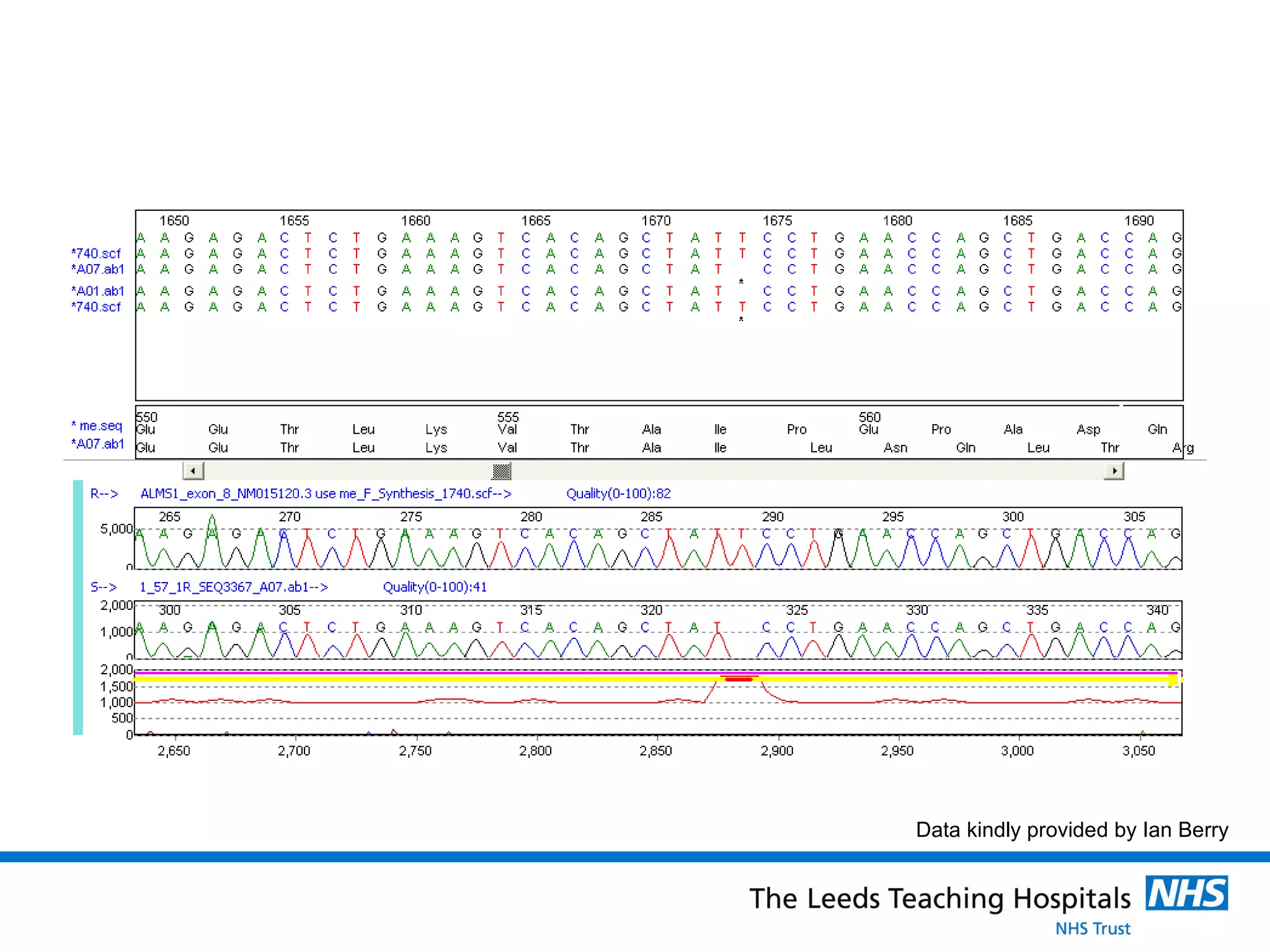
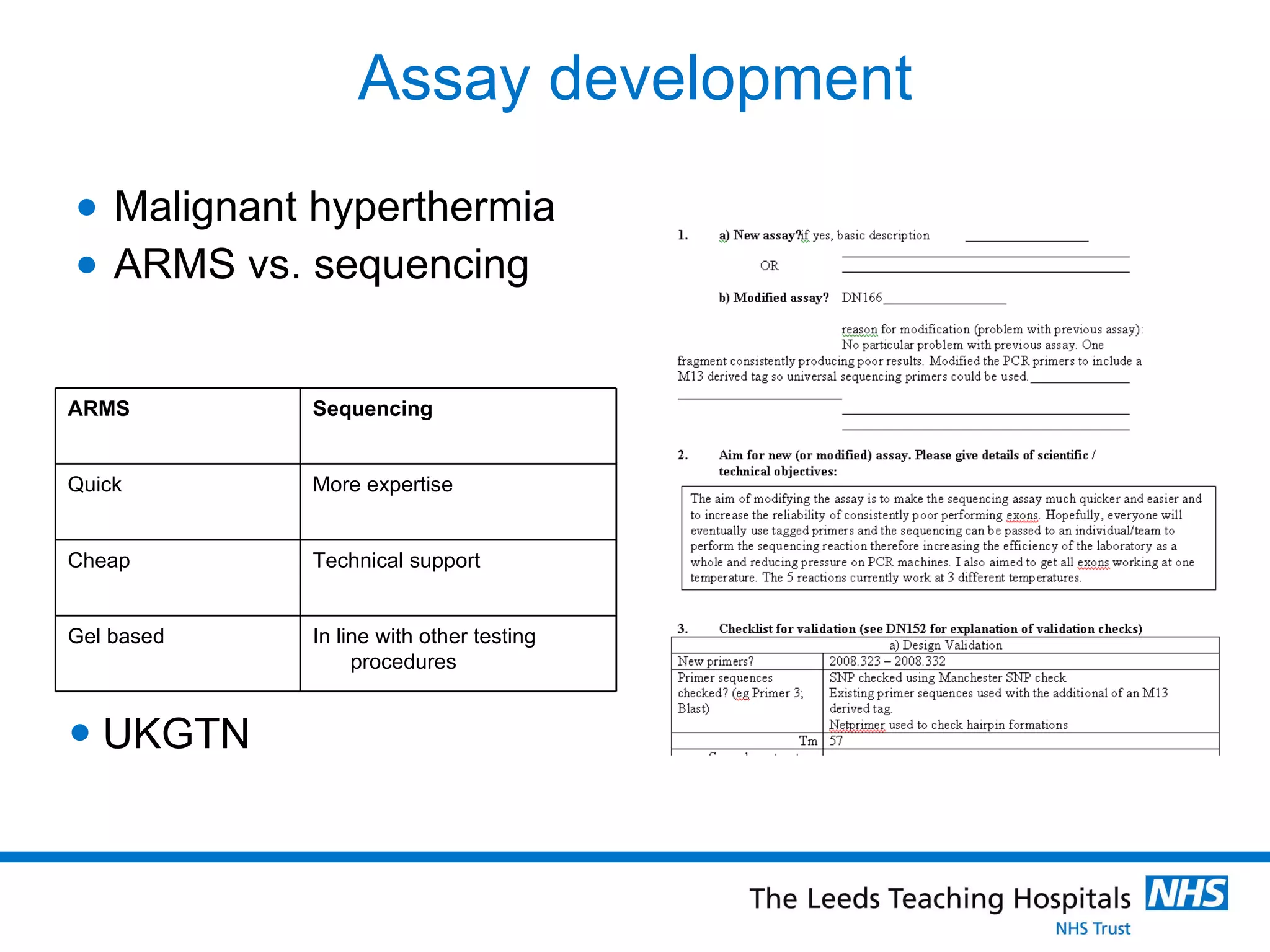
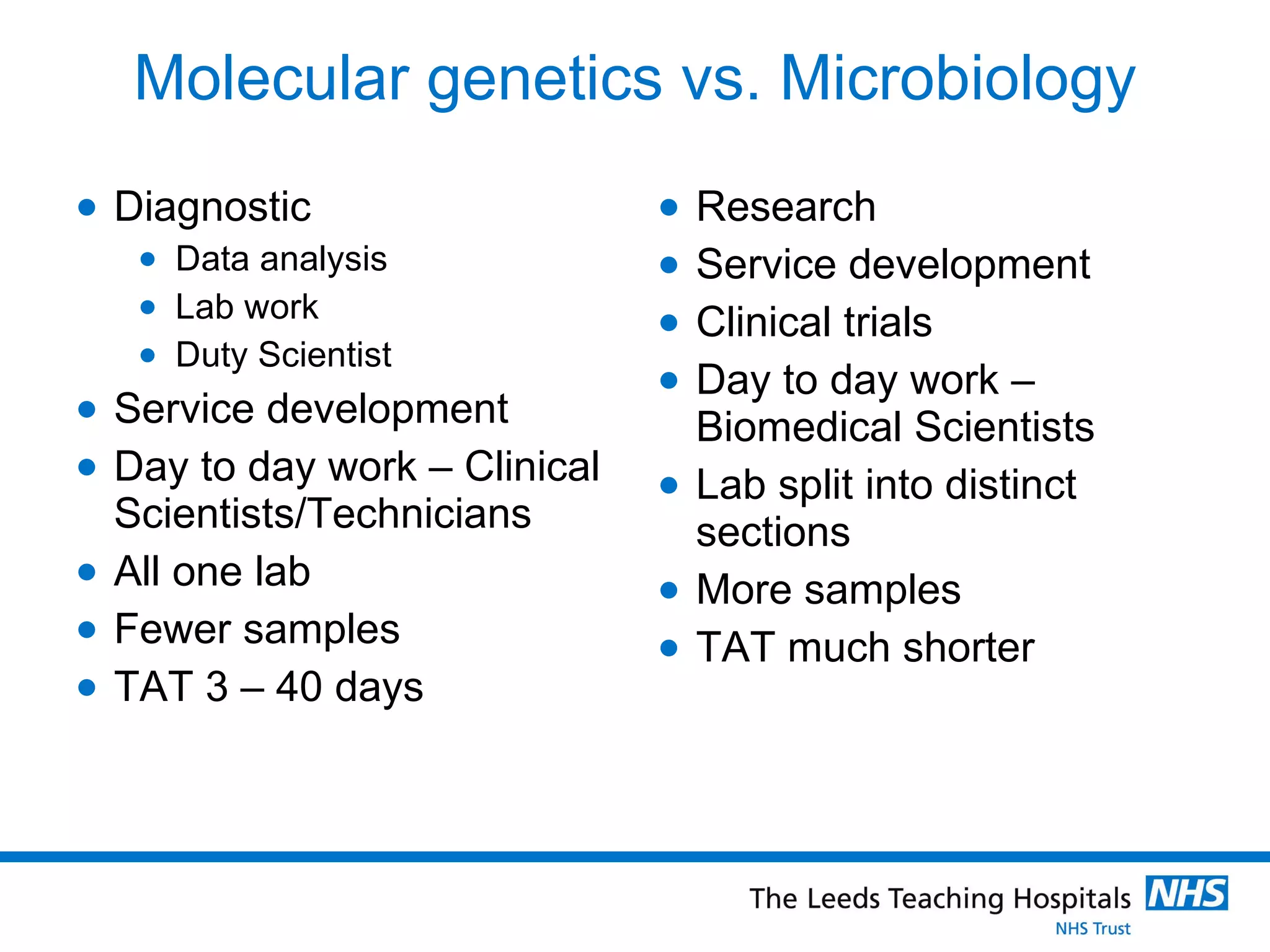
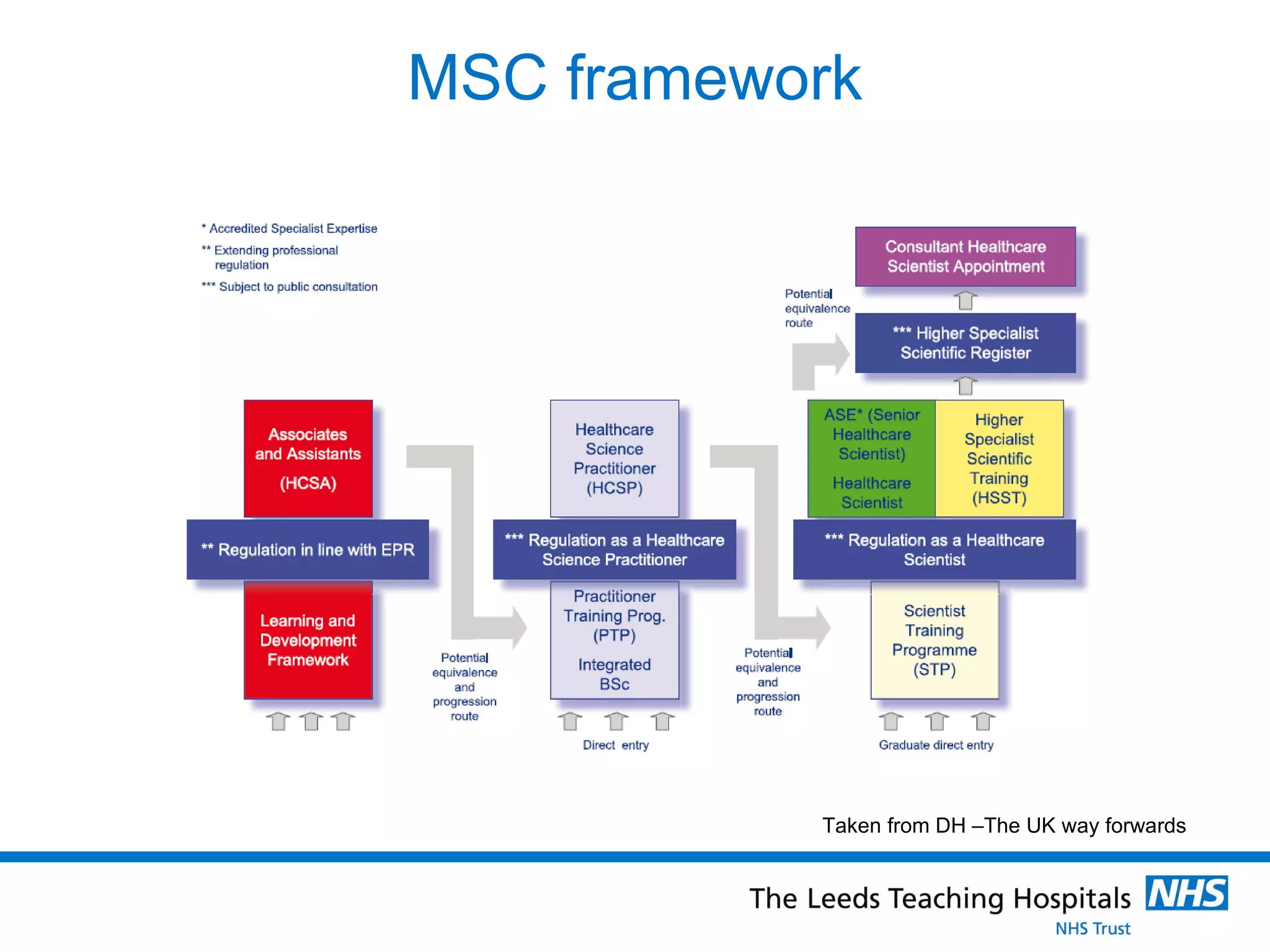
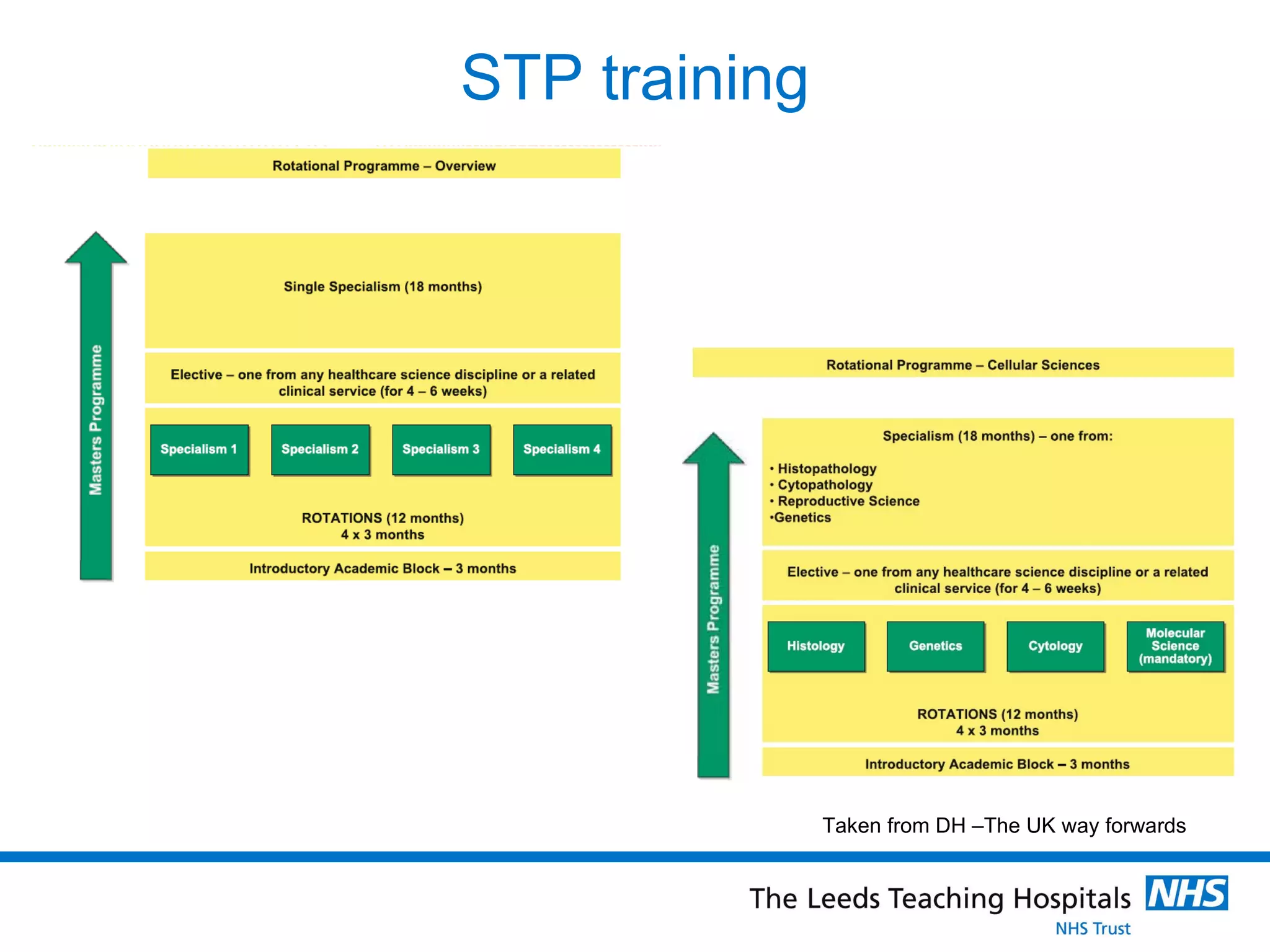
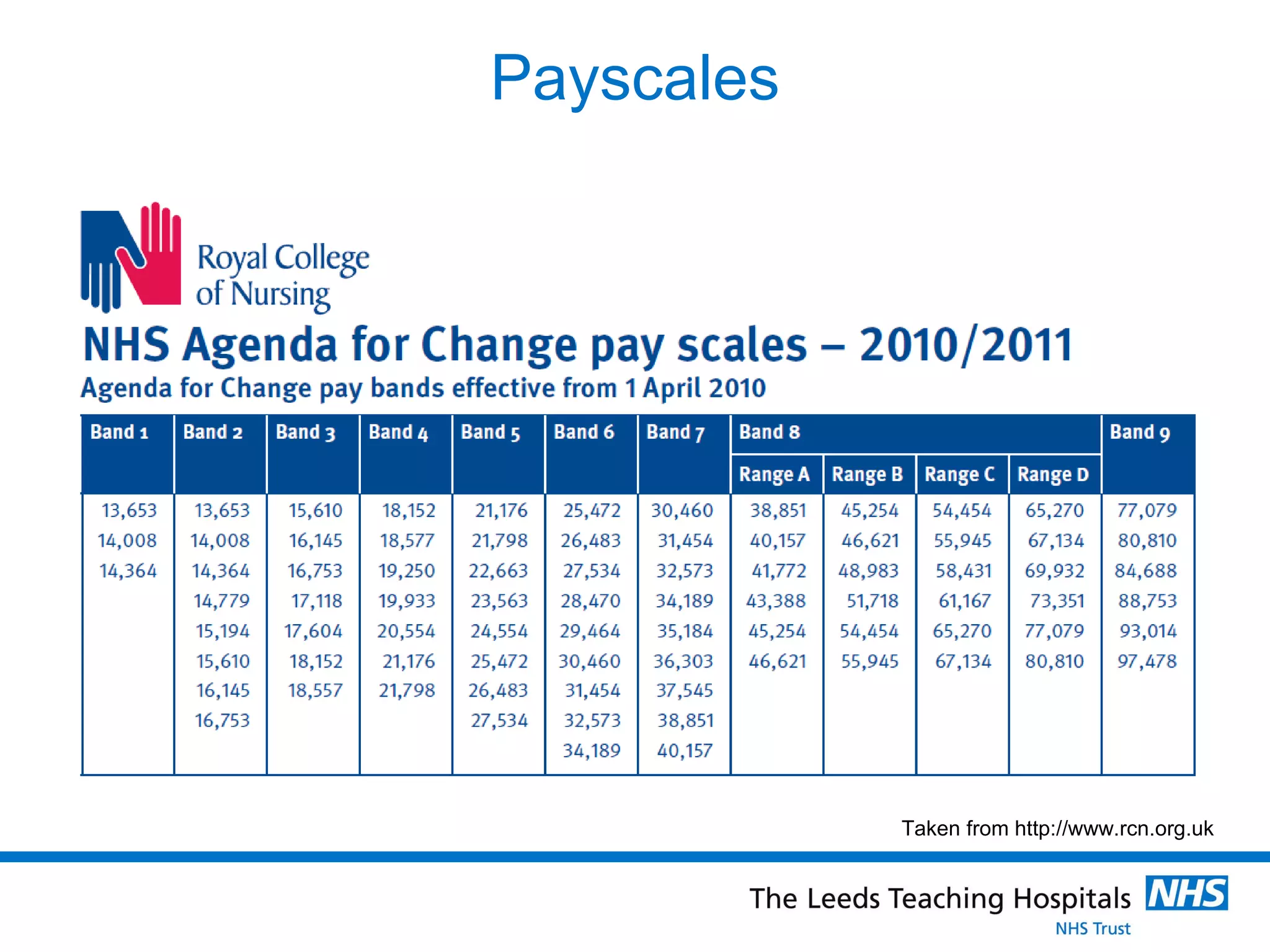
The document provides an overview of the career path and training required to become a Clinical Scientist in Molecular Genetics in the UK. It details the educational requirements, two training routes, certification process, and typical daily responsibilities in the laboratory. The document also compares roles in Molecular Genetics versus Microbiology and provides tips and resources for those interested in pursuing this career path.