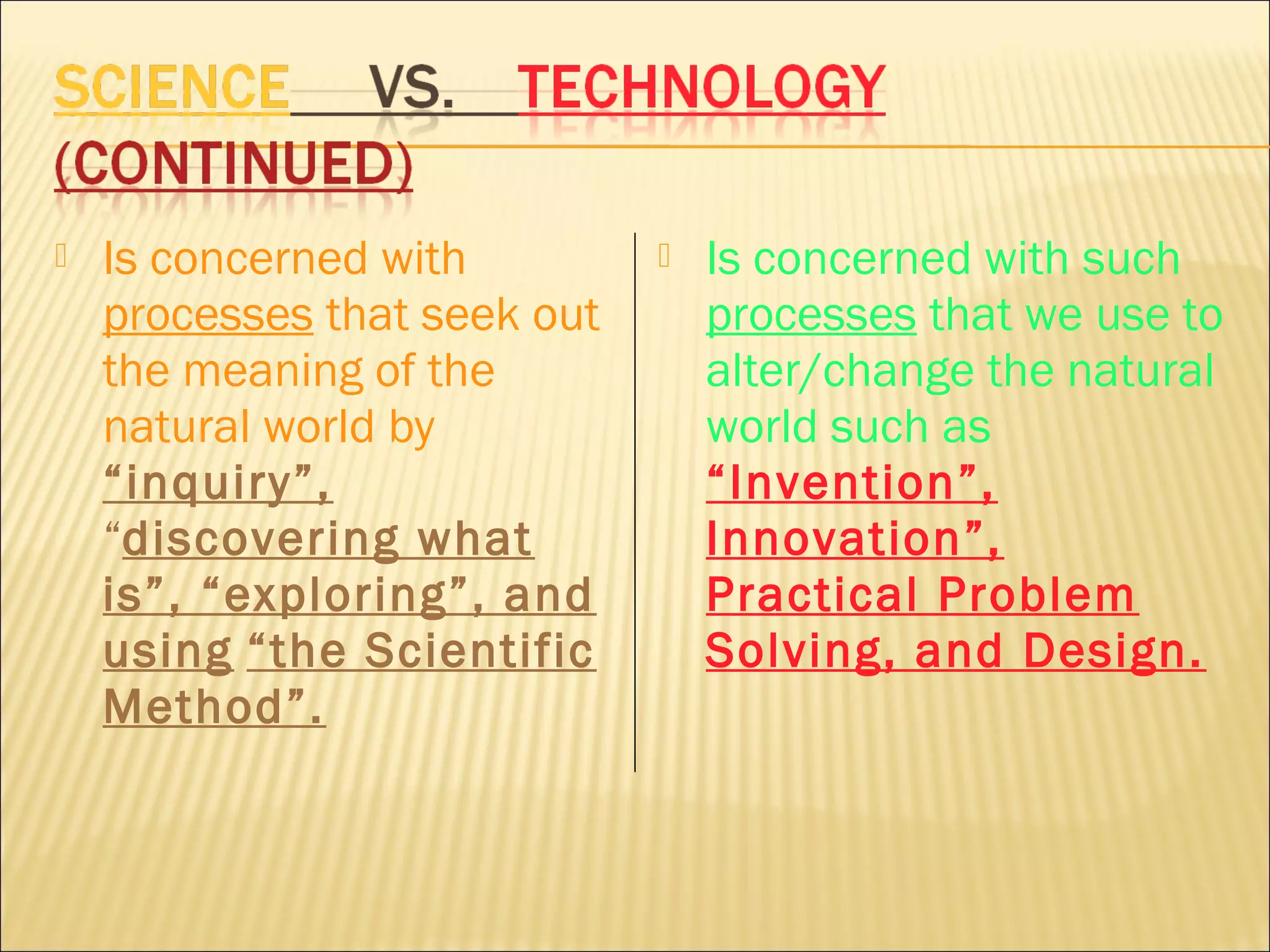
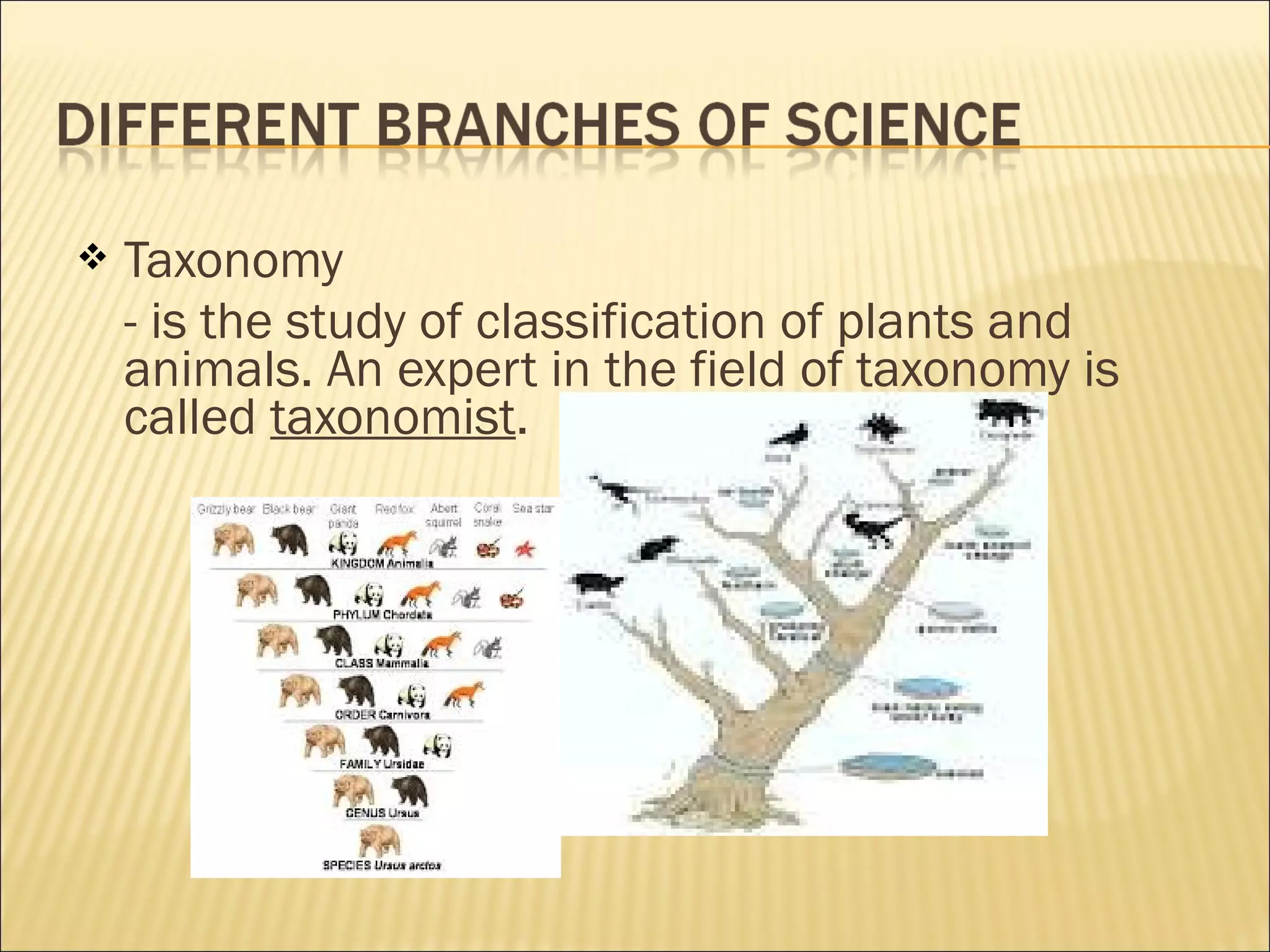
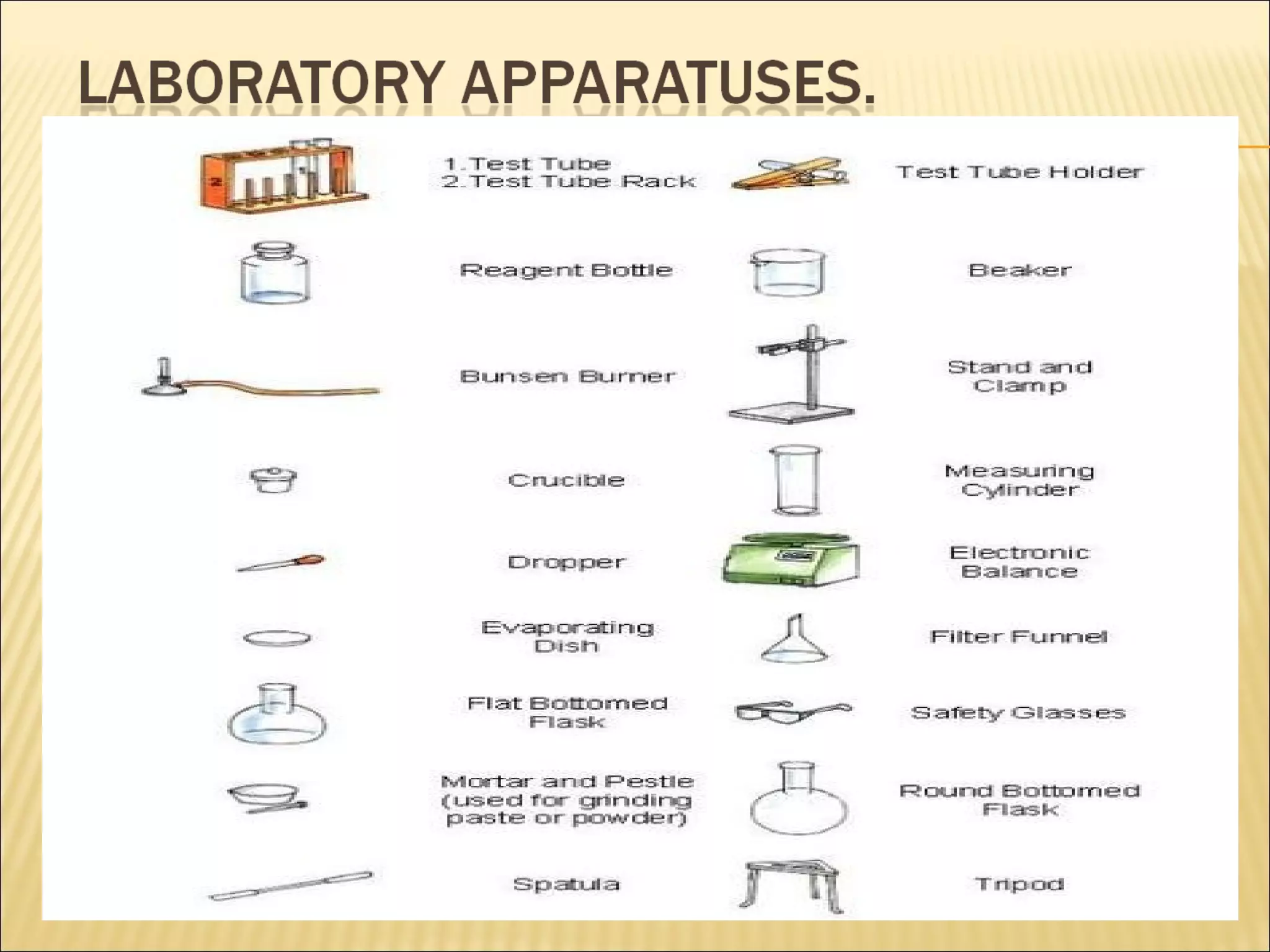
This document defines technology and discusses the differences between technology and science. It provides examples of different fields of science such as biology, chemistry, physics, geology and their experts. Technology is defined as humans modifying nature to meet needs and wants through processes like invention, innovation and problem solving. Science seeks to understand nature through inquiry and exploration, while technology seeks to change it. Both science and technology are important but have different goals.