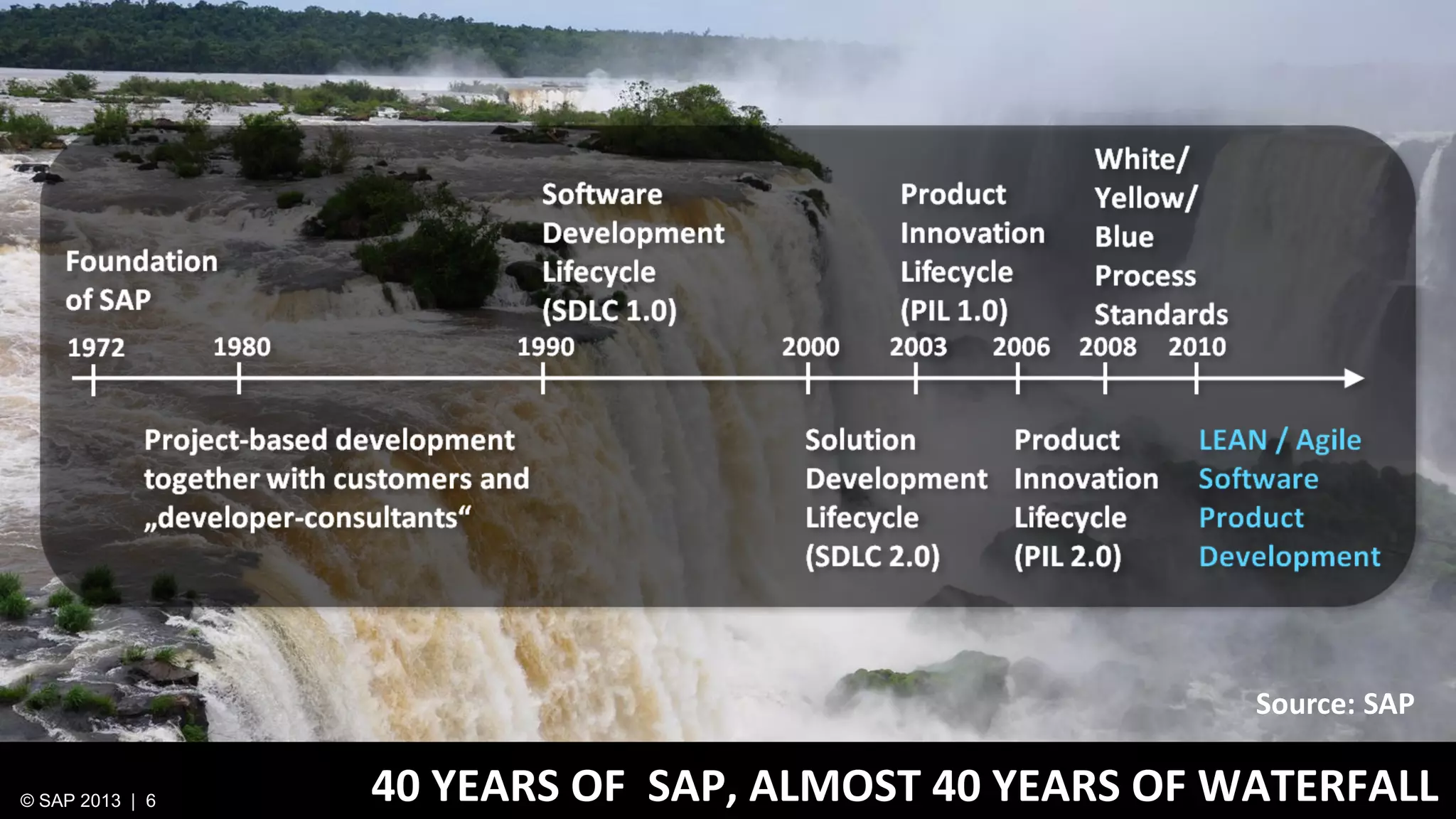
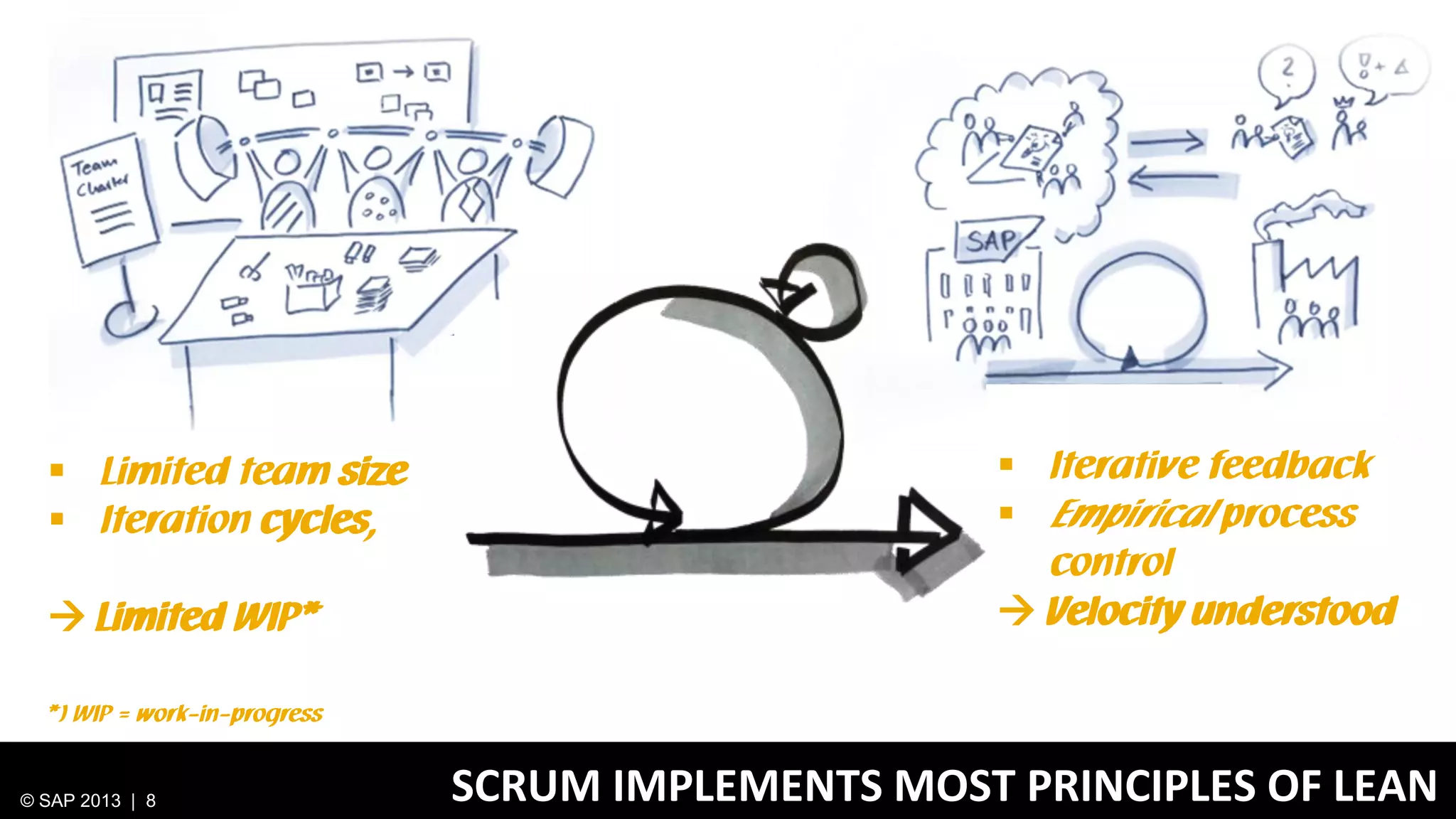
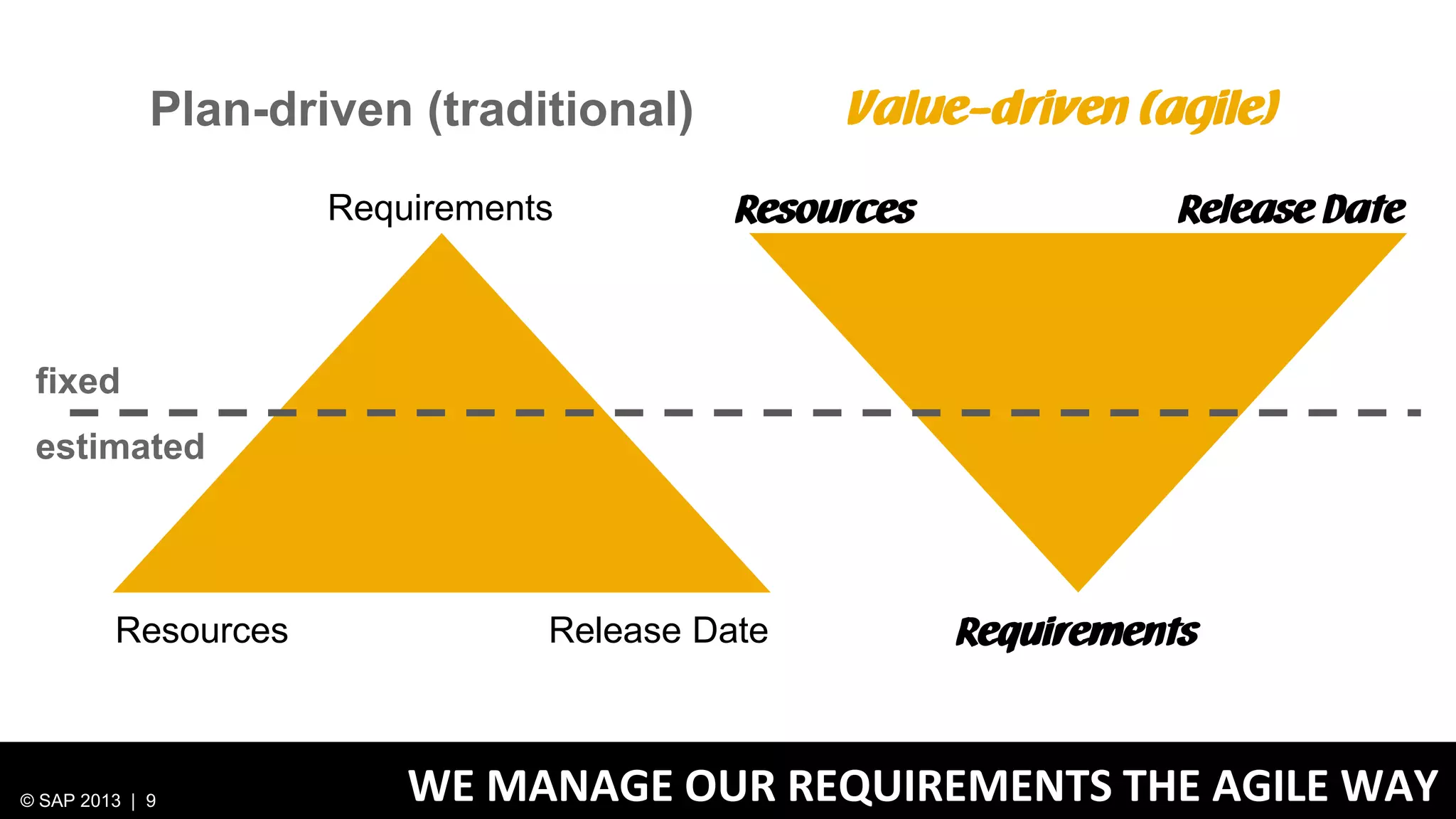
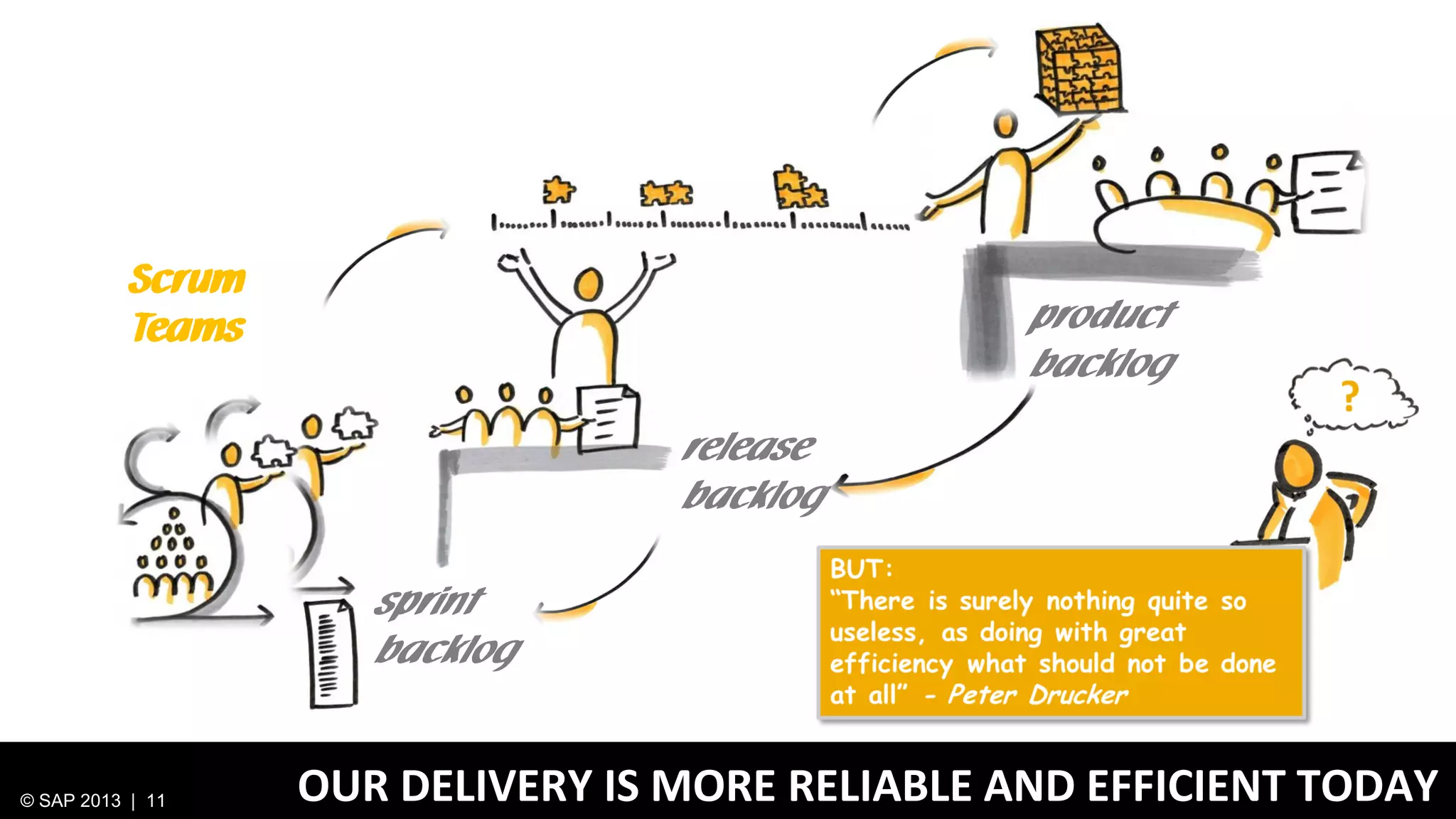
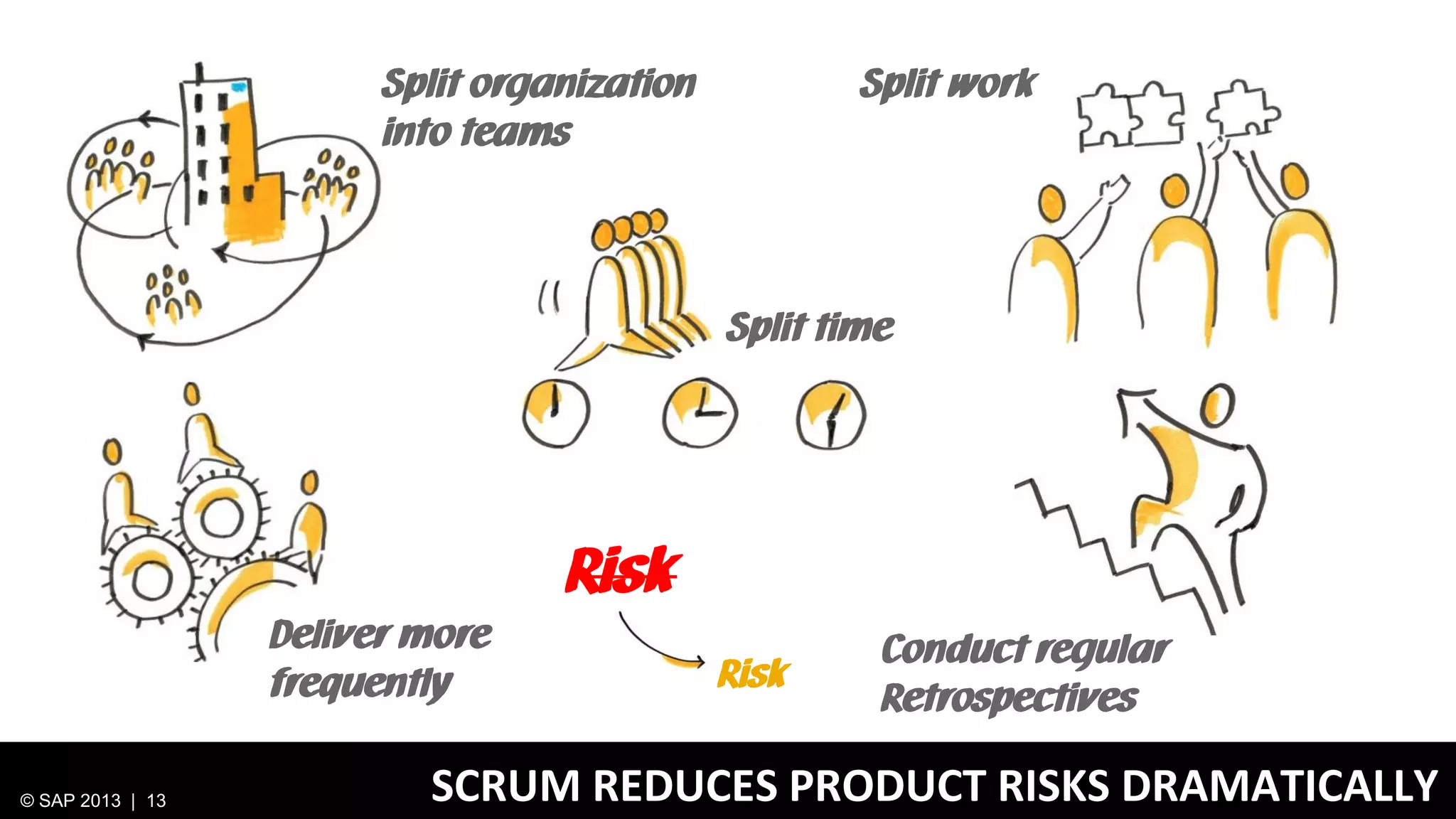
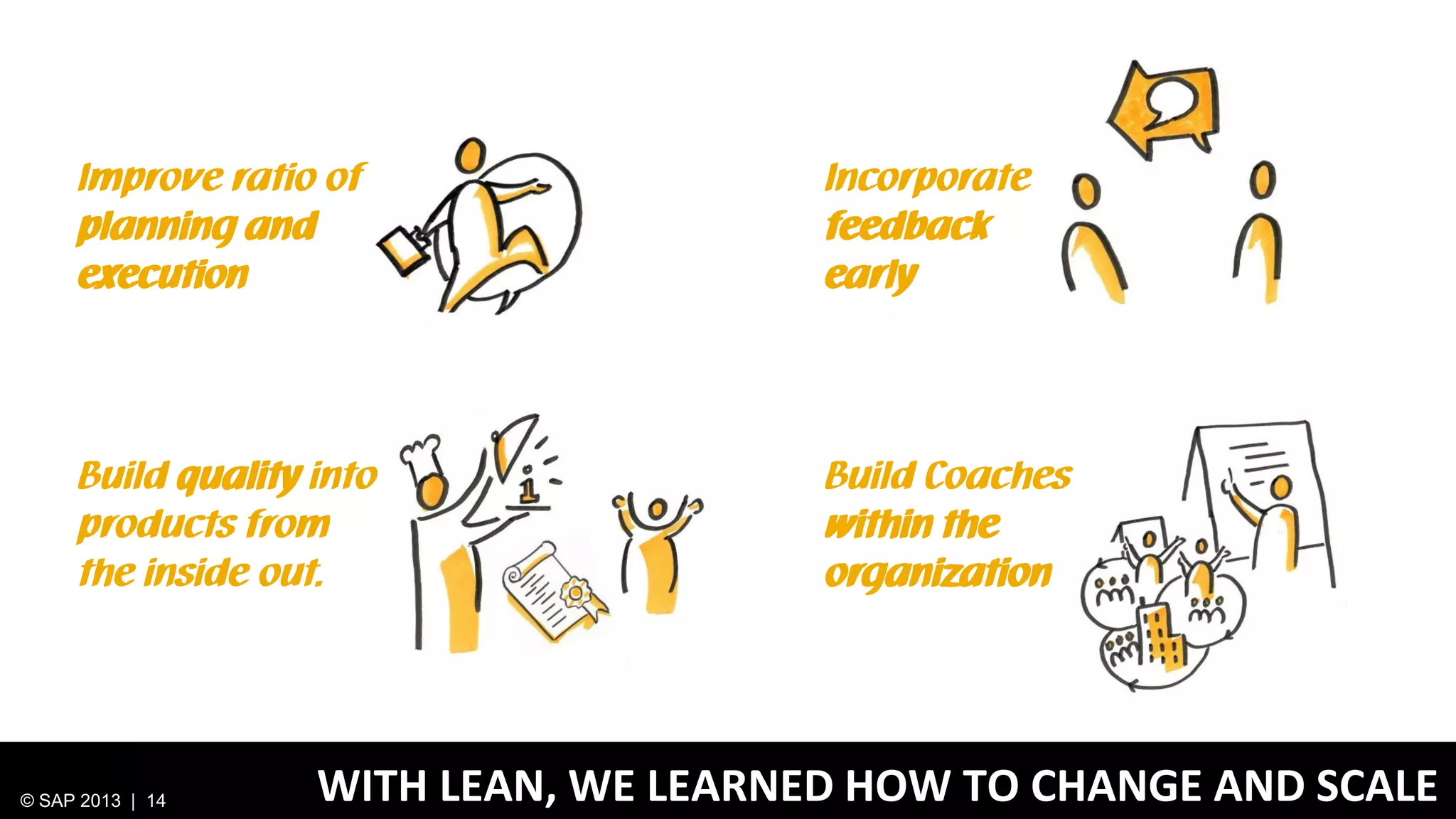
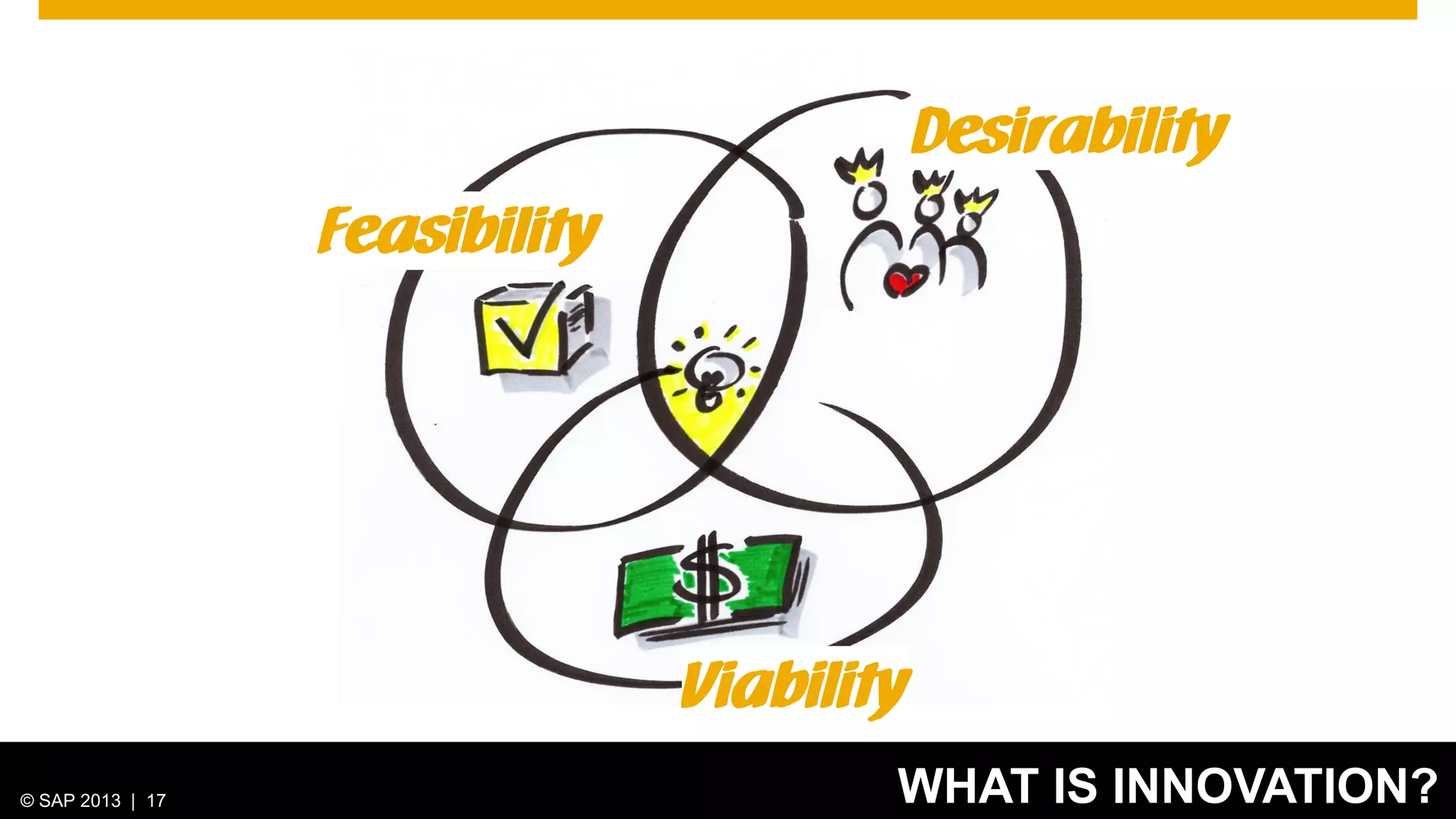
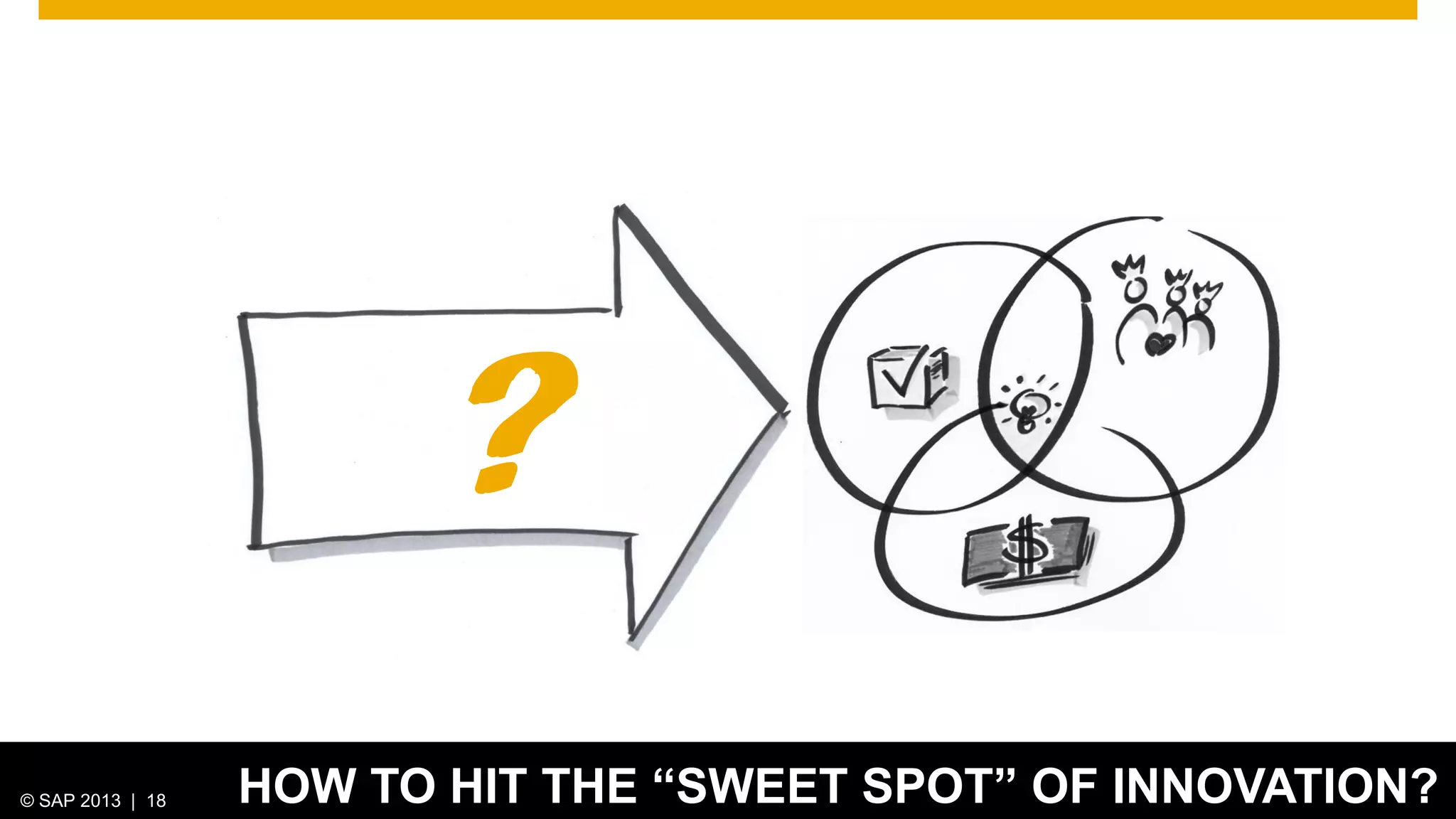
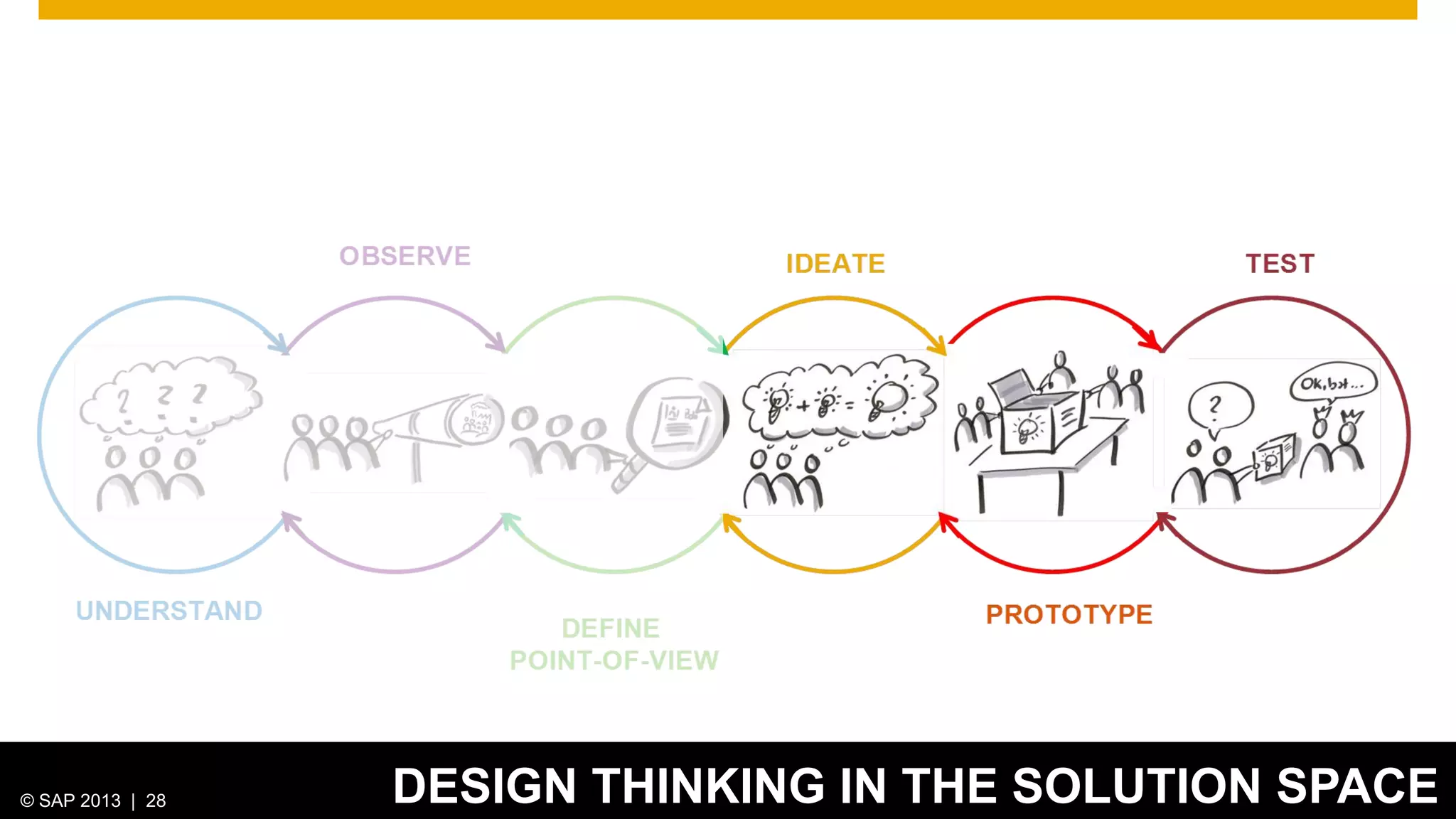
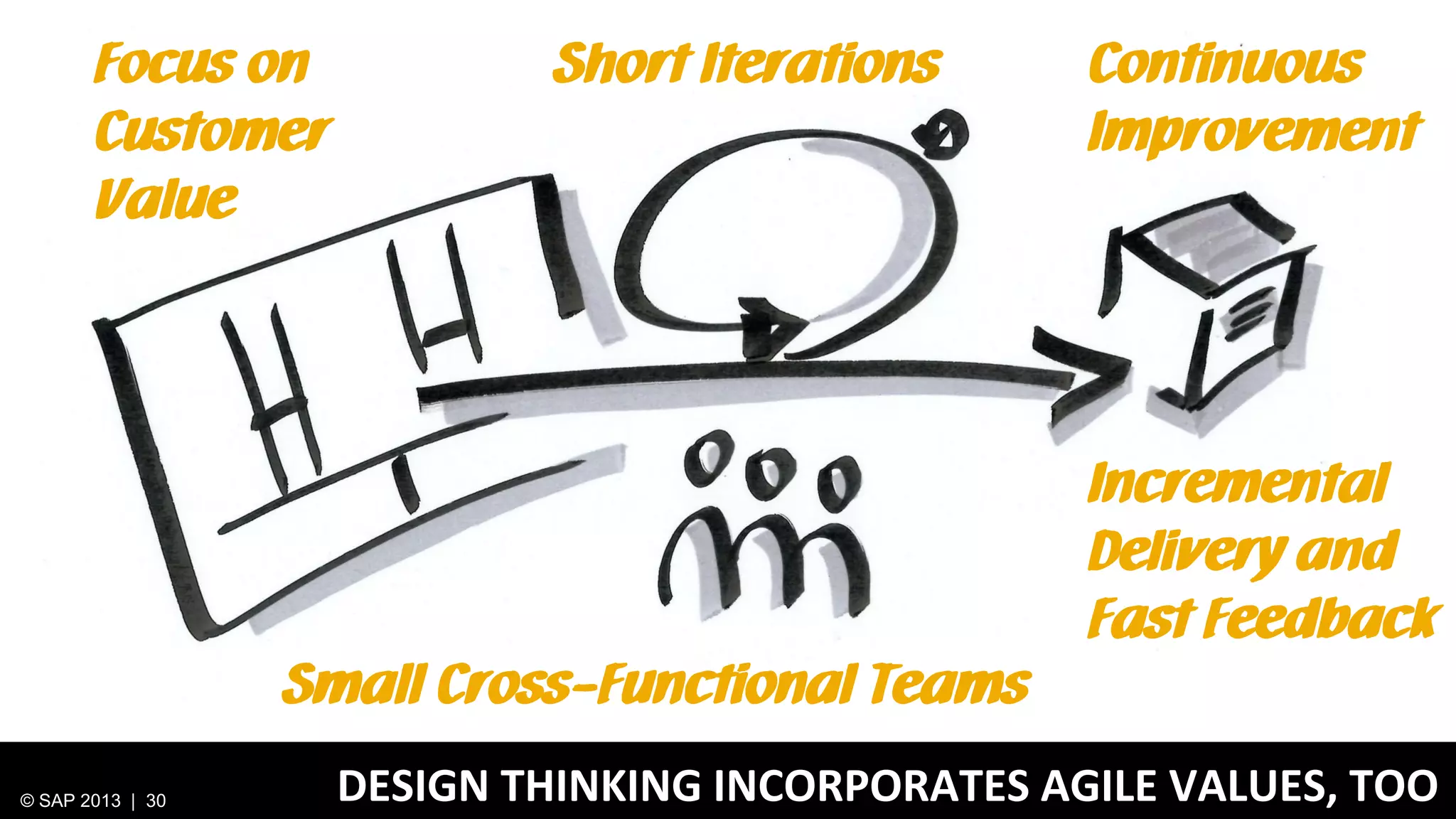
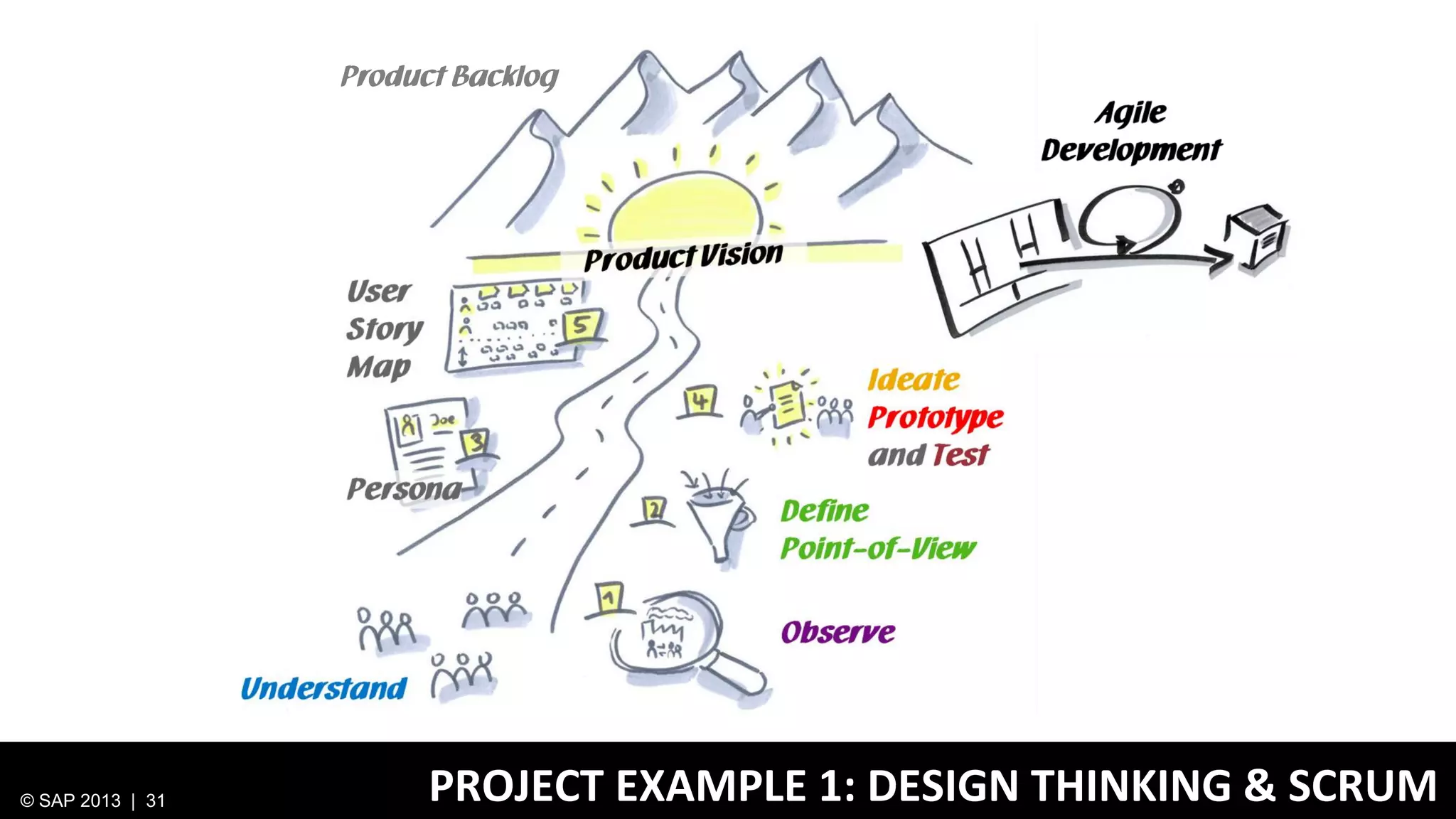
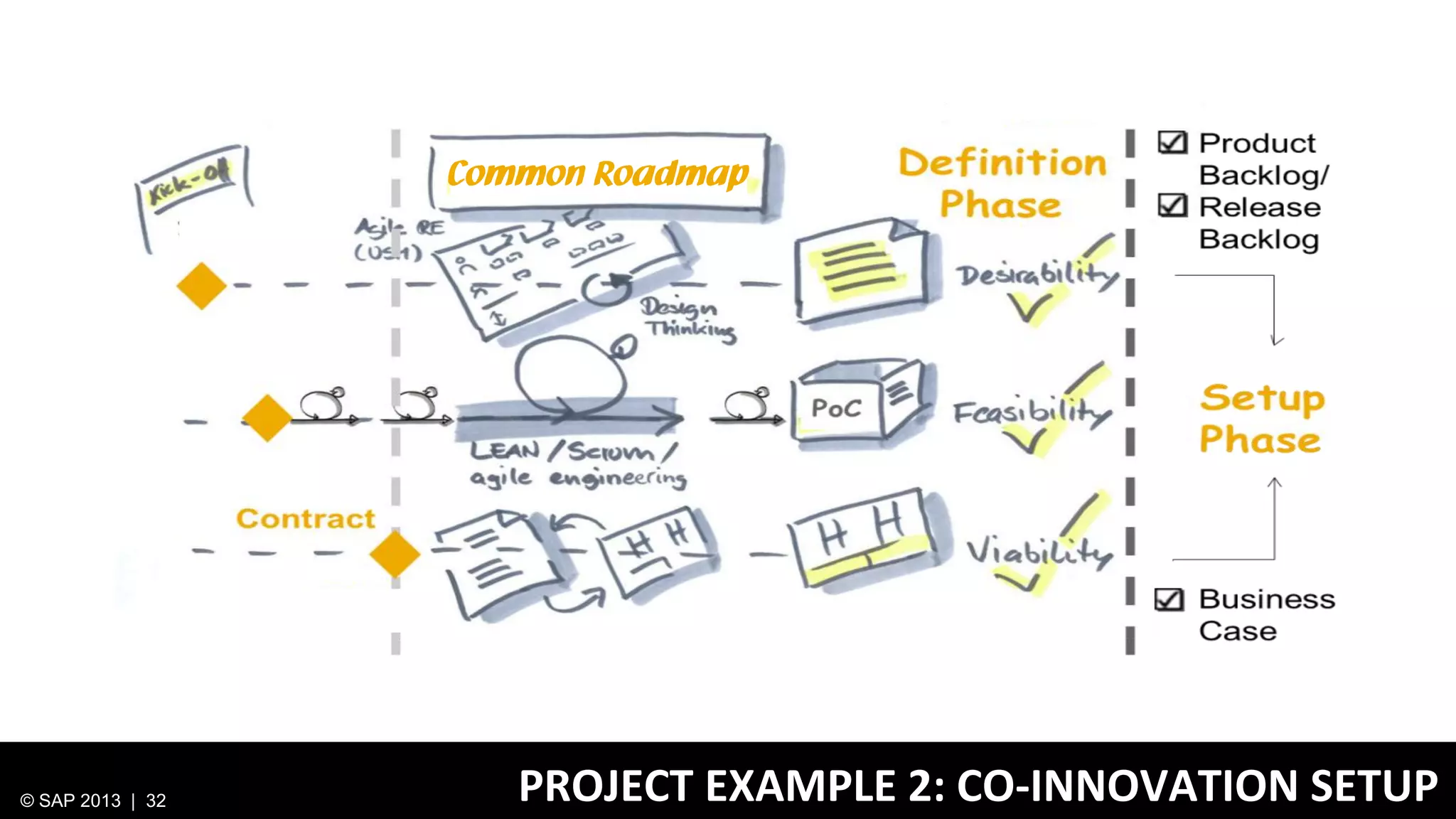
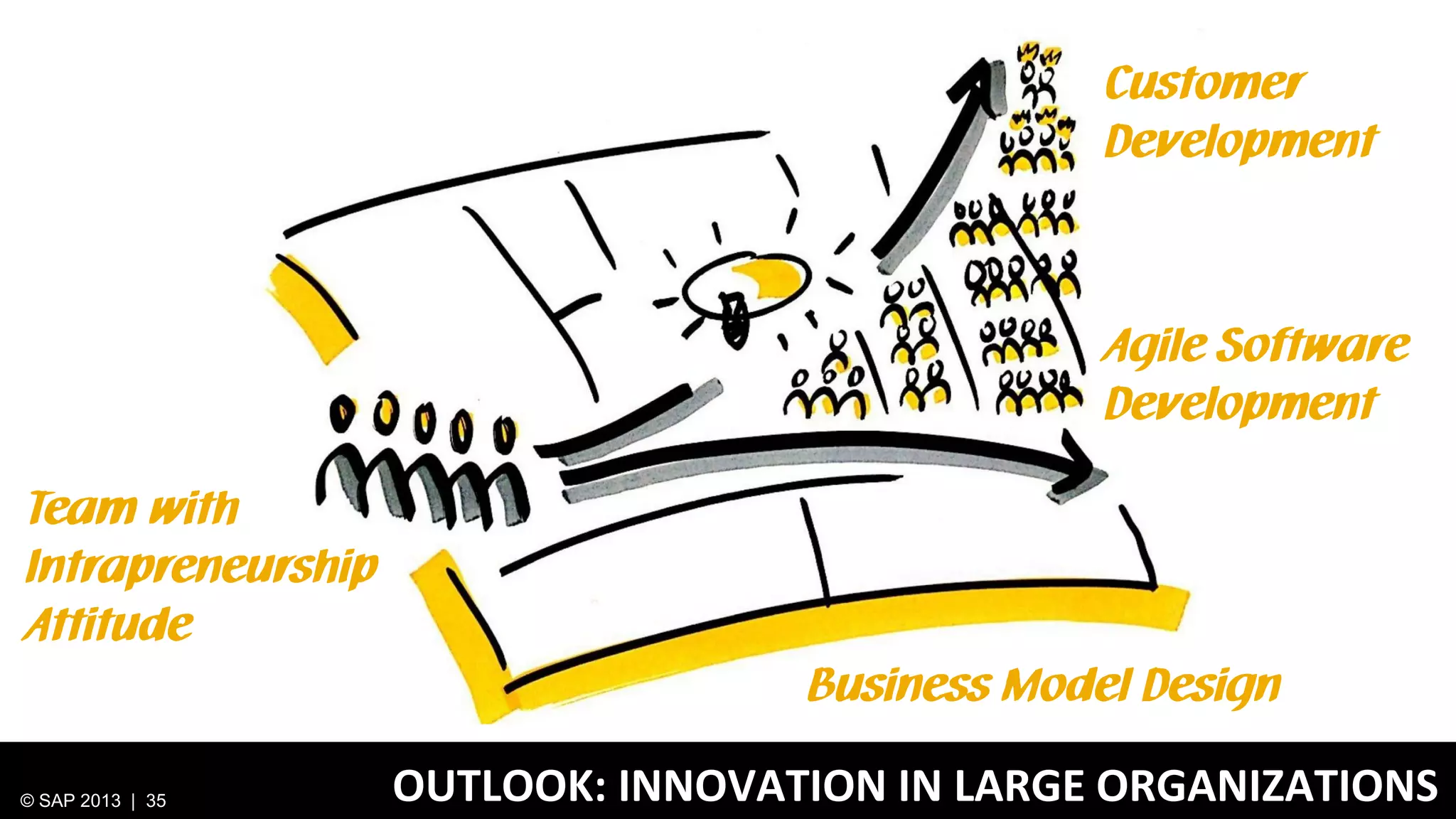
The document discusses SAP's approach to innovation through design thinking and lean development, emphasizing the importance of employee motivation, team organization, and agile methodologies like Scrum. It highlights the process of delivering reliable and efficient results while focusing on user needs and incorporating feedback early in the development cycle. Ultimately, it demonstrates how design thinking and lean practices together enhance both innovation and effectiveness within large organizations.