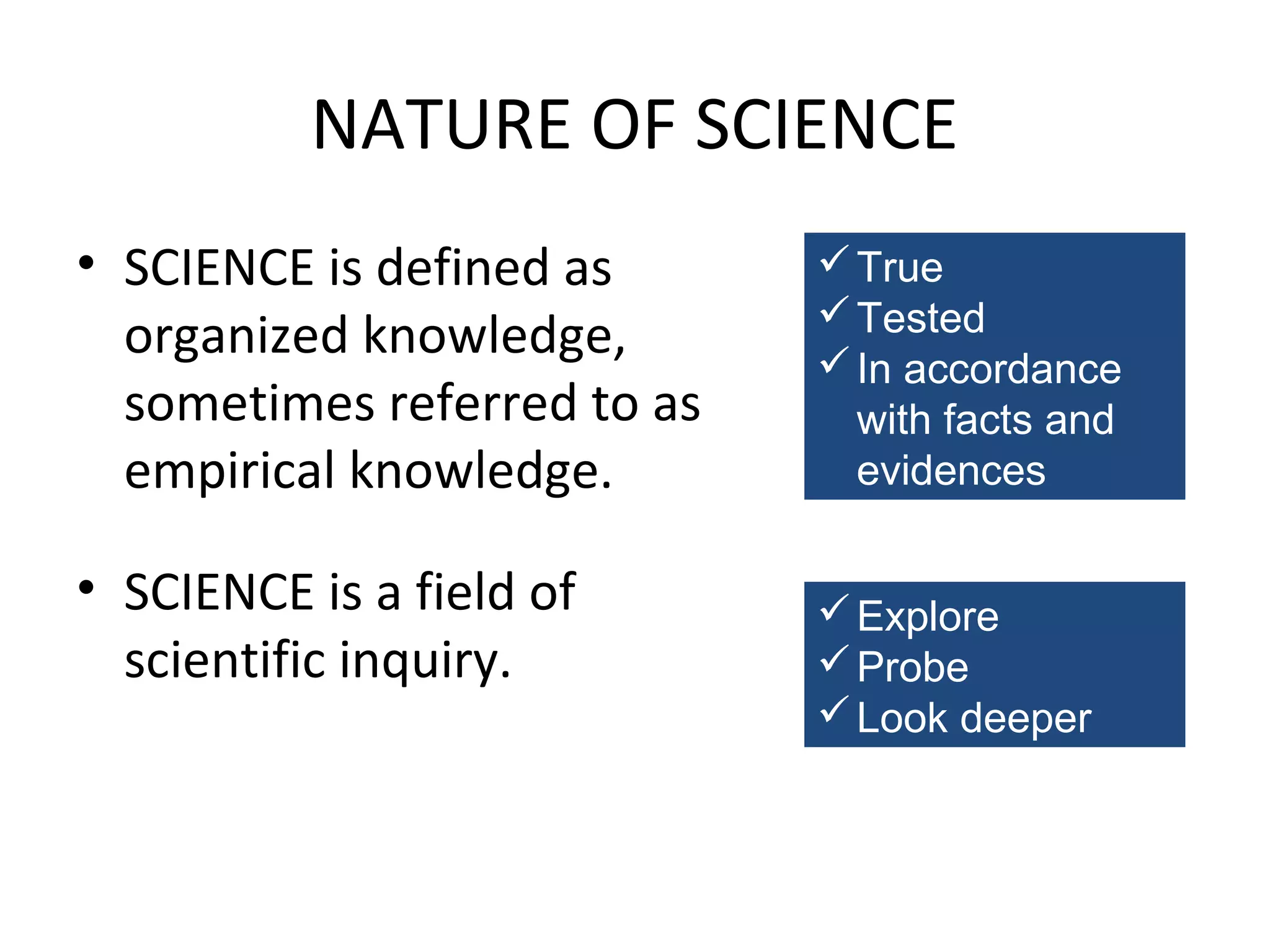
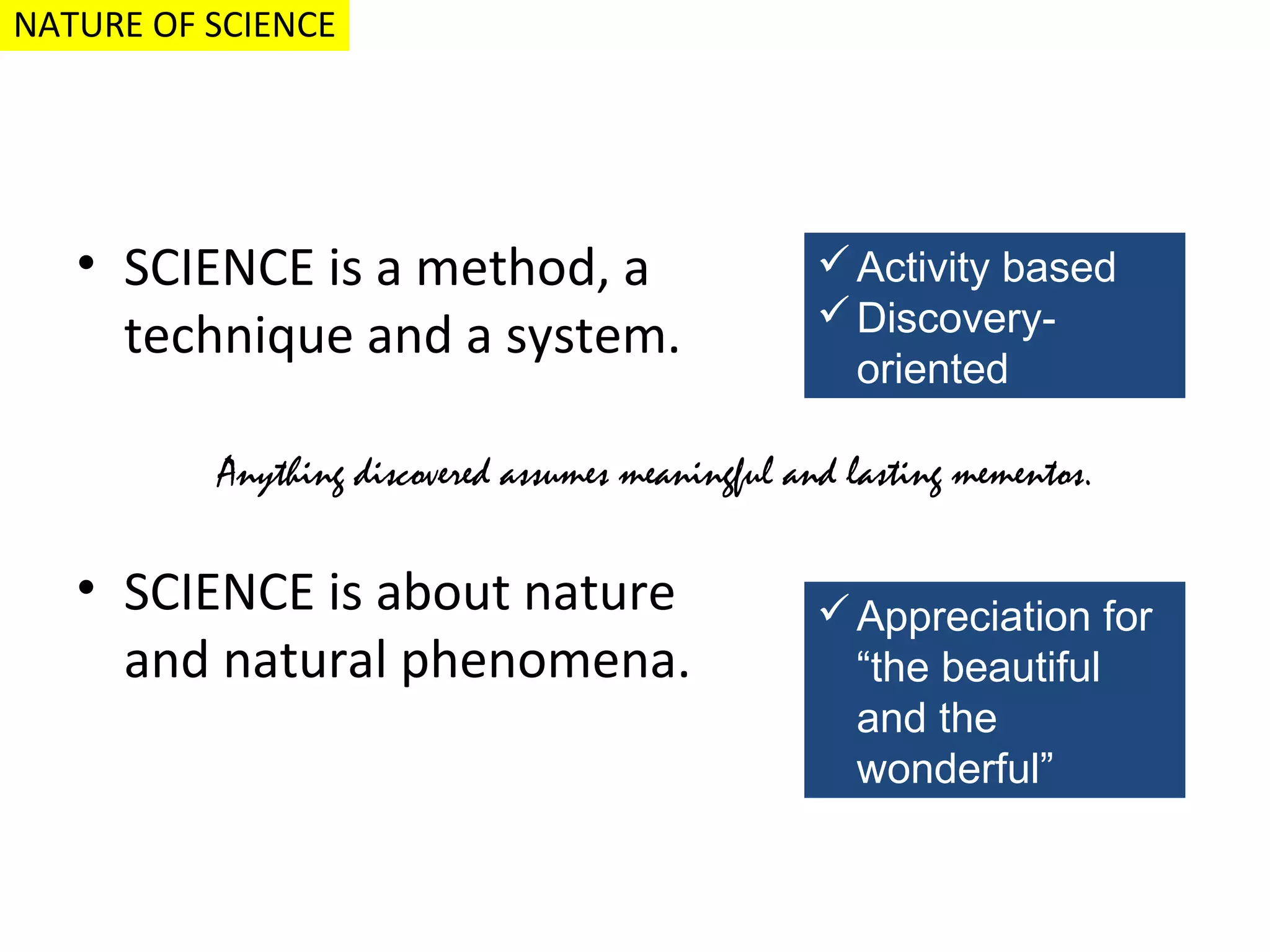
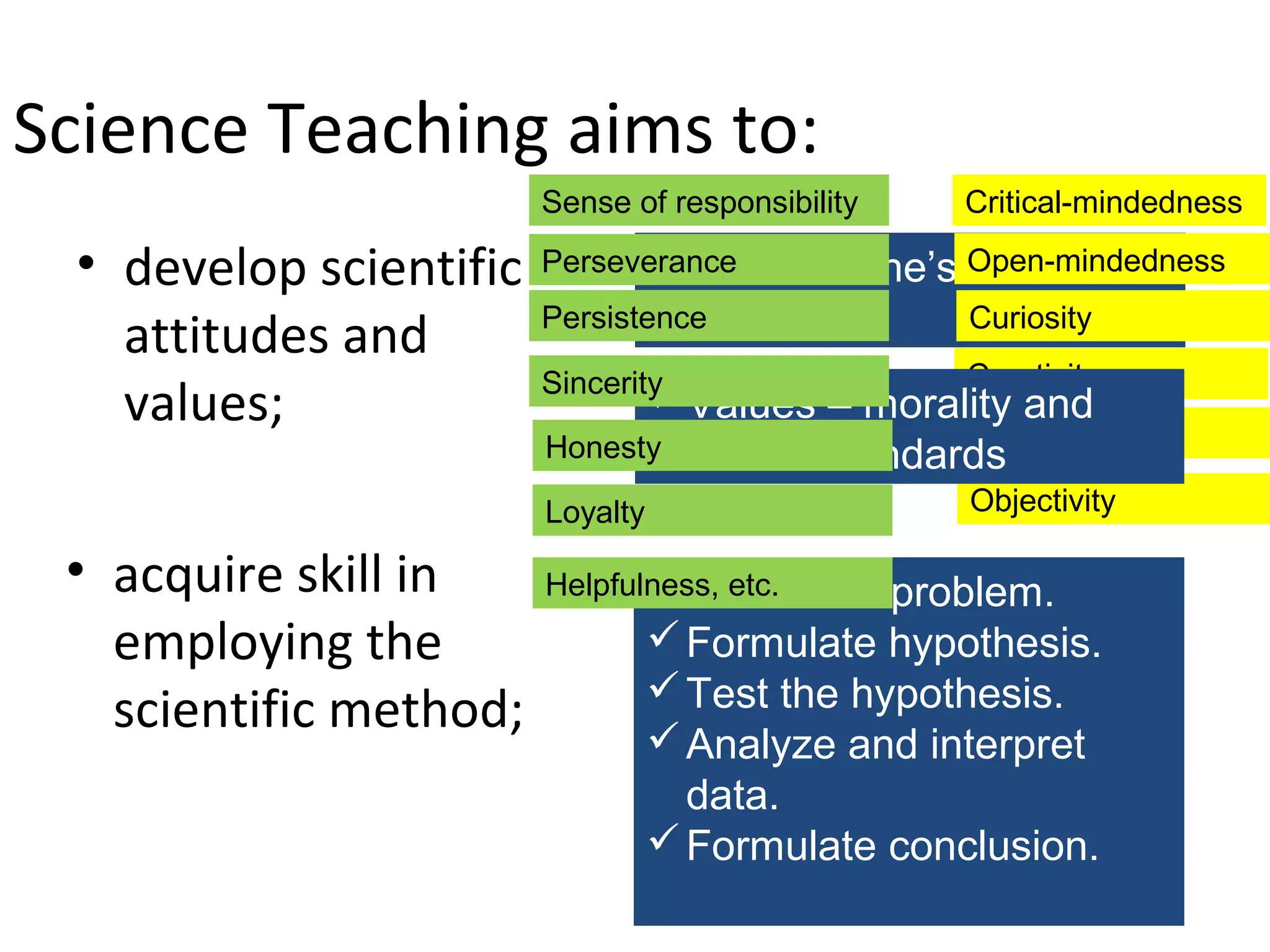
This document discusses the goals and nature of science teaching. It aims to develop scientific attitudes, values, and skills in employing the scientific method in students. The goals are to acquire functional knowledge and information that can be applied to real life, and to arouse and sustain interest in future science-based pursuits. Objectives of science instruction are stated behaviorally and include students gaining applicable knowledge, developing skills in investigating and interpreting information using science processes, and fostering values and attitudes that lead to interests in science-related hobbies and careers.