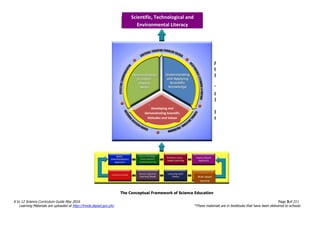
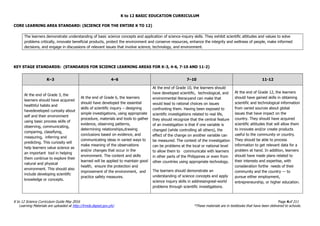
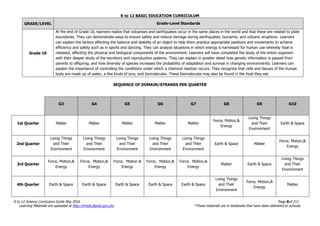
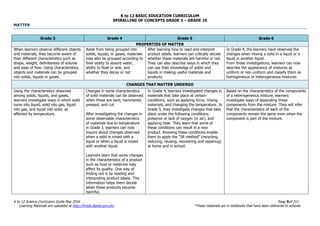
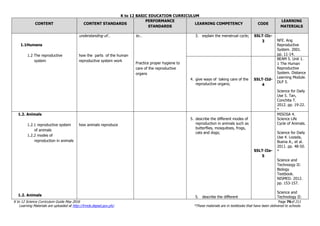
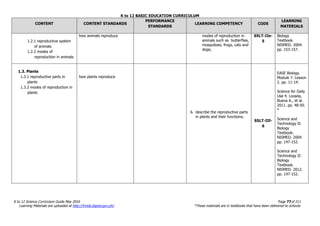
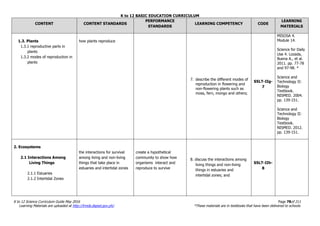
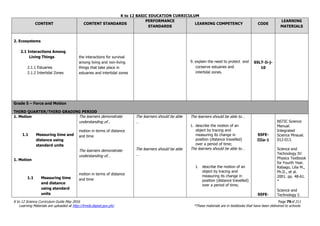
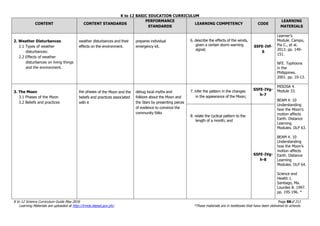
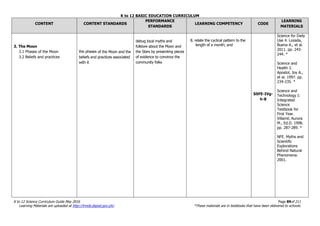
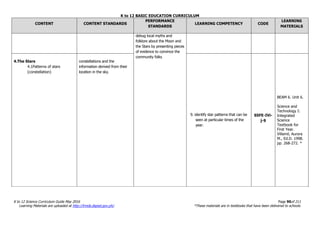
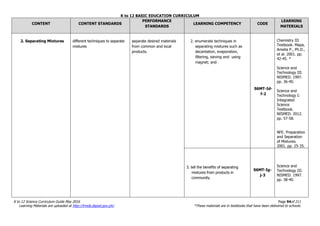
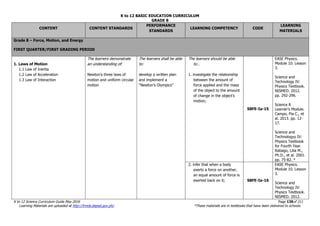
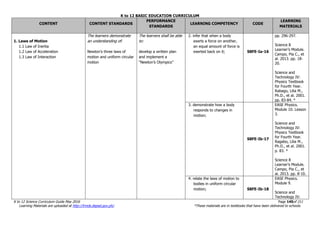
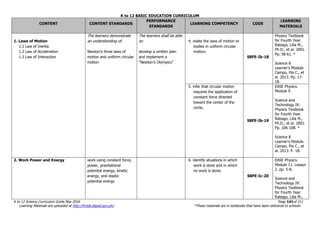
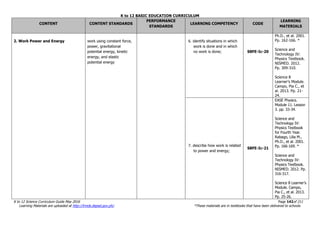
The document is the K to 12 Science Curriculum Guide from the Department of Education of the Republic of the Philippines. It outlines the conceptual framework and standards for the science curriculum from Kindergarten to Grade 10. The goals are to develop scientific literacy, problem-solving skills, and positive scientific attitudes and values among students. The curriculum covers content in Life Sciences, Physics, Chemistry, and Earth Sciences using inquiry-based and interdisciplinary approaches. It emphasizes understanding concepts, performing scientific processes, and demonstrating scientific attitudes and values.