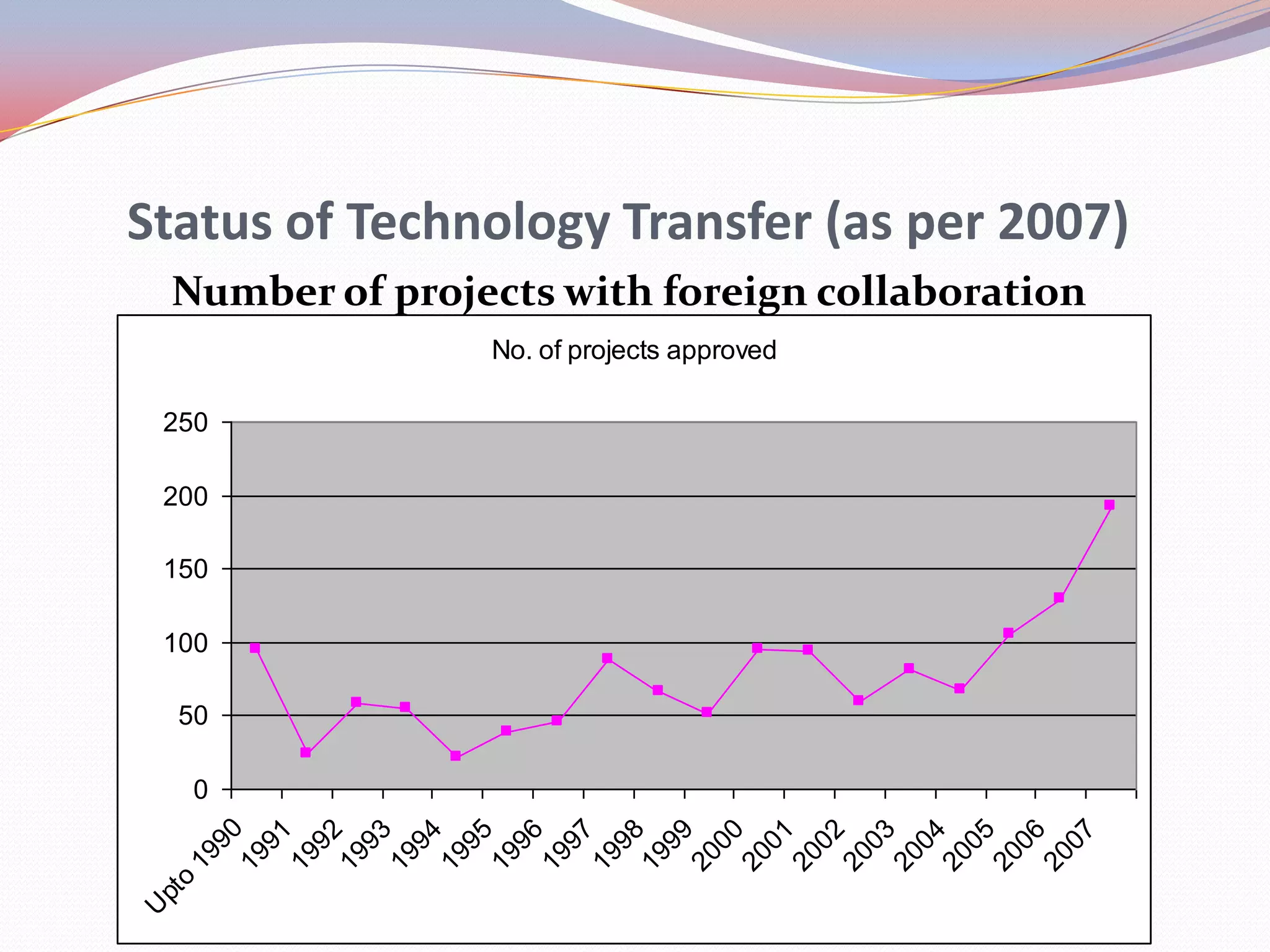
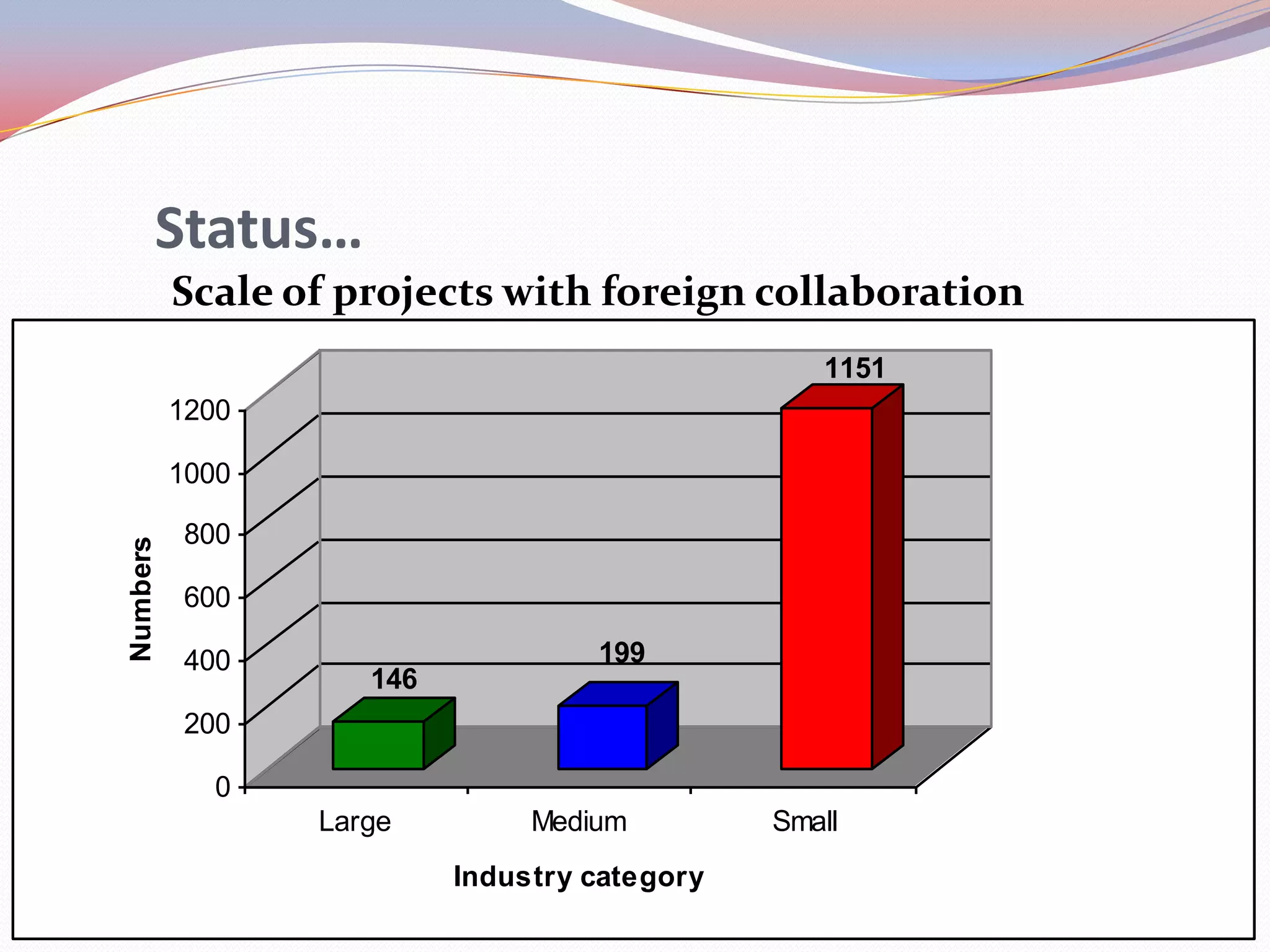
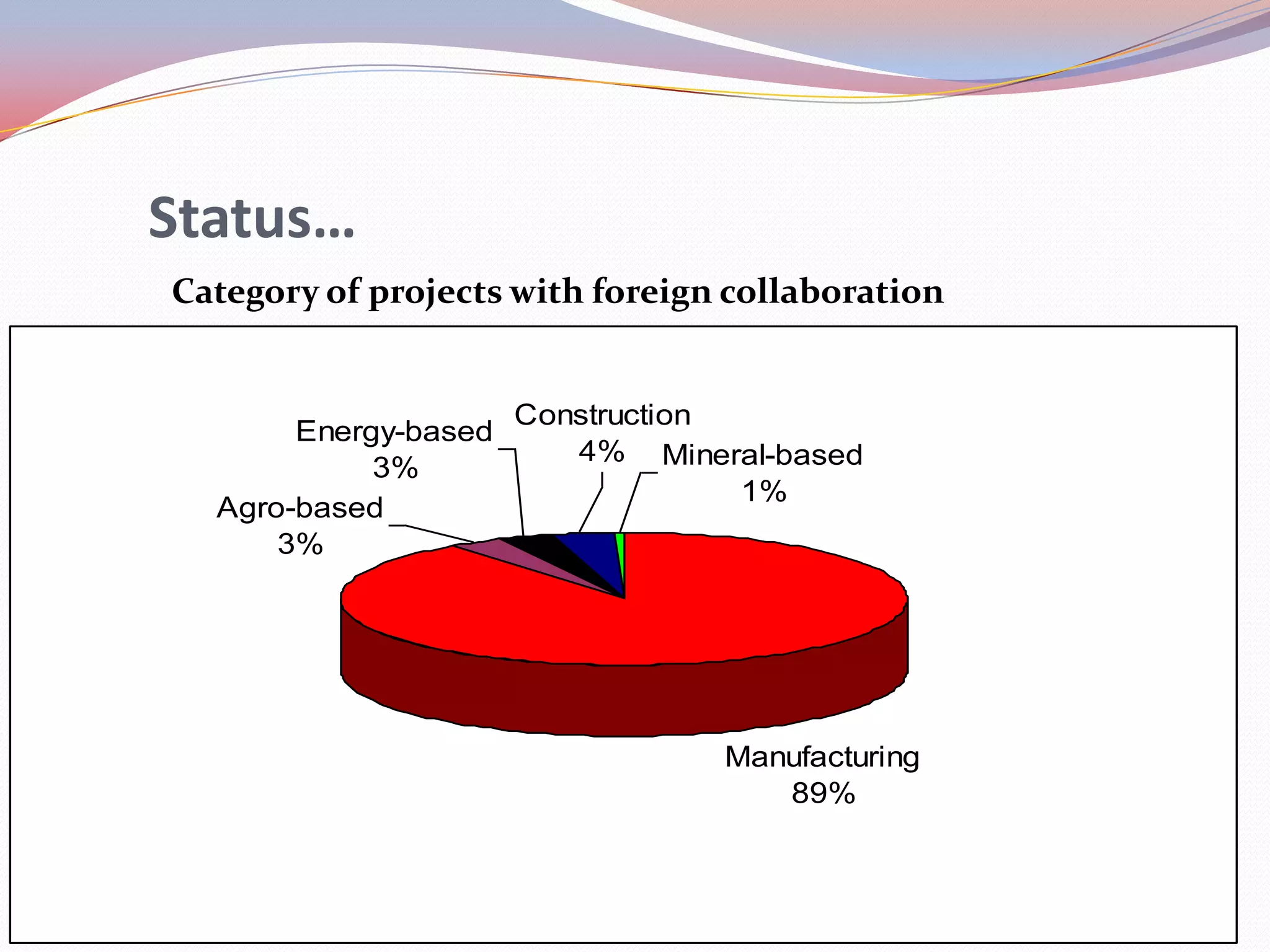
Nepal is transitioning from a rural to urban economy and has a literacy rate of 68.2%. Agriculture accounts for about 40% of GDP and 80% of the population derives their livelihood from it. Technology is viewed as a means to increase productivity by combining resources. Nepal's industrial sector relies on imported and low grade technologies with little focus on R&D. Exports are mainly raw materials and skill development lags requirements. Technology transfer occurs through foreign investment but the scale of projects is generally small. Information technology is increasing access to education and tourism information but remains limited outside urban areas.