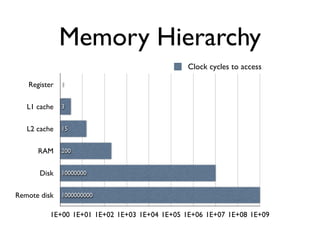
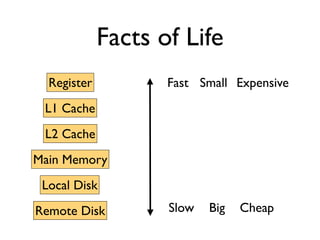
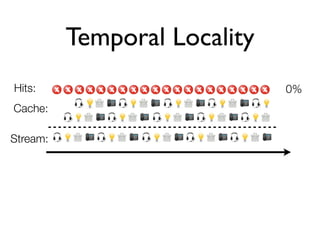
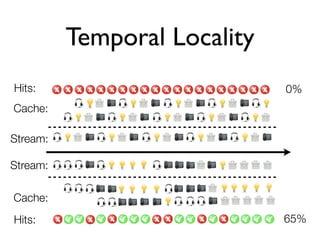
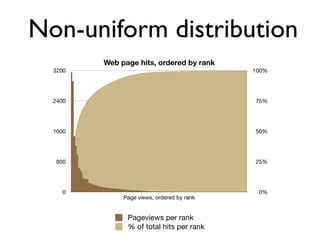
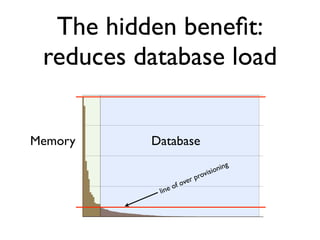
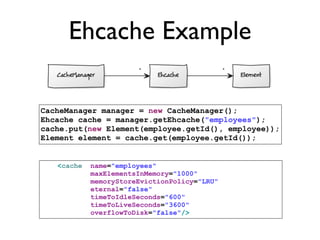
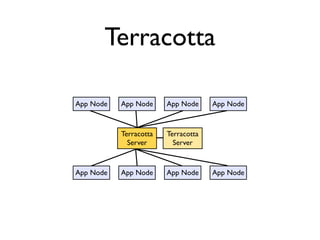
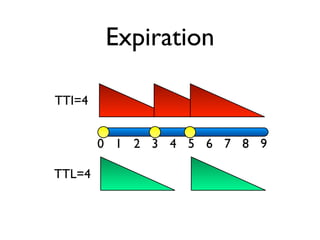
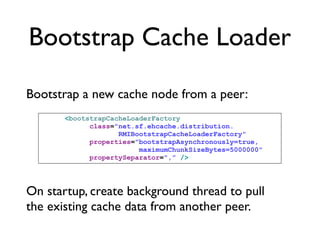
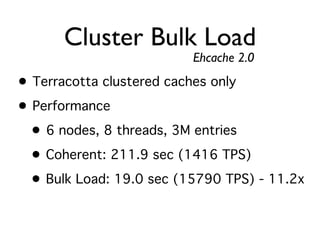
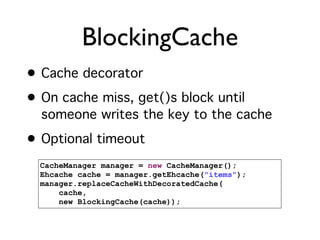
The document discusses caching architecture, focusing on its importance, challenges, and design choices for effective implementation. It covers methods for memory management, including eviction policies like 'least recently used,' and various caching strategies such as write-through and write-behind caching using Ehcache and Terracotta technologies. Additionally, it addresses concerns regarding data staleness, concurrency, and the scalability of caching solutions.