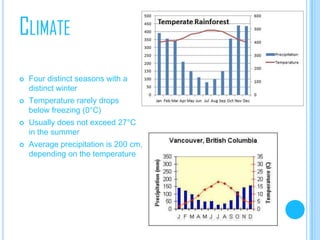
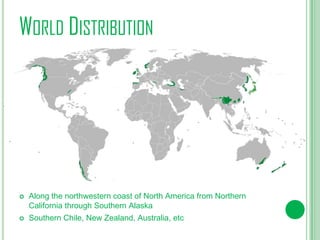
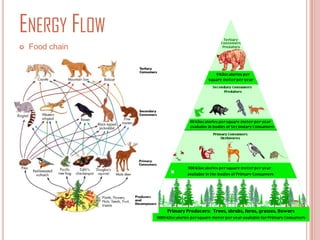
This document summarizes key aspects of temperate rainforests. It outlines important abiotic factors like sunlight, precipitation, climate, and soil. It then lists common plant and animal species found in these forests, including big coniferous trees, deciduous trees, mosses, lichens, and animals like deer, bears, birds, fish and more. The document also discusses the climate, world distribution, threats like bioaccumulation, invasive species, energy flow, symbiosis, succession, and predator-prey relationships of temperate rainforests.