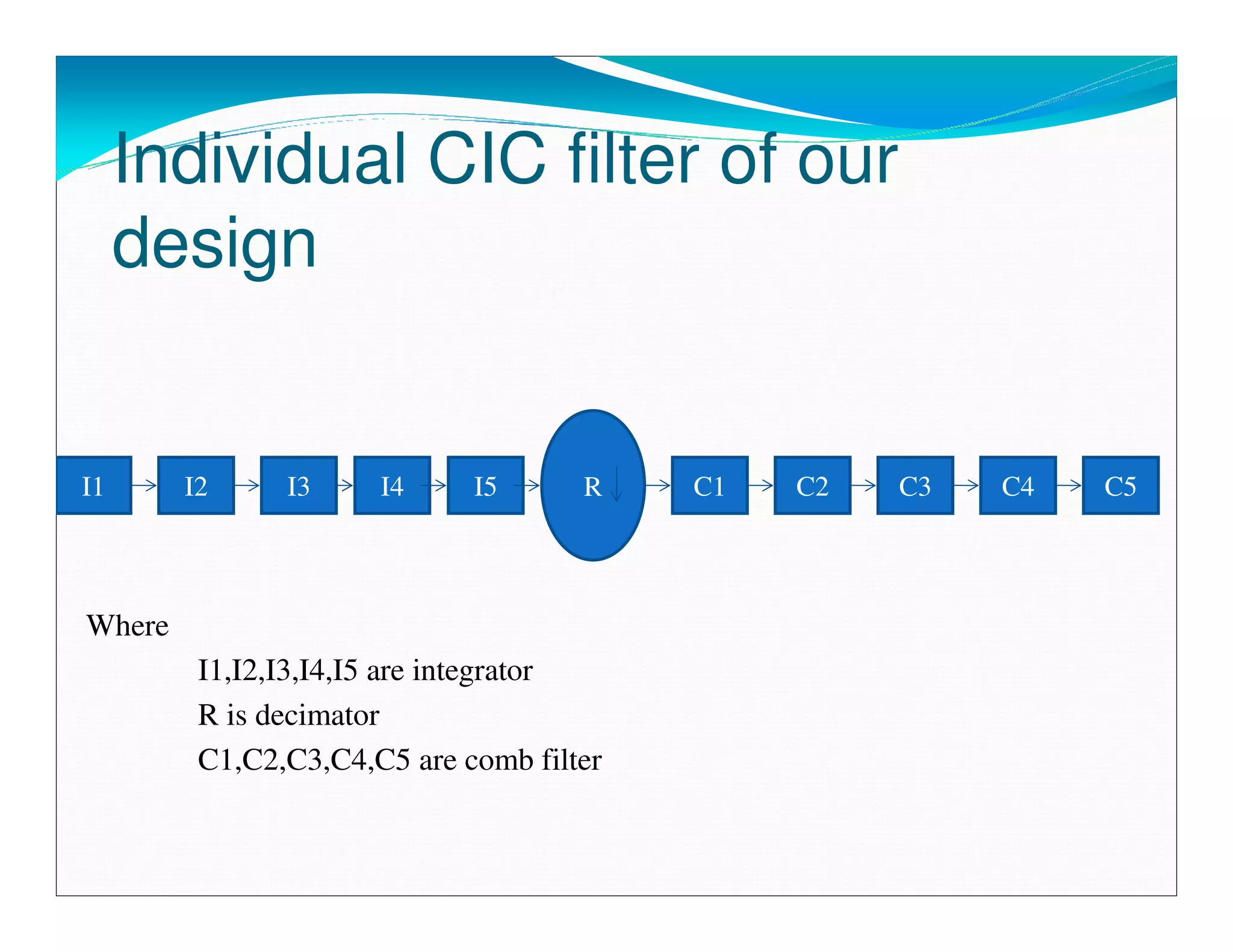
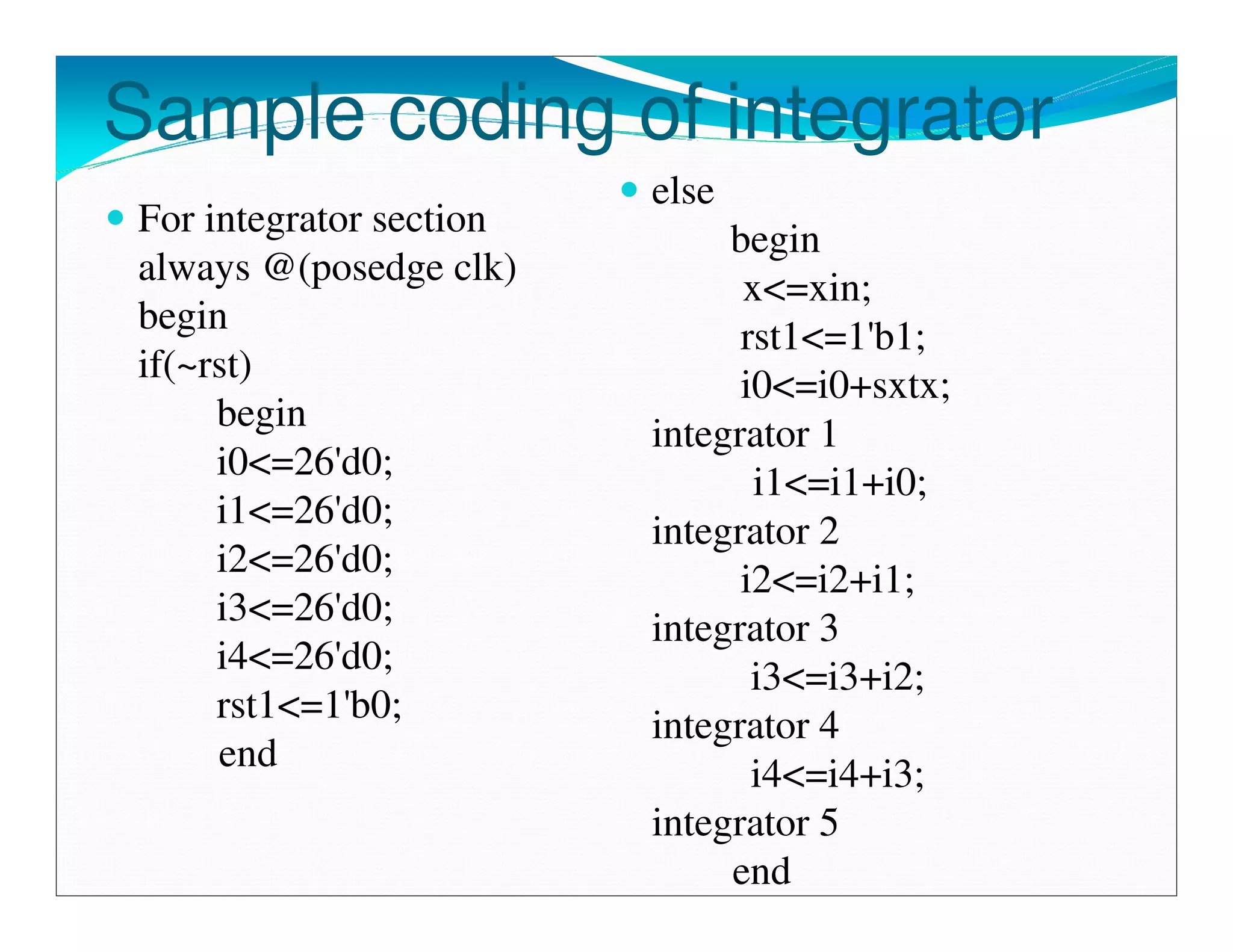
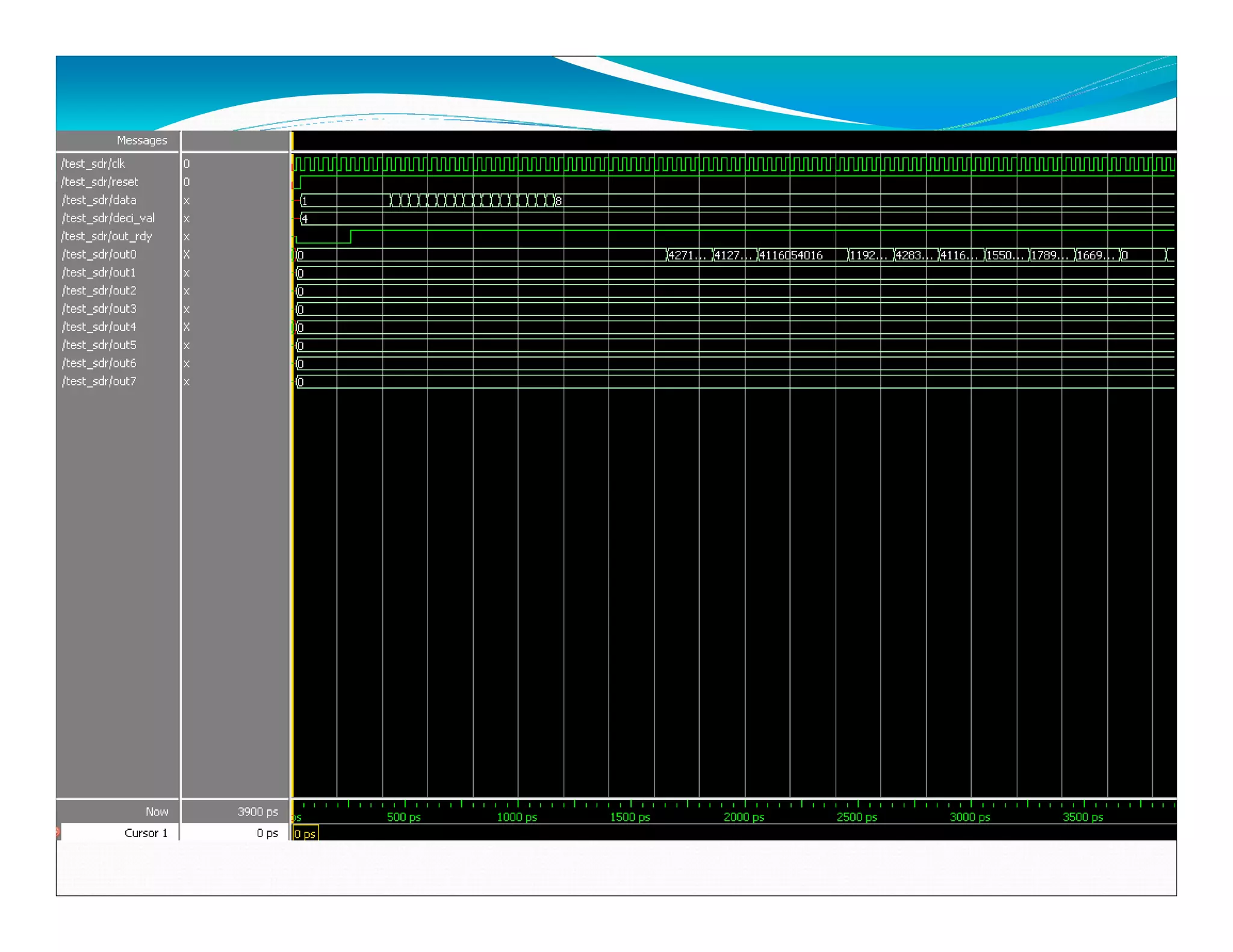
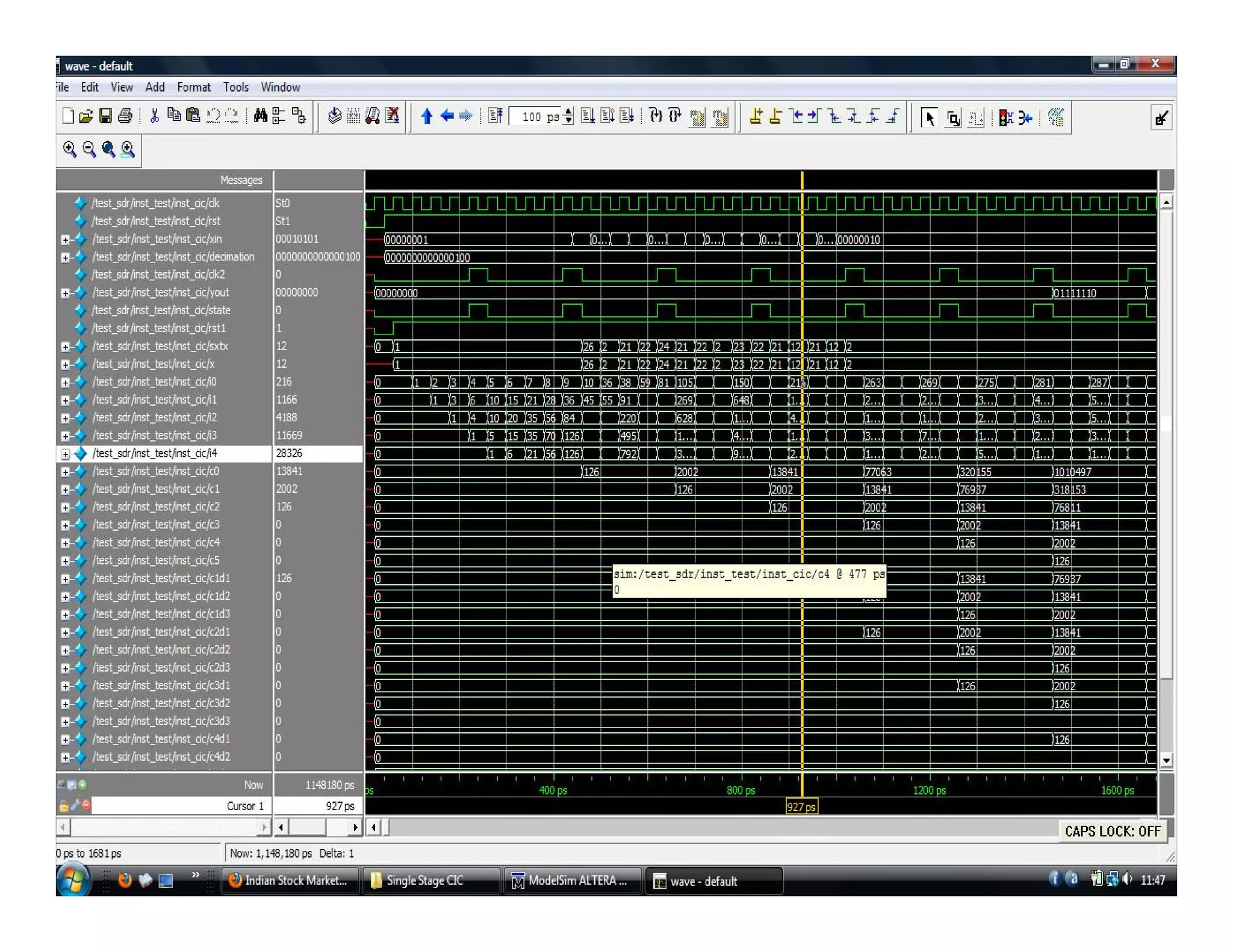
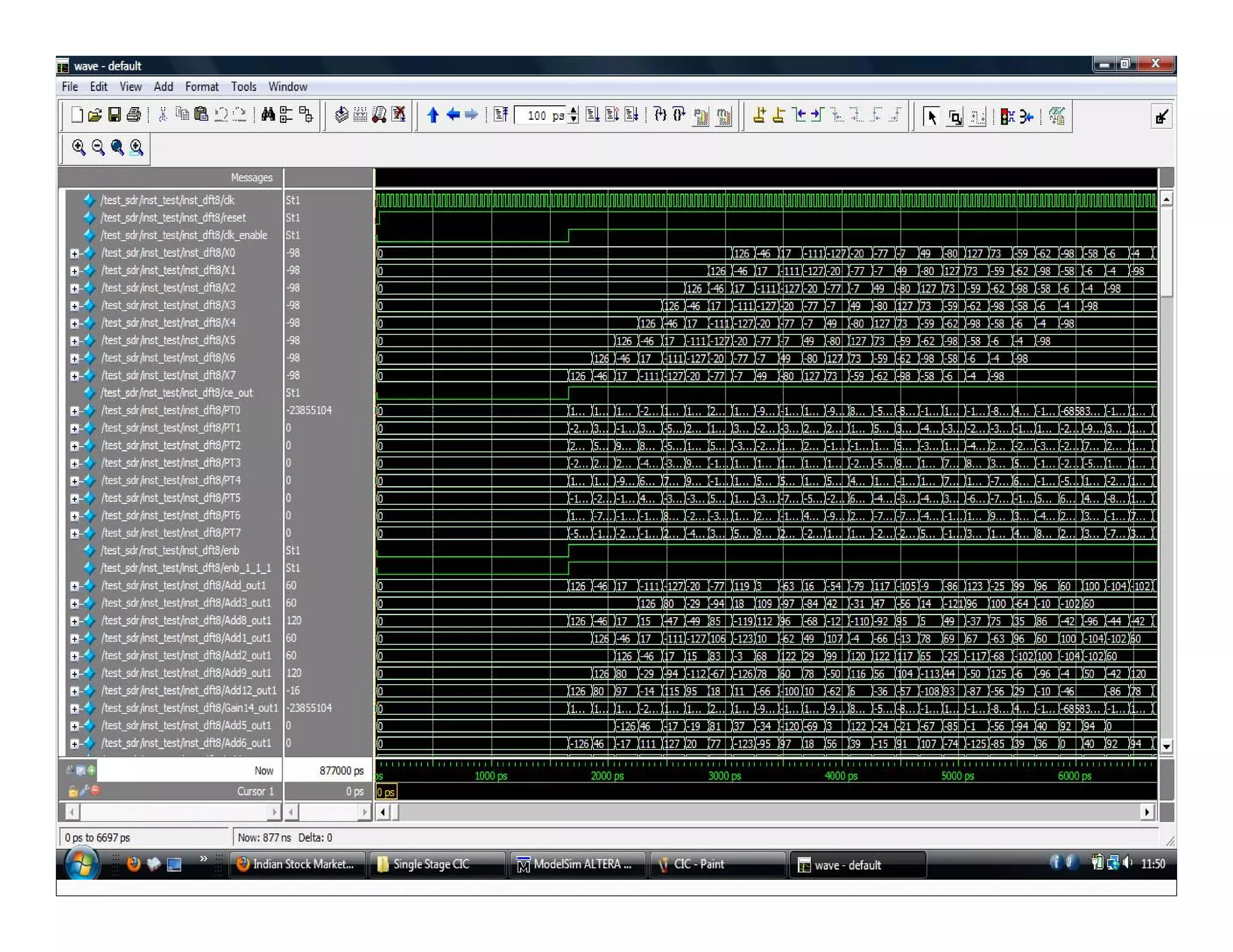
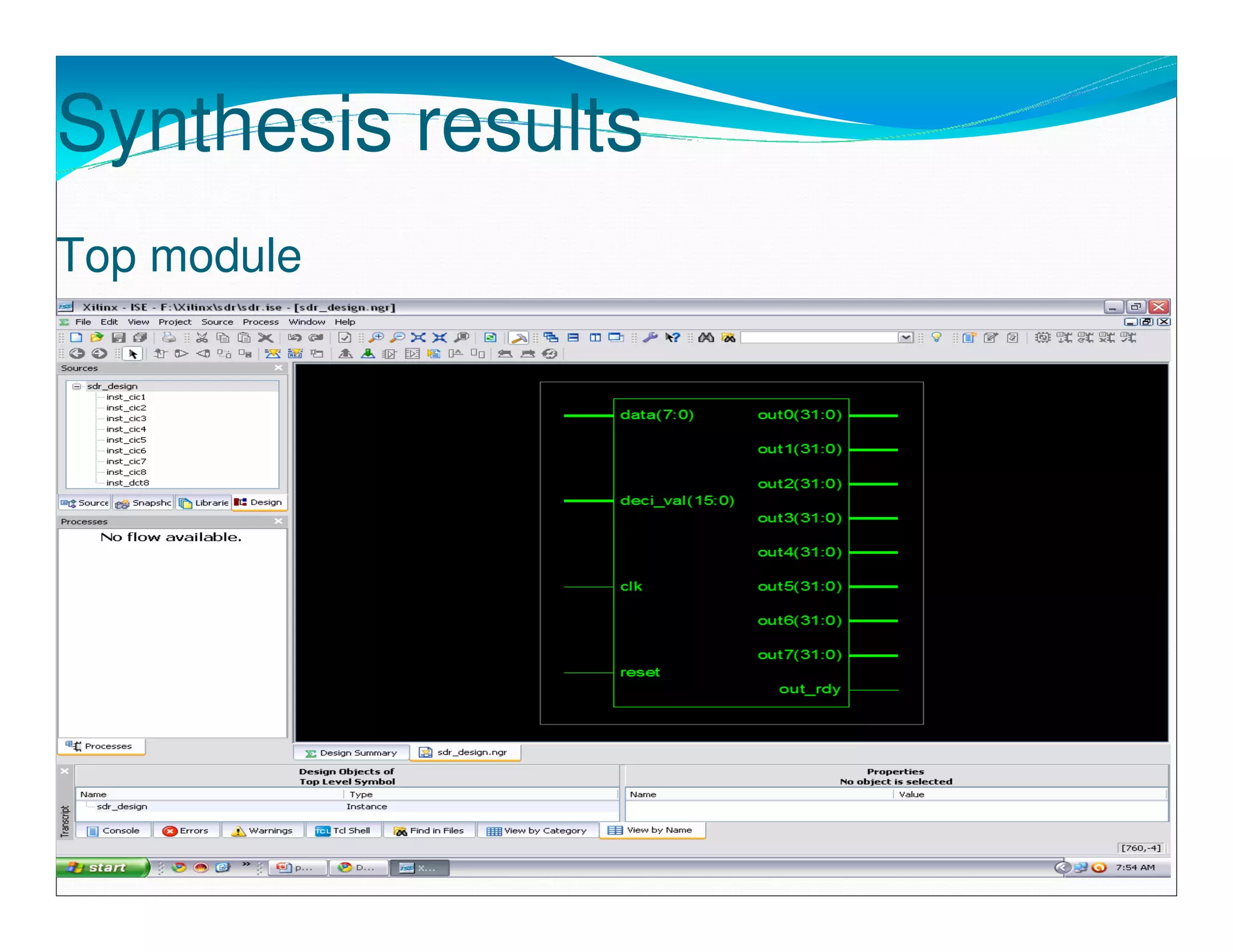
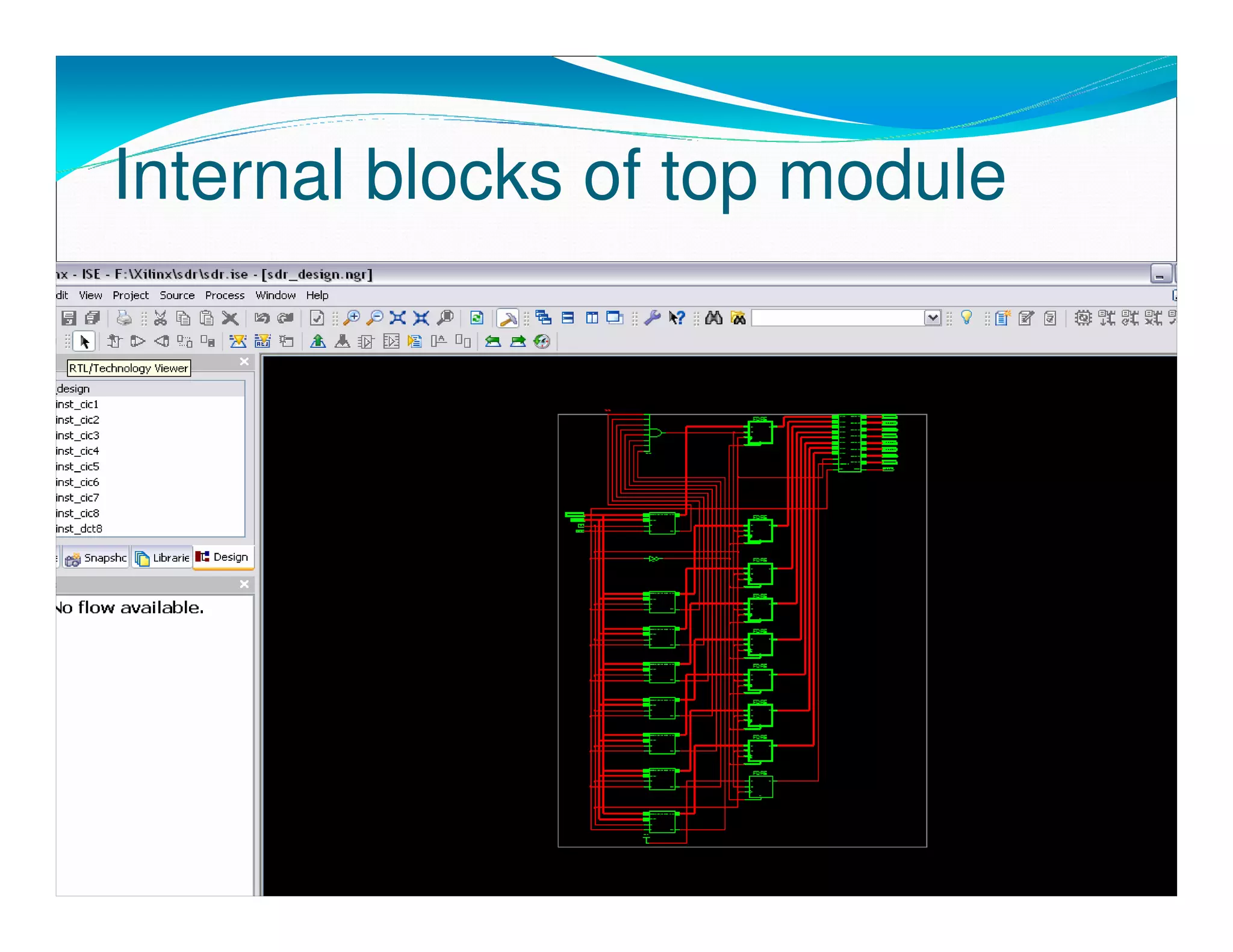
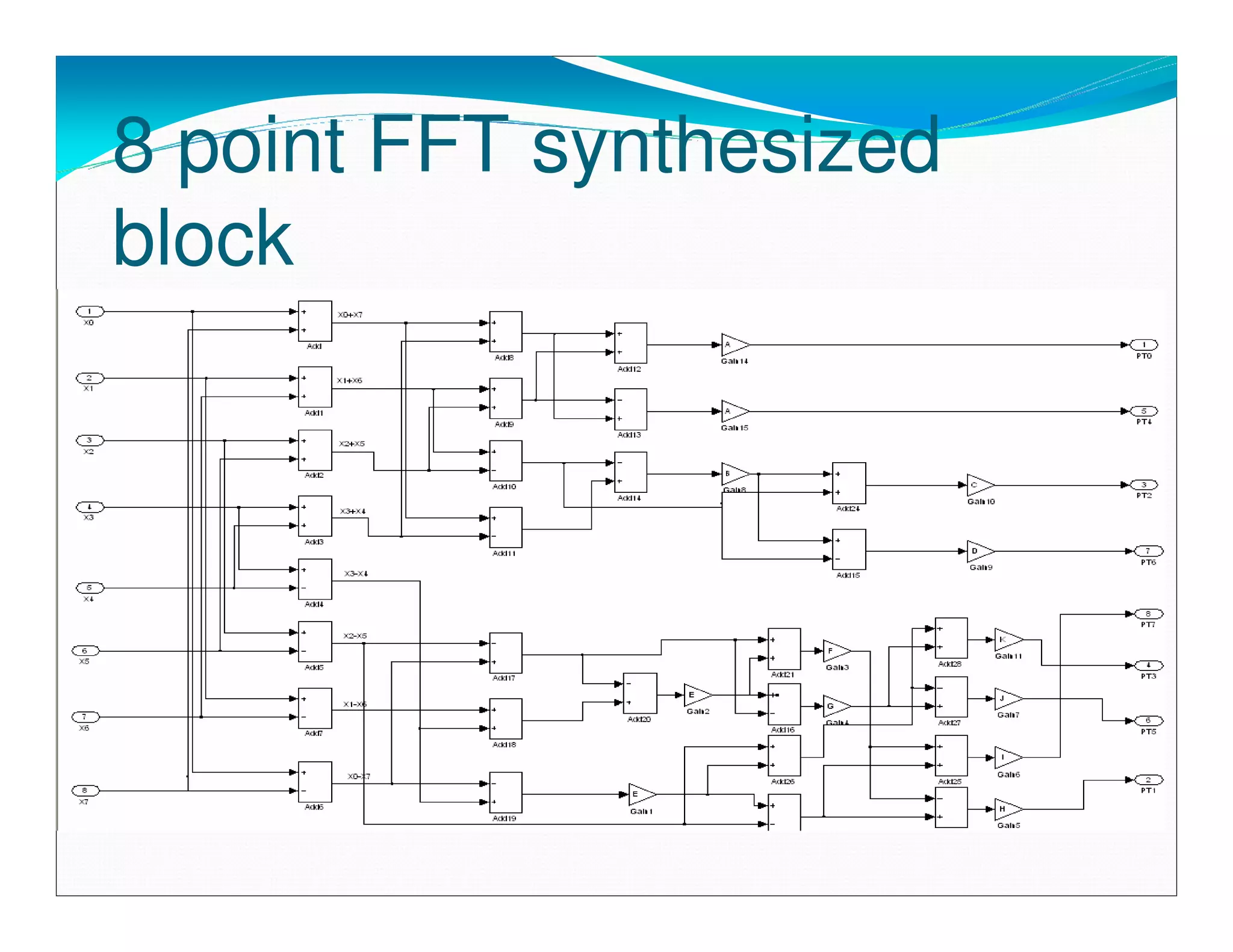
The document summarizes the proposed design of a power efficient channelizer for software defined radio using VLSI. It discusses the basic architecture of the channelizer which uses a cascaded integrator-comb (CIC) filter block followed by an 8-point fast Fourier transform (FFT). The CIC filter block contains 5 stages of integrators and 5 stages of comb filters with 1 decimator, totaling 8 complete stages. Simulation results and synthesis results showing the internal blocks and 8-point FFT are also presented. The designed channelizer is concluded to have promising decreases in noise and be suitable for real-time software defined radio channels.