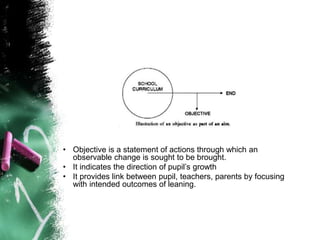
The document discusses the objectives of science teaching. It defines objectives as specific, measurable goals that are attainable and vary between subjects. The key objectives of teaching science include developing better understanding of the nature of science, acquiring skills, fostering scientific attitudes like curiosity and critical thinking, training in the scientific method, cultivating interest and appreciation for science, helping students fit into society, and guiding career choices. Specific objectives outlined include understanding concepts, gaining skills like observation and problem-solving, appreciating science in daily life, promoting cooperation, and arousing curiosity in young learners. Objectives should be determined by people's needs and involve practical learning to develop scientific attitudes.