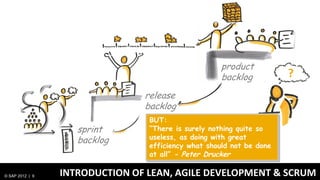
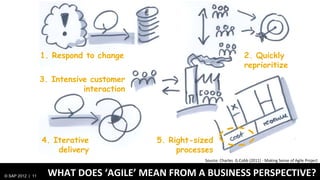
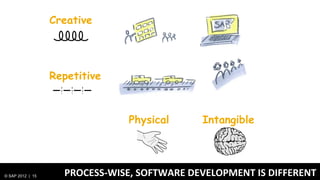
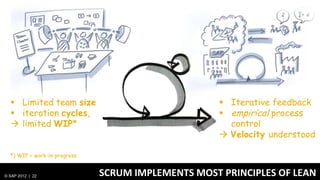
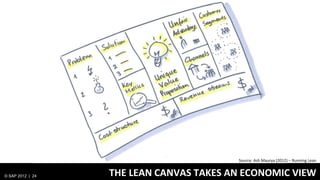
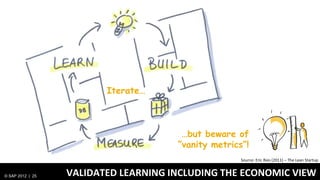
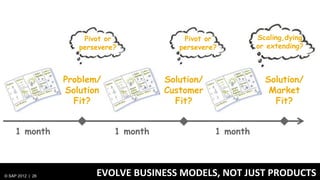
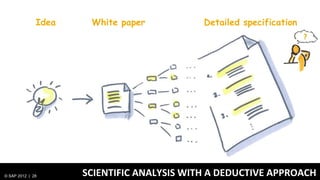
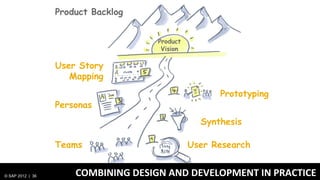
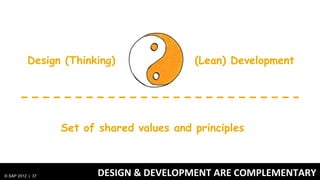
1) Traditionally, design and development were separate processes but agile methodologies aim to combine them through practices like user story mapping and prototyping.
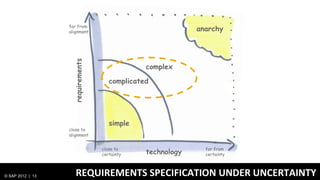
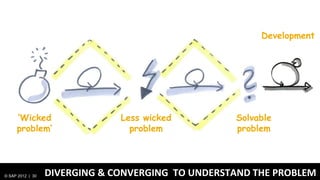
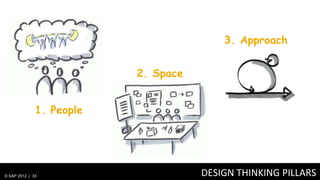
2) Design thinking focuses on understanding problems from the user perspective through techniques like personas and user research to create the right solutions.
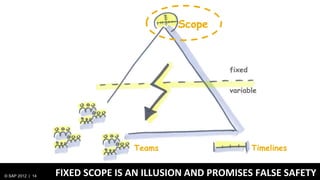
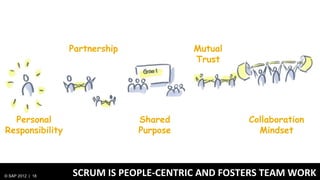
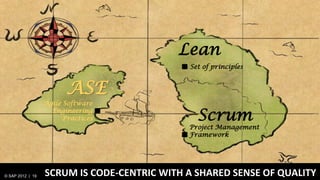
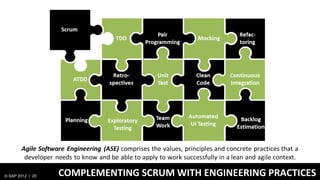
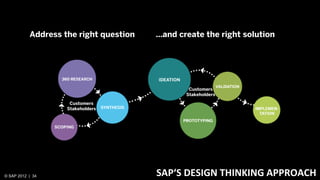
3) At SAP, design and development teams work collaboratively using shared principles and practices like product vision, product backlog, and iterative development to better meet user needs.