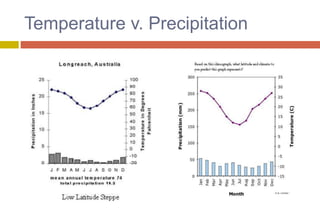
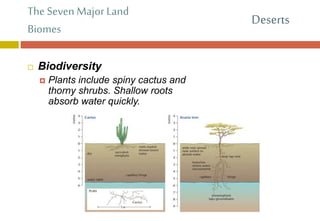
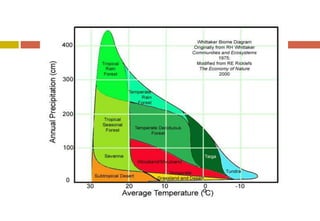
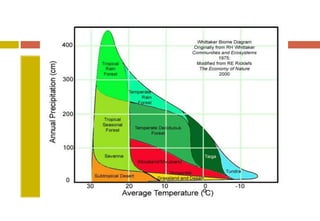
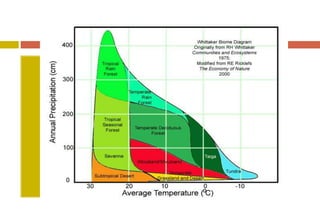
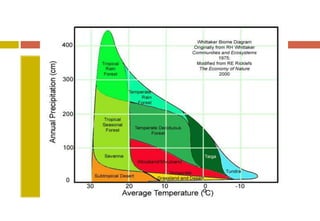
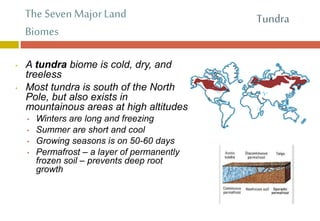
The document outlines the characteristics and biodiversity of seven major land biomes: deserts, grasslands, tropical rainforests, temperate rainforests, temperate deciduous forests, taiga, and tundra. It describes the unique climate, soil, and plant and animal life found in each biome, as well as human impacts such as deforestation and habitat destruction. The information emphasizes the importance of conserving these ecosystems and the biodiversity they support.