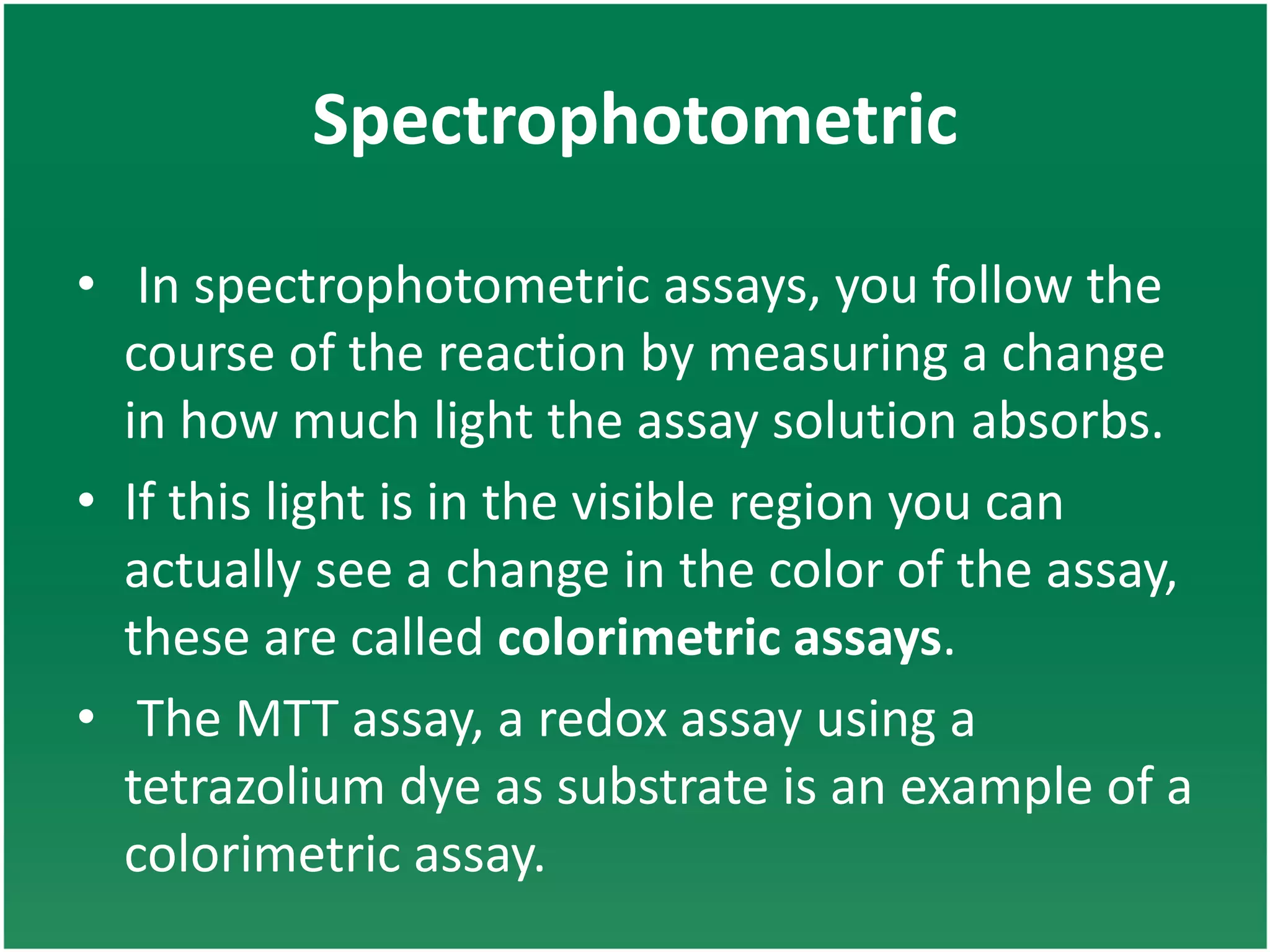
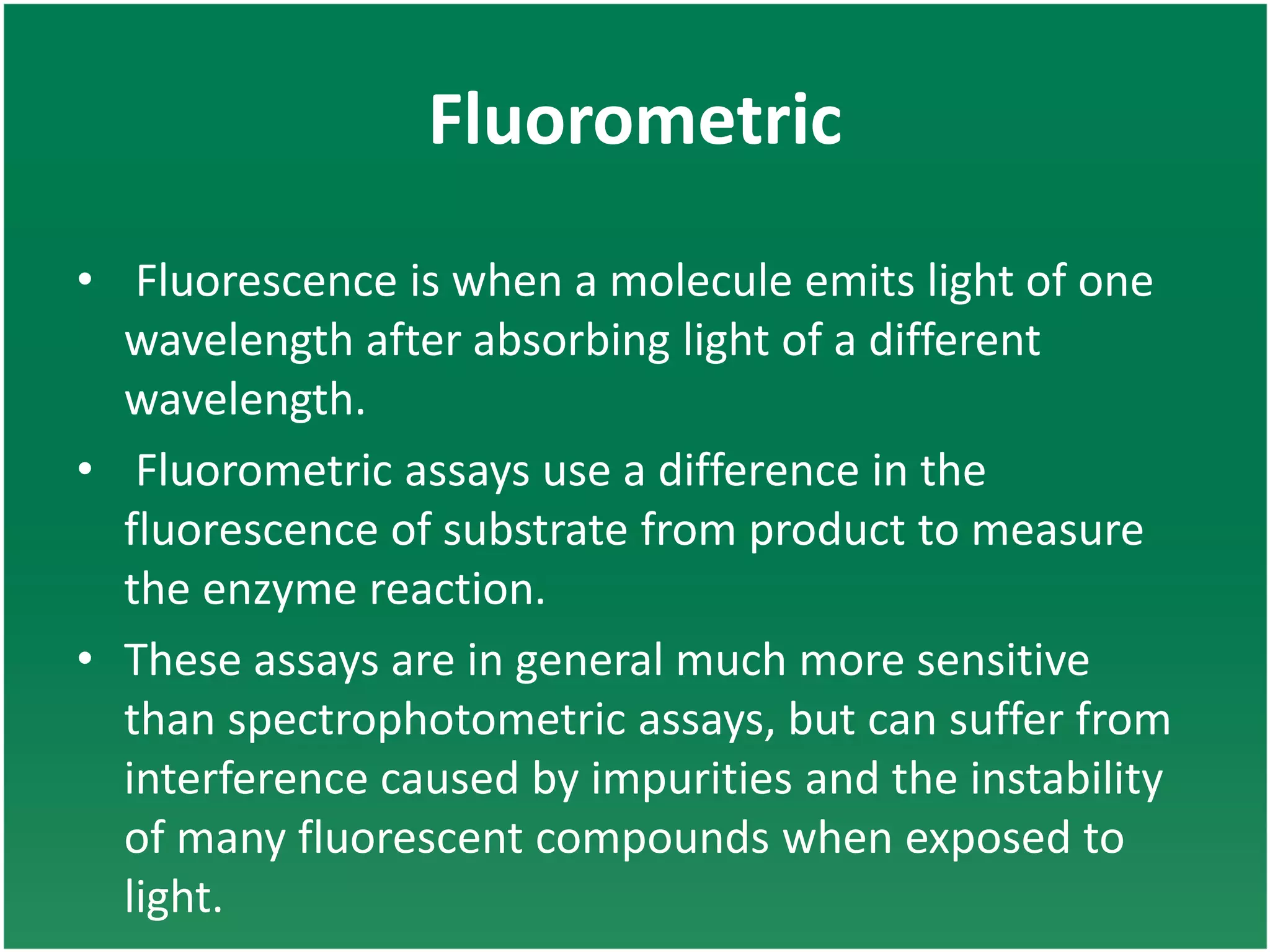
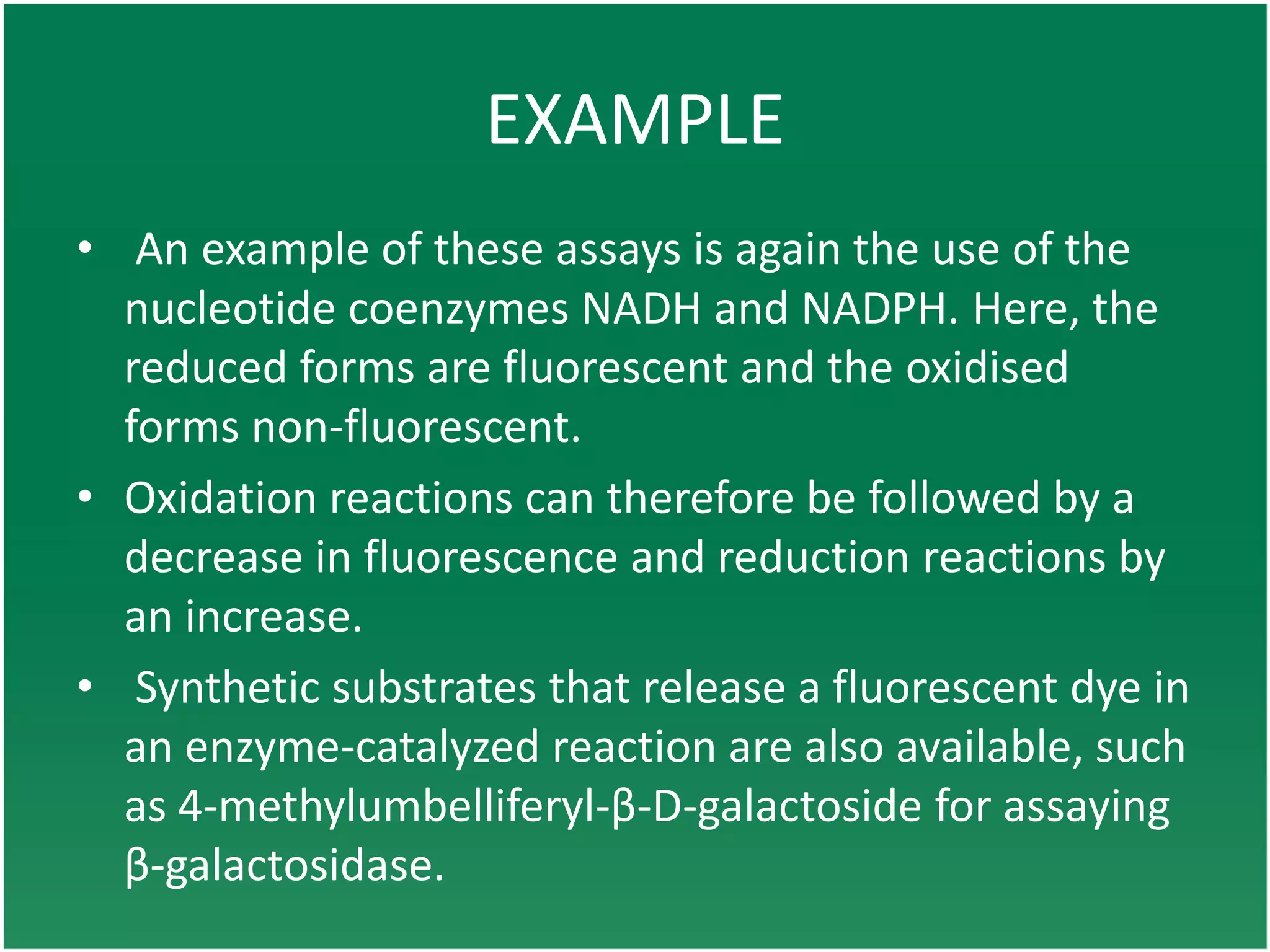
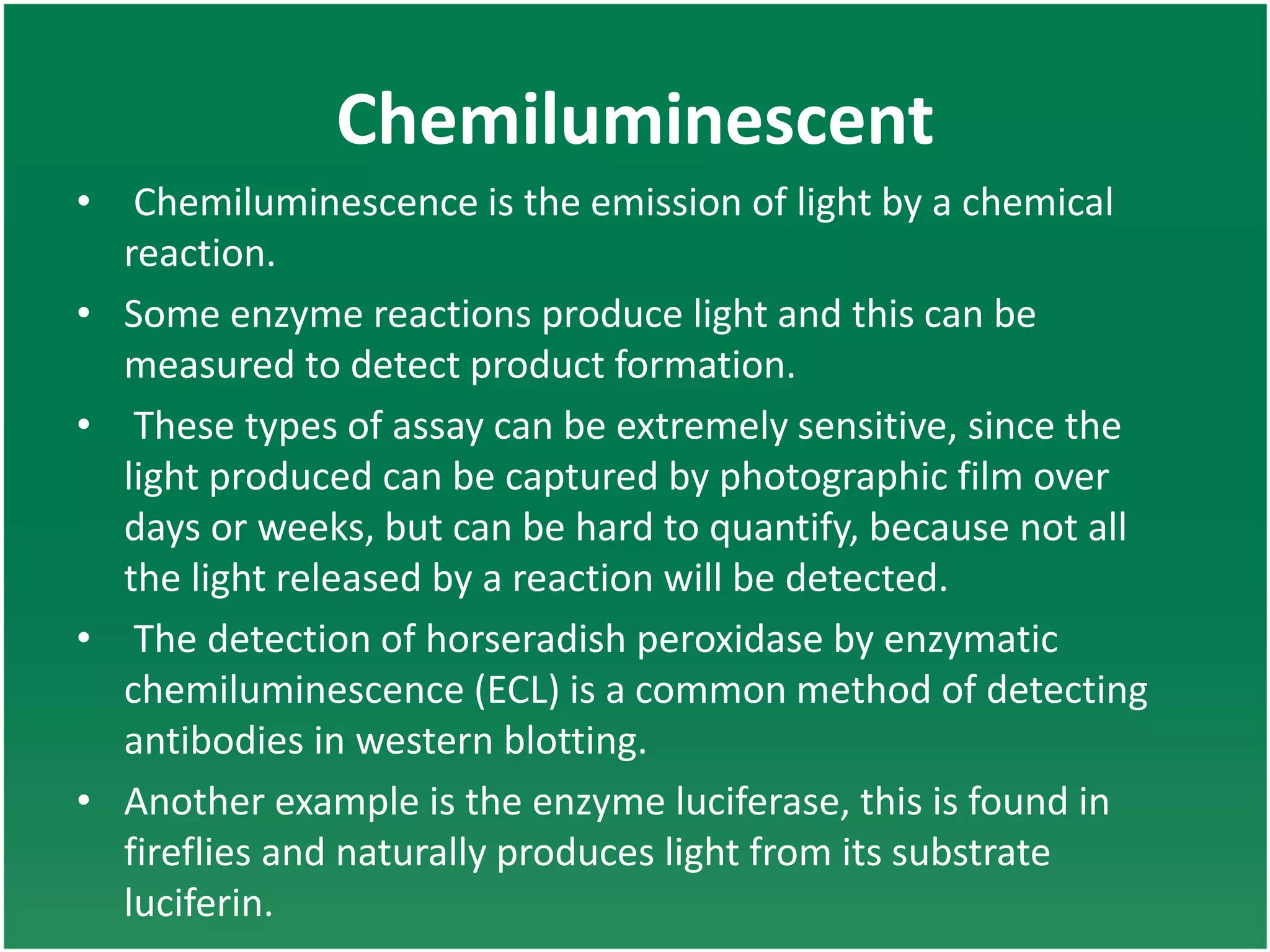
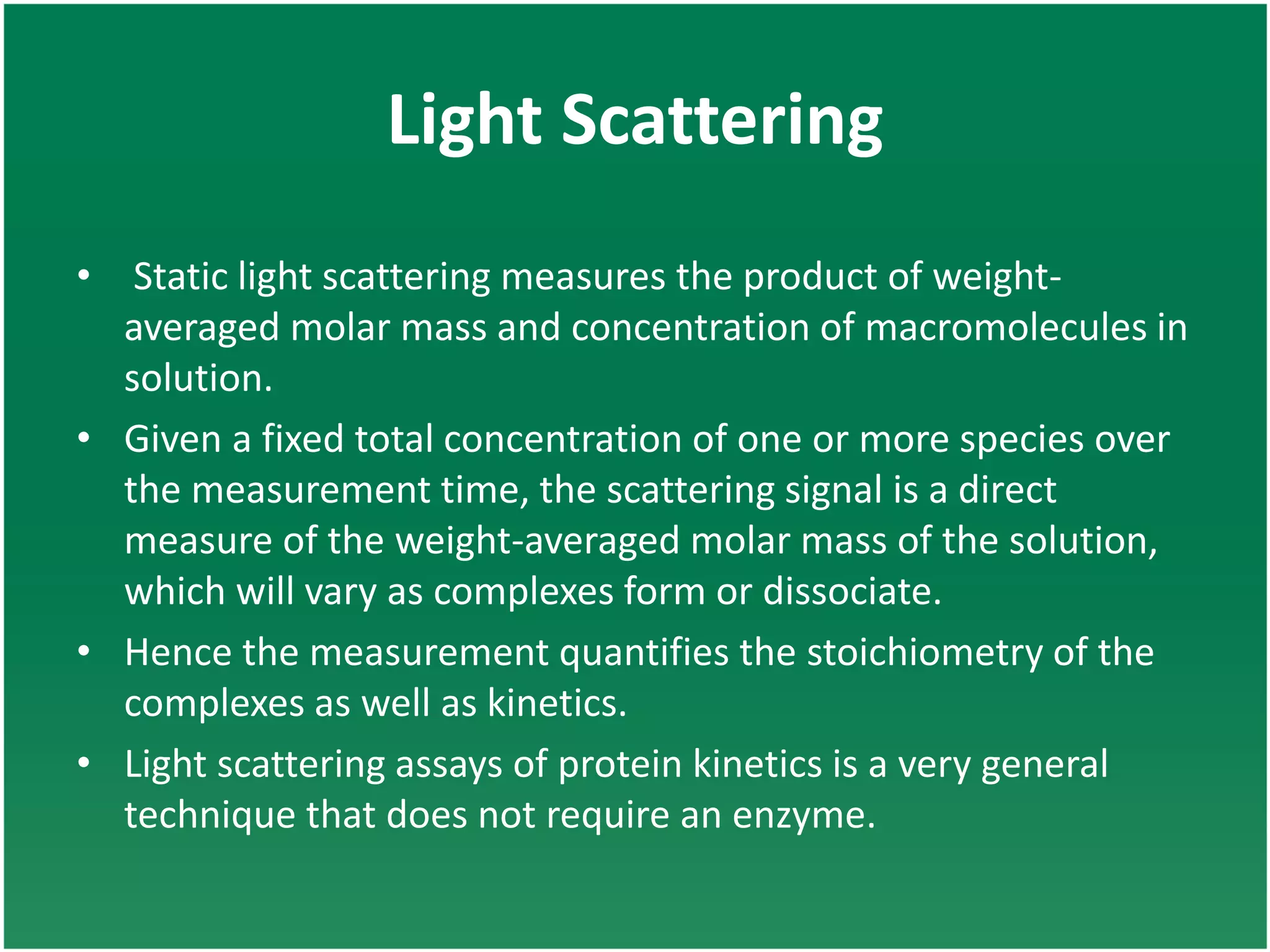
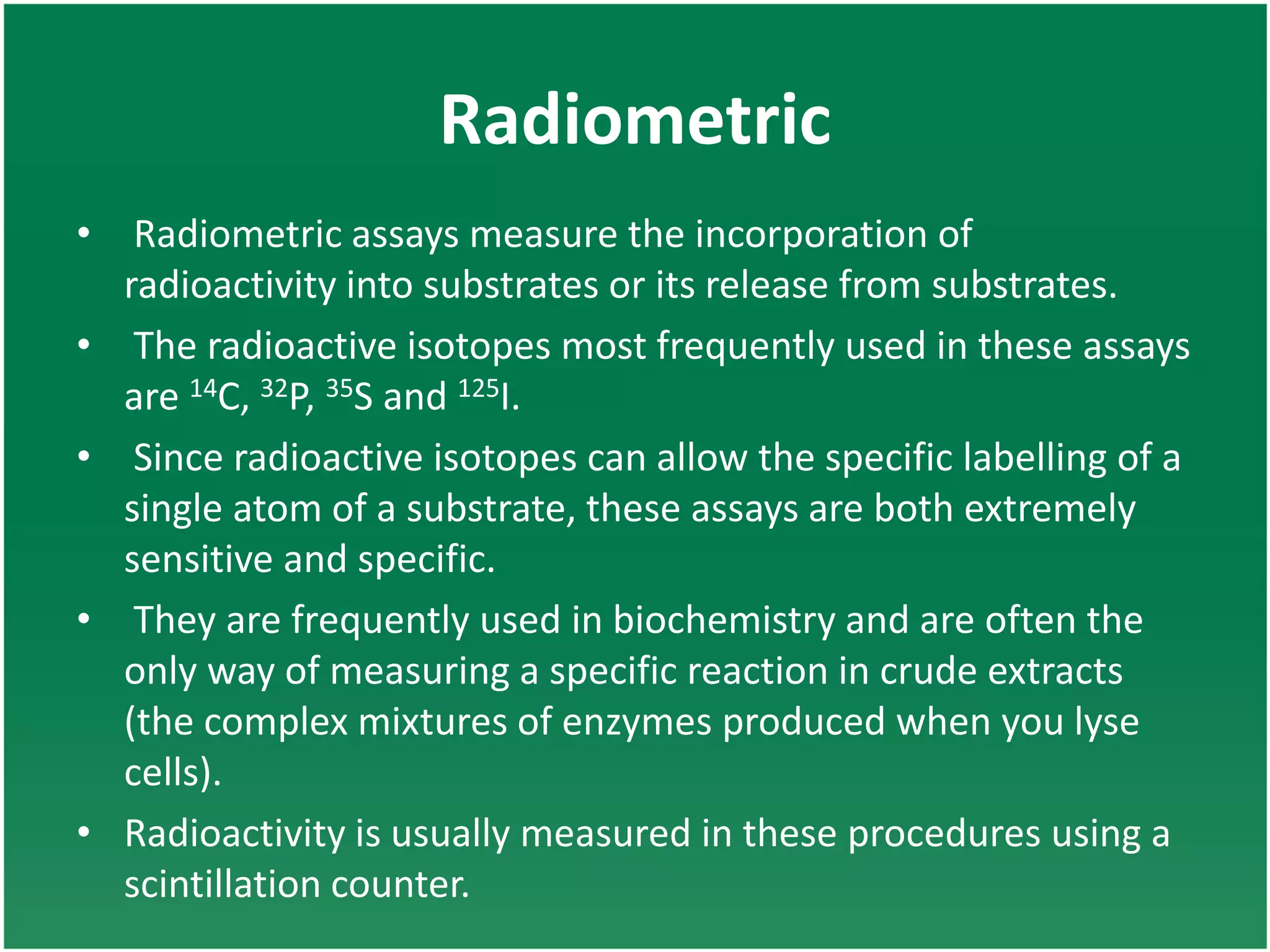
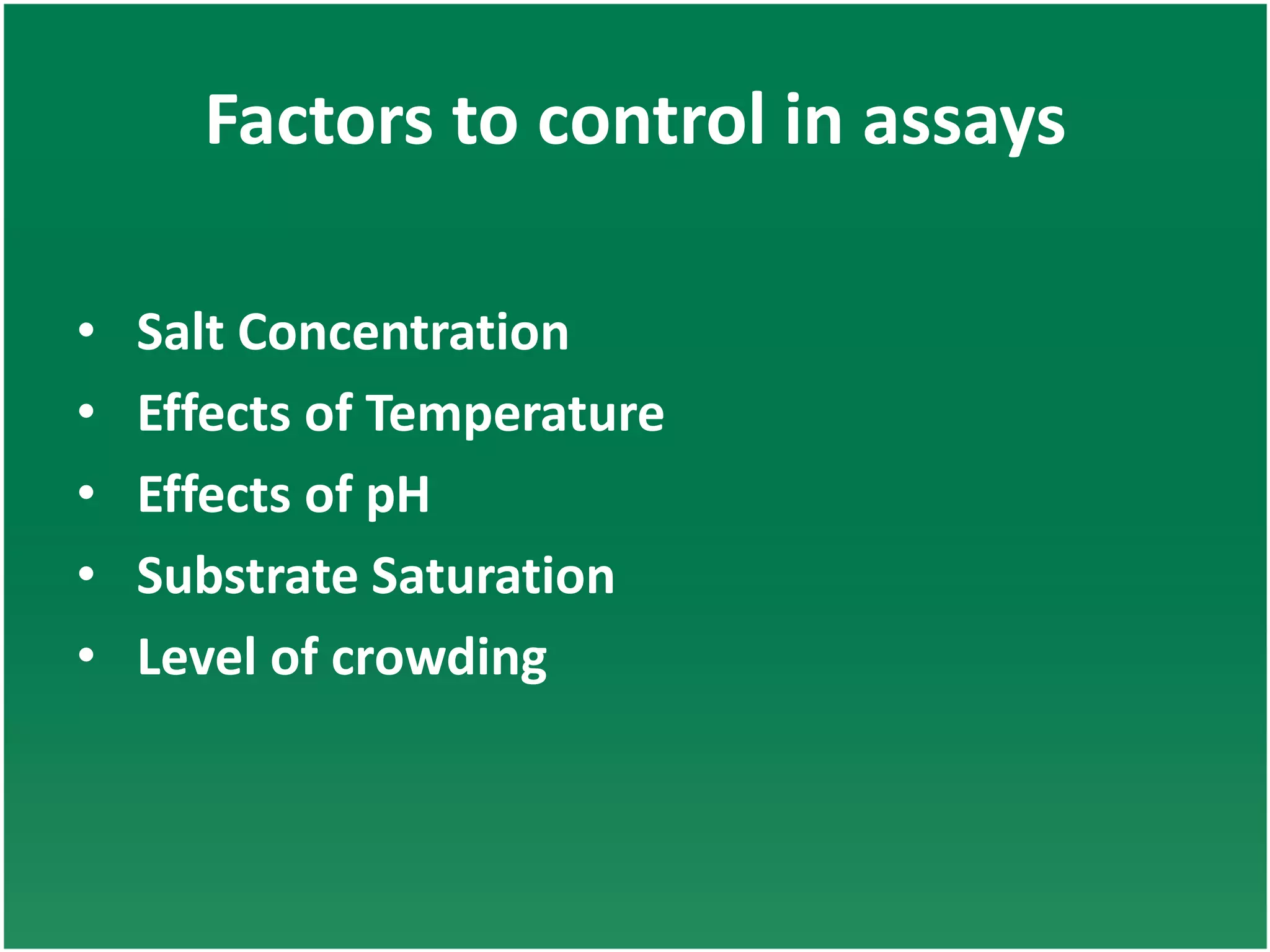
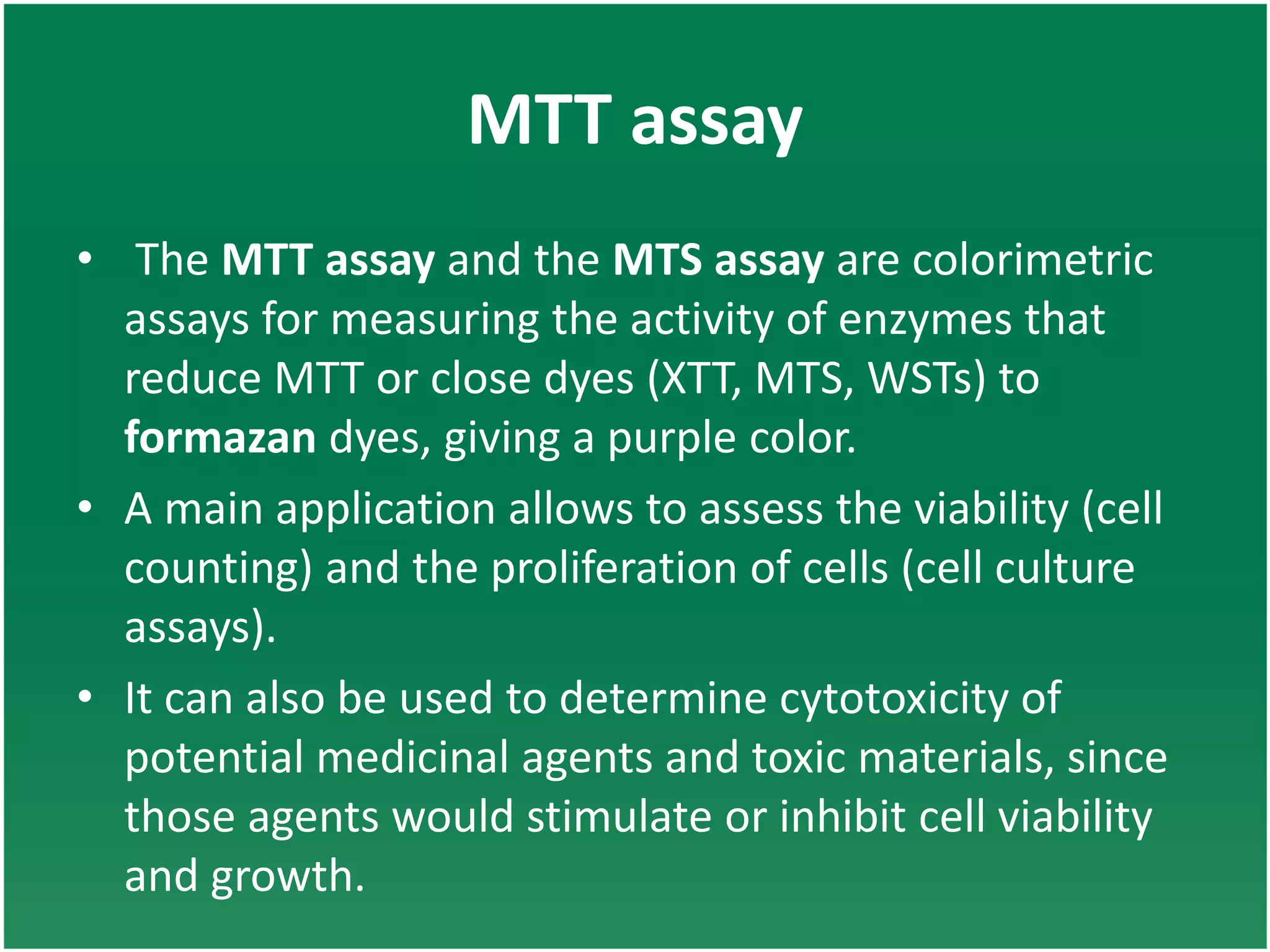
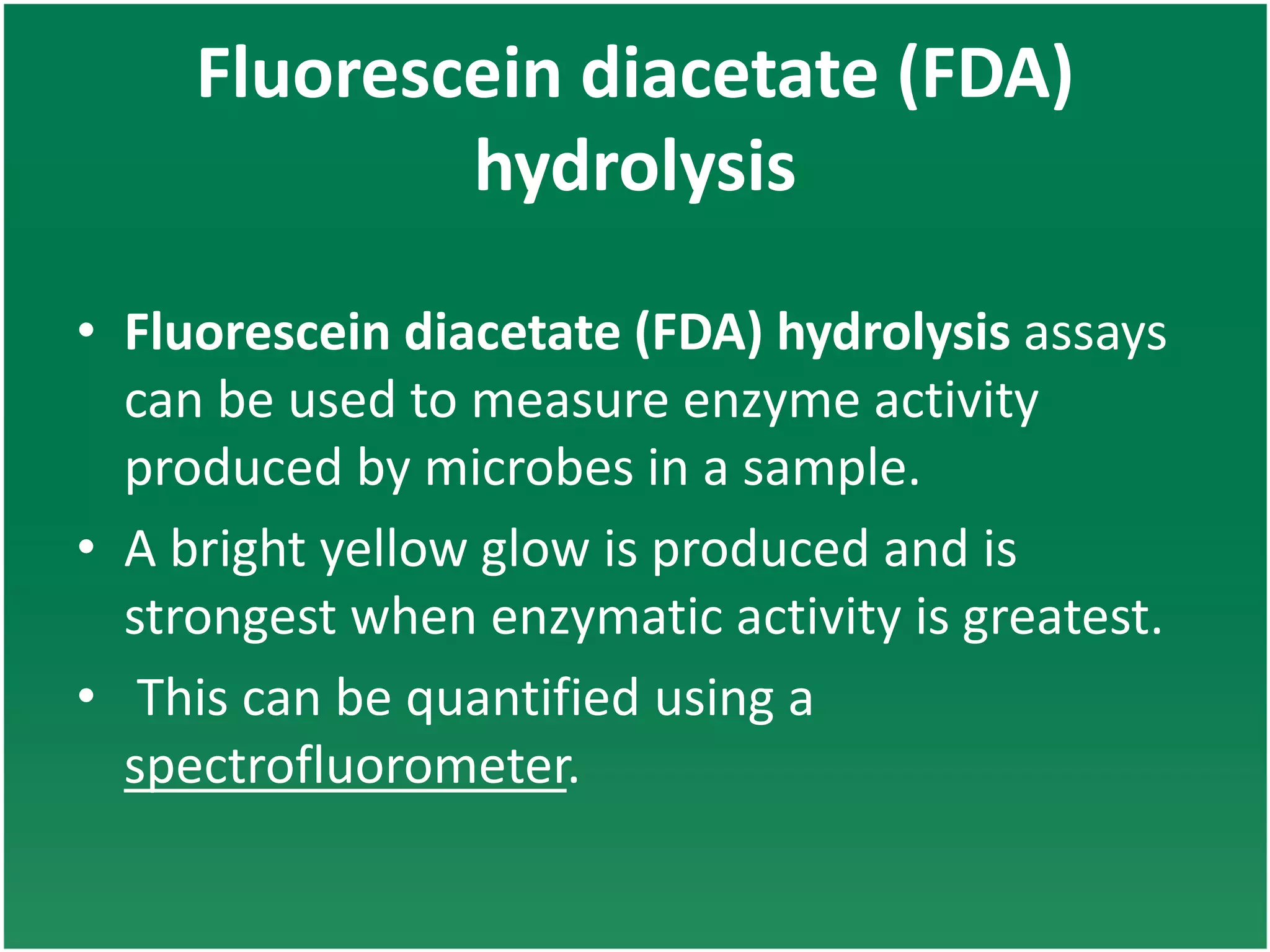
Enzyme assays are laboratory methods used to measure enzymatic activity. There are two main types - continuous assays that provide continuous readings of activity, and discontinuous assays where samples are taken and reactions stopped to determine substrate/product concentrations. Common continuous assay methods include spectrophotometric, fluorometric, calorimetric, and chemiluminescent assays, while discontinuous assays include radiometric and chromatographic methods. Proper controls must be established to account for factors like temperature, pH, substrate saturation, and salt/crowding effects. Specific examples provided are NADH oxidation, beta-galactosidase, and MTT/FDA hydrolysis assays.