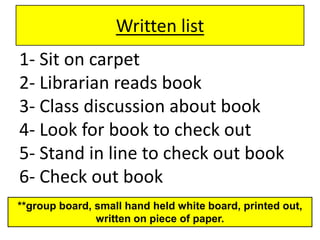
1) The document provides guidance for librarians on including students with special needs such as autism, emotional-behavioral disorders, intellectual disabilities, and learning disabilities in mainstream classrooms.
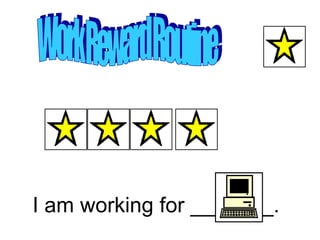
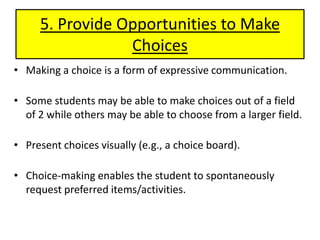
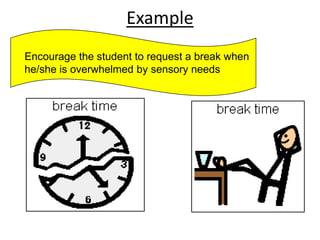
2) It recommends nine strategies: using visual schedules and cues, clear communication, reinforcement, choice-making, addressing sensory needs, peer and paraprofessional support, collaboration, and accountability measures.
3) The strategies are meant to help librarians implement accommodations from students' IEPs and meet the varied needs of all students in an inclusive setting.