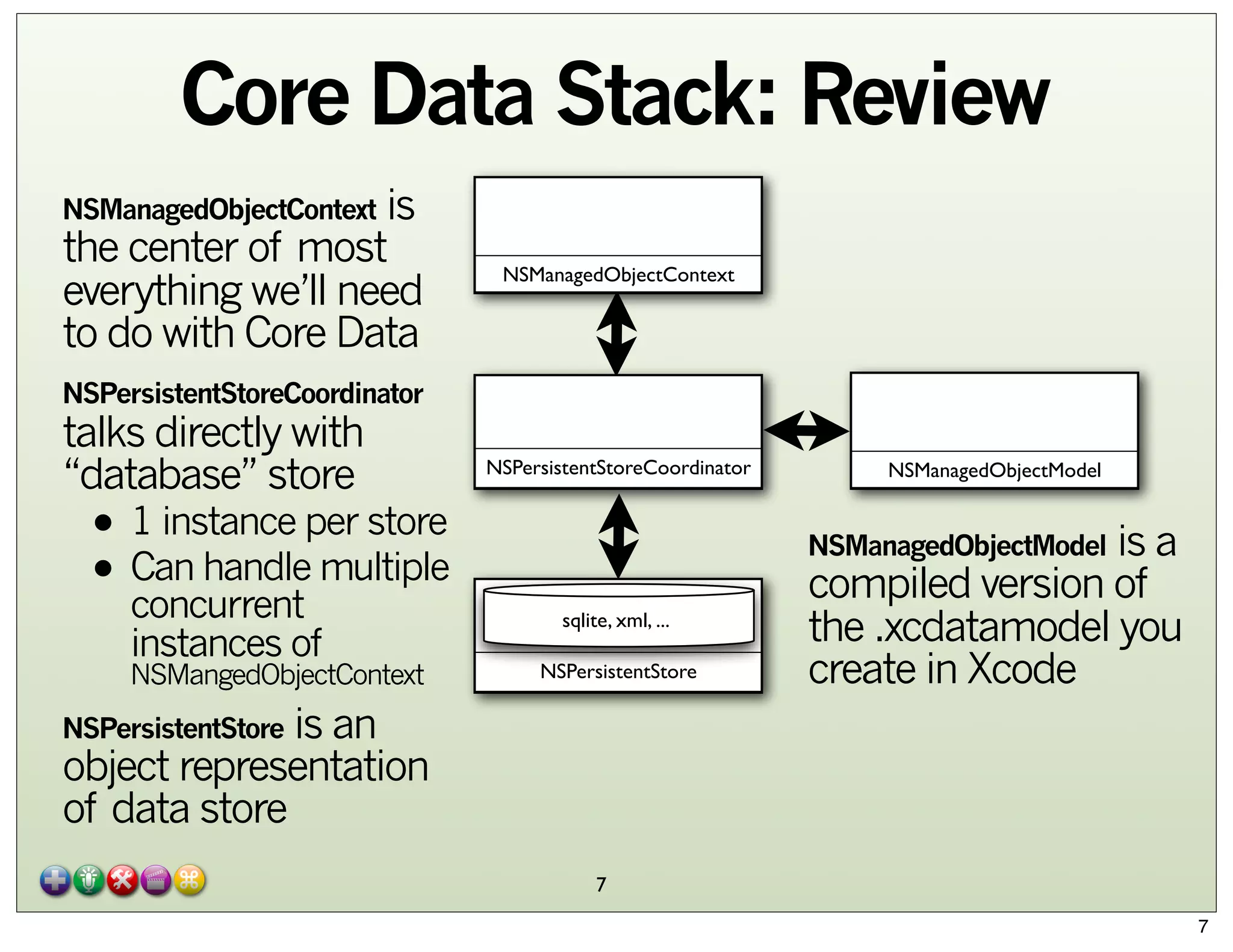
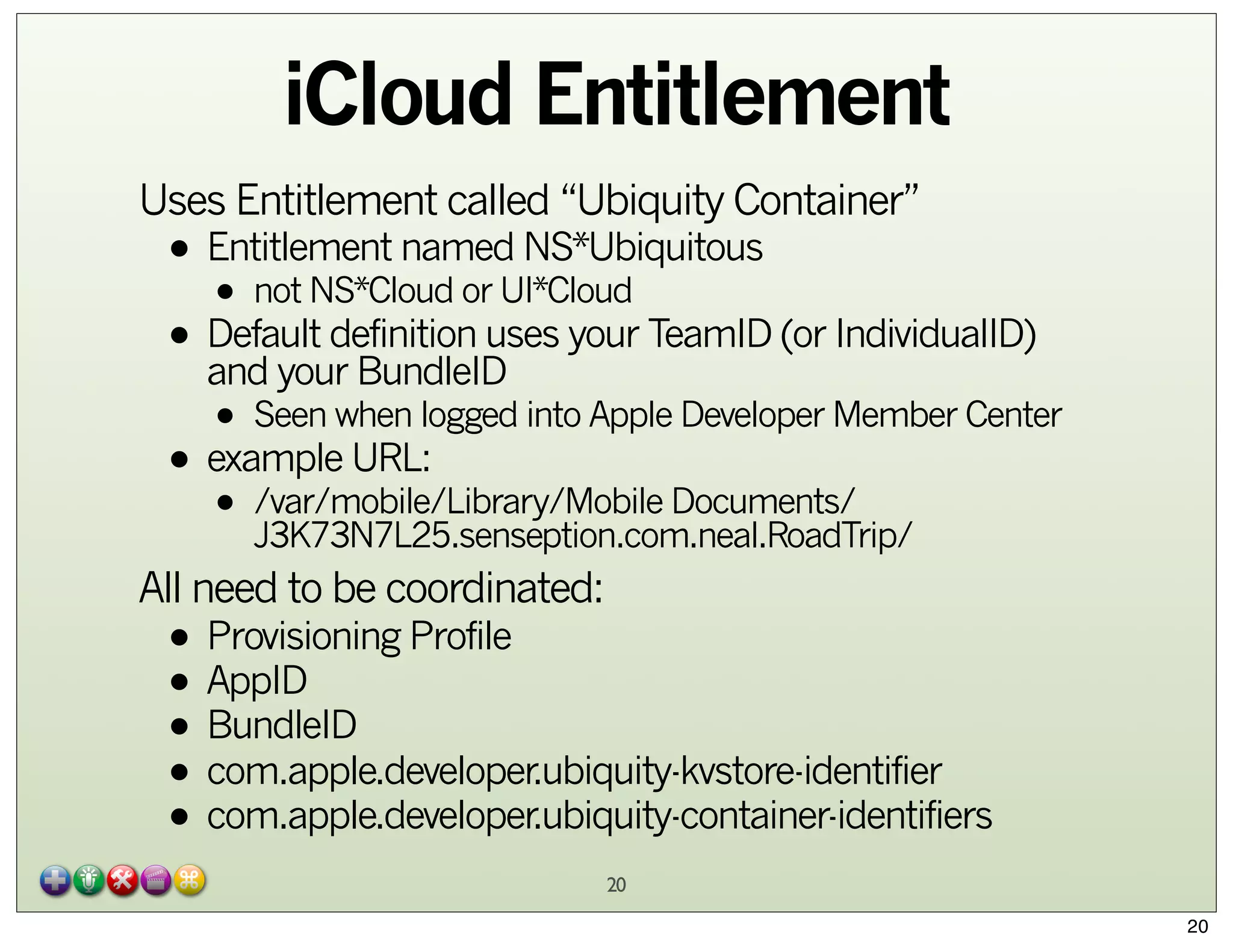
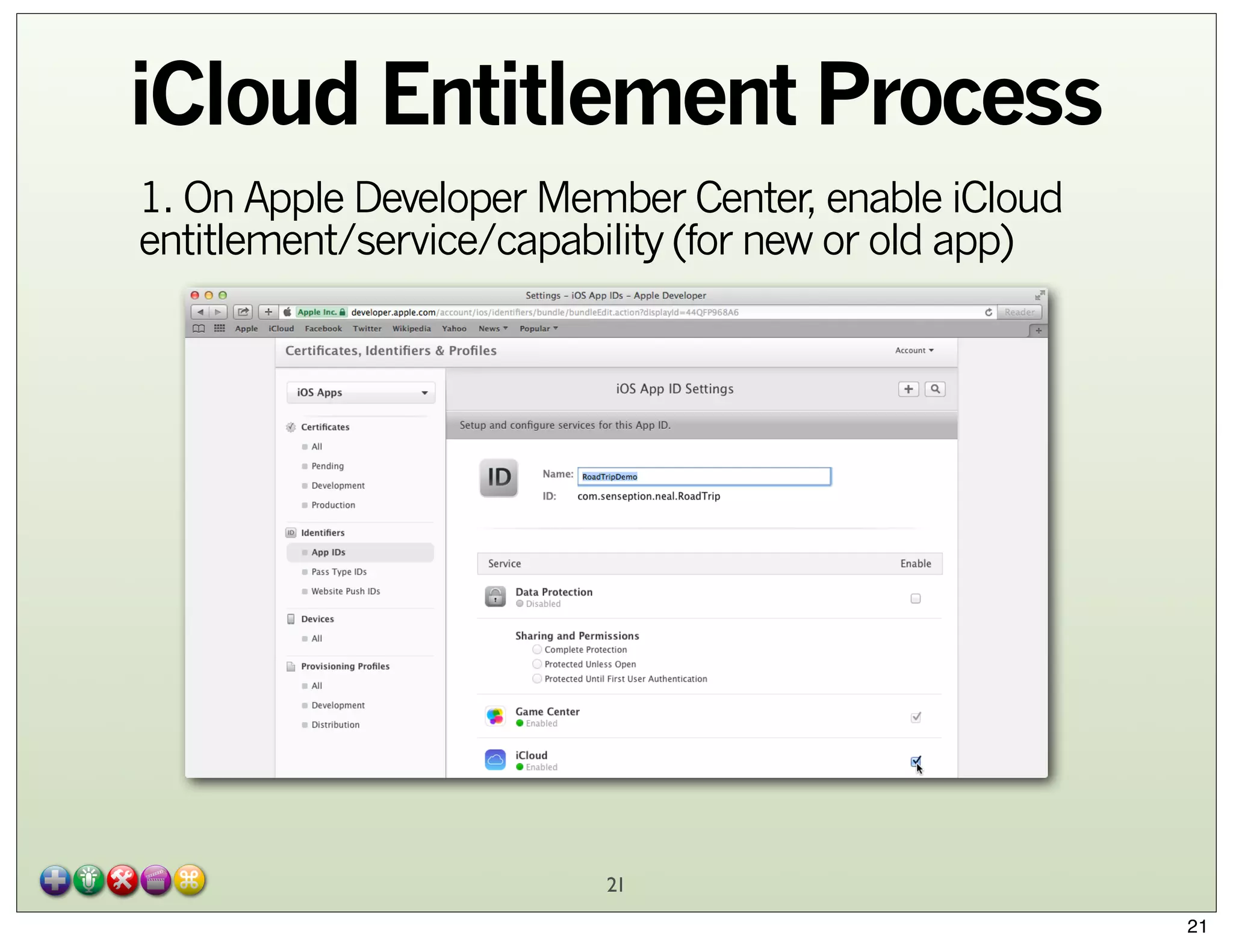
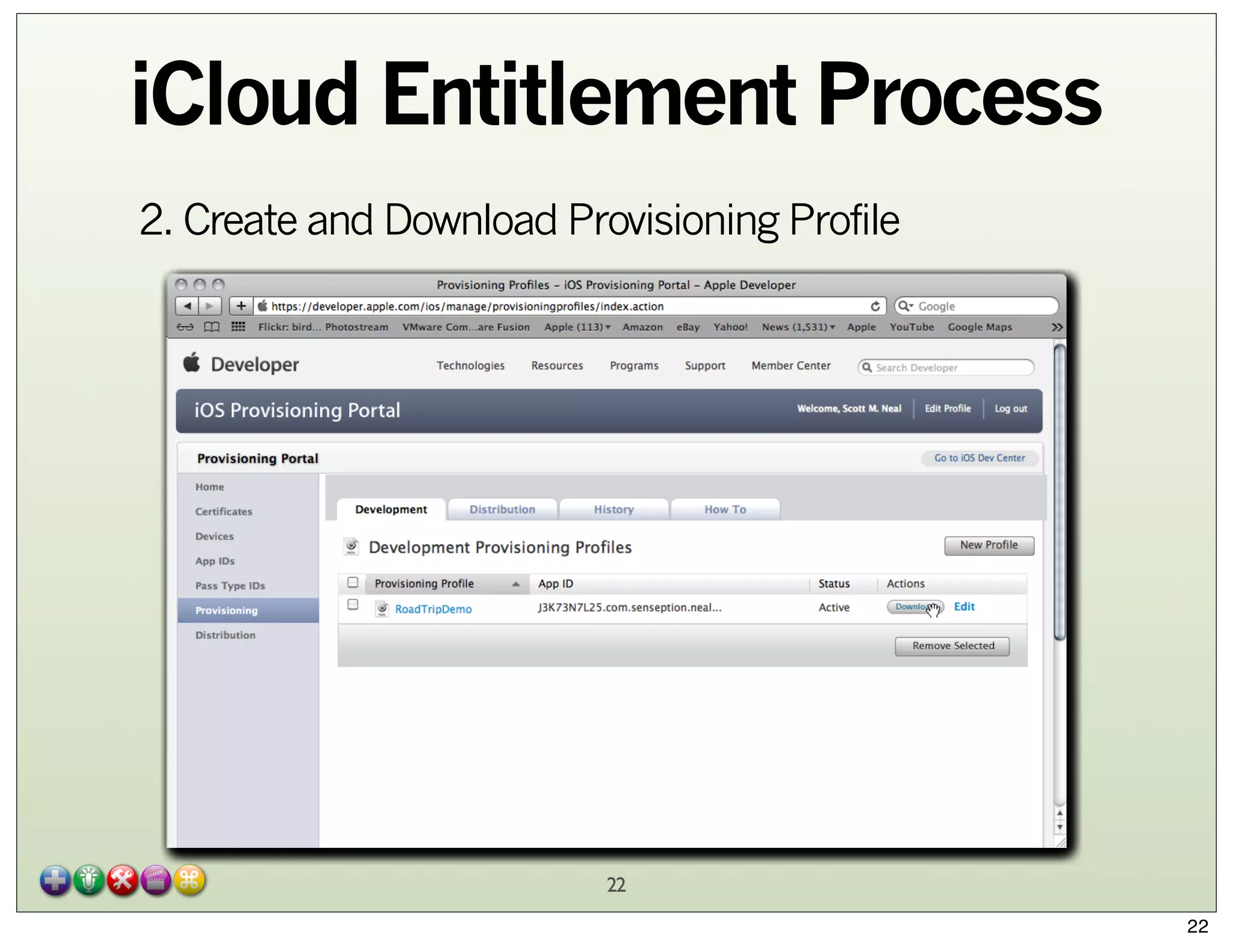
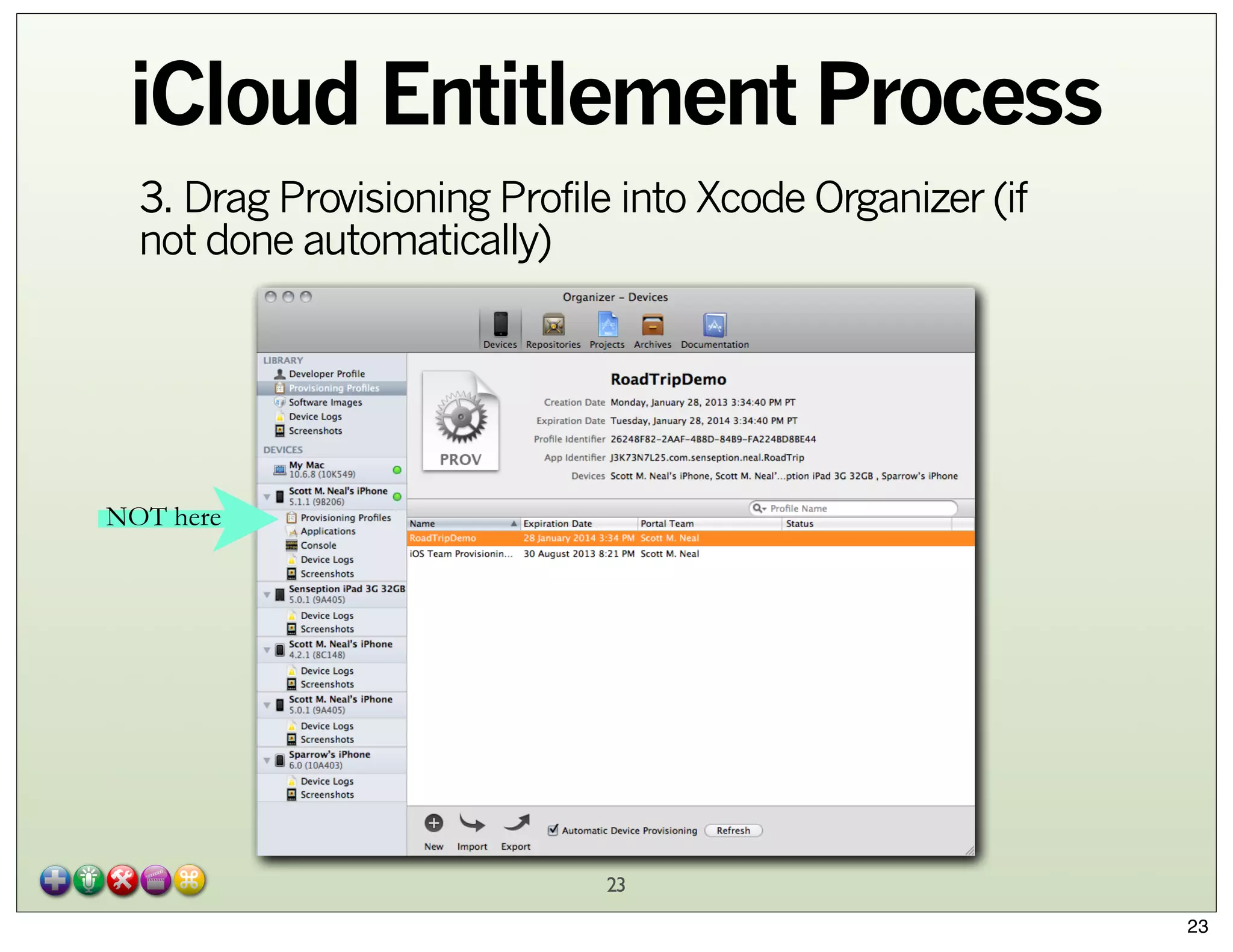
The document explores Core Data and its integration with iCloud, detailing concepts such as managed object contexts, persistent stores, and fetch requests. It highlights the advantages of using Core Data, including its object-oriented storage model and managing relationships between data entities. Additionally, the document covers iCloud features such as container storage, key/value storage, and the entitlement process required for seamless data synchronization across devices.







![Predicate Basics
Most common way to create predicates:
predicateWithFormat:
• The predicate format string syntax is different from
regular expression syntax
• The regular expression syntax is defined by the ICU—see
http://www.icu-project.org/userguide/regexp.html
can use regex with MATCHES
• YouThe left hand expression equals the right hand expression
•
using a regex-style comparison according to ICU v3
diacritic
• String comparisons are by default case andthe key
sensitive. You can modify an operator using
characters c and d within square braces to specify case
and diacritic insensitivity respectively, for example
firstName BEGINSWITH[cd] $FIRST_NAME.
12
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cocoaheads201401coredatamobilecloud-140127214704-phpapp02/75/CocoaHeads-PDX-2014-01-23-CoreData-and-iCloud-Improvements-iOS7-OSX-Mavericks-12-2048.jpg)
![Review:
Fetching with Core Data
NSManagedObjectContext *moc = [self managedObjectContext];
NSEntityDescription *entityDescription = [NSEntityDescription
entityForName:@"Employee" inManagedObjectContext:moc];
NSFetchRequest *request = [[[NSFetchRequest alloc] init] autorelease];
[request setEntity:entityDescription];
// Set example predicate and sort orderings...
NSNumber *minimumSalary = ...;
NSPredicate *predicate = [NSPredicate predicateWithFormat: @"(lastName
LIKE[c] 'Lindsay') AND (salary > %@)", minimumSalary];
[request setPredicate:predicate];
NSSortDescriptor *sortDescriptor = [[NSSortDescriptor alloc]
initWithKey:@"firstName" ascending:YES];
[request setSortDescriptors:[NSArray arrayWithObject:sortDescriptor]];
[sortDescriptor release];
NSError* error = nil;
NSArray* array = [moc executeFetchRequest:request error:&error];
if (nil == array) || (nil != error)
{
// Deal with error...
}
...
14
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cocoaheads201401coredatamobilecloud-140127214704-phpapp02/75/CocoaHeads-PDX-2014-01-23-CoreData-and-iCloud-Improvements-iOS7-OSX-Mavericks-14-2048.jpg)
![Review:
Insert/Save in Core Data
NSManagedObjectContext *moc = [self managedObjectContext];
NSManagedObject *aUser = [NSEntityDescription
insertNewObjectForEntityForName:@"User"
inManagedObjectContext:moc];
[aUser setValue:@"Scott" forKey:@"name"];
[aUser setValue:@"Portland" forKey:@"city"];
[aUser setValue:@"Oregon" forKey:@"state"];
NSError *error;
if (![moc save:&error])
{
NSLog(@"Whoops, couldn't save: %@", [error localizedDescription]);
}
15
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cocoaheads201401coredatamobilecloud-140127214704-phpapp02/75/CocoaHeads-PDX-2014-01-23-CoreData-and-iCloud-Improvements-iOS7-OSX-Mavericks-15-2048.jpg)





![iCloud Key/Value Storage
// Get an app’s default store
NSUbiquitousKeyValueStore* kvStore = [NSUbiquitousKeyValueStore
defaultStore];
// Register notification to see if data on the cloud has changed
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserver:self
selector: @selector(ubiquitousKeyValueStoreDidChange:)
name: NSUbiquitousKeyValueStoreDidChangeExternallyNotification
object: kvStore];
// Values not stored to/from iCloud until you synchronize
[kvStore synchronize];
// Store a value in the kv store
[keyStore setString:@”Saved String” forKey:@"MyString"];
// Values not stored to/from iCloud until you synchronize
[kvStore synchronize];
26
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cocoaheads201401coredatamobilecloud-140127214704-phpapp02/75/CocoaHeads-PDX-2014-01-23-CoreData-and-iCloud-Improvements-iOS7-OSX-Mavericks-26-2048.jpg)
![iCloud Key/Value Storage
Reason that notification was fired is returned in notification
• Initial download from iCloud
• Other device modified data (“push”)
• Over iCloud quota
// Get an app’s default store
- (void)ubiquitousKeyValueStoreDidChange:(NSNotification* theNotif)
{
" NSDictionary* userInfo = [notification userInfo];
// get reason for change
" int reason = [[userInfo
objectForKey:NSUbiquitousKeyValueStoreChangeReasonKey] intValue];
// get the changed keys--ONLY the changed keys
" NSArray* changedKeys = [userInfo
objectForKey:NSUbiquitousKeyValueStoreChangedKeysKey];
// store the changed values locally
...
}
27
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cocoaheads201401coredatamobilecloud-140127214704-phpapp02/75/CocoaHeads-PDX-2014-01-23-CoreData-and-iCloud-Improvements-iOS7-OSX-Mavericks-27-2048.jpg)

![iCloud Container Storage
Container URL
• The network path to desired document
• Avoid getting on the main thread
To Check for iCloud availability:
• iOS 6 / Mtn Lion (or later):
id token = [[NSFileManager defaultManager]
ubiquityIdentityToken];
if(token) ...
• iOS 5 / Lion (or later):
NSURL *ubiq = [[NSFileManager defaultManager]
"
URLForUbiquityContainerIdentifier:nil];
if (!ubiq) ...
30
30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cocoaheads201401coredatamobilecloud-140127214704-phpapp02/75/CocoaHeads-PDX-2014-01-23-CoreData-and-iCloud-Improvements-iOS7-OSX-Mavericks-30-2048.jpg)
![iCloud Container Storage
Asynchronous method
// Register notification to see if iCloud available
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserver:self
selector:@(handleUbiquityIdentityChanged:)
name:NSUbiquityIdentityDidChangeNotification object:nil];
// Get container URL on not-the-main thread
dispatch_async(
dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_PRIORITY_QUEUE_DEFAULT, 0),
^{
NSURL *containerURL = [[NSFileManager defaultManager]
"
URLForUbiquityContainerIdentifier:nil];
}
);
31
31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cocoaheads201401coredatamobilecloud-140127214704-phpapp02/75/CocoaHeads-PDX-2014-01-23-CoreData-and-iCloud-Improvements-iOS7-OSX-Mavericks-31-2048.jpg)
![iCloud Document w/o
Core Data
UIDocument / NSDocument
1. Determine whether iCloud is enabled on device by
sending
• [NSFileManager URLForUbiquityContainerIdentifier:]
Will return something like
•
•
N42E42A42L.com.neal.RoadTrip
32
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cocoaheads201401coredatamobilecloud-140127214704-phpapp02/75/CocoaHeads-PDX-2014-01-23-CoreData-and-iCloud-Improvements-iOS7-OSX-Mavericks-32-2048.jpg)
![iCloud Document w/o
Core Data
2. Add file presenters
• Adopt NSFilePresenter protocol
changes through
• Make allfile for editing NSFileCoordinator object
locks
•
background
• preventstime your code iCloud processes from modifying file
at same
is
• UIDocument already conforms to NSFilePresenter
3. Explicitly move your files to iCloud
• Use value returned in step 1 with
• [NSFileManager
setUbiquitous:itemAtURL:destinationURL:error]
33
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cocoaheads201401coredatamobilecloud-140127214704-phpapp02/75/CocoaHeads-PDX-2014-01-23-CoreData-and-iCloud-Improvements-iOS7-OSX-Mavericks-33-2048.jpg)




![iCloud with Core Data
//add the store, use the "LocalConfiguration" to make sure
state entities all end up in this store and that no iCloud
entities end up in it
_localStore = [_psc
addPersistentStoreWithType:NSSQLiteStoreType
configuration:@"LocalConfig"
URL:storeURL
options:nil
error:&localError];
39
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cocoaheads201401coredatamobilecloud-140127214704-phpapp02/75/CocoaHeads-PDX-2014-01-23-CoreData-and-iCloud-Improvements-iOS7-OSX-Mavericks-39-2048.jpg)
![iCloud with Core Data
- (BOOL)loadiCloudStore:(NSError * __autoreleasing *)error
{
BOOL success = YES;
NSError *localError = nil;
NSFileManager *fm = [[NSFileManager alloc] init];
_ubiquityURL = [fm URLForUbiquityContainerIdentifier:nil];
NSURL *iCloudStoreURL = [self iCloudStoreURL];
NSURL *iCloudDataURL = [self.ubiquityURL
URLByAppendingPathComponent:@"iCloudData"];
NSDictionary *options = @{
NSPersistentStoreUbiquitousContentNameKey : @"iCloudStore",
NSPersistentStoreUbiquitousContentURLKey : iCloudDataURL };
_iCloudStore = [self.psc
addPersistentStoreWithType:NSSQLiteStoreType
configuration:@"CloudConfig"
URL:iCloudStoreURL
options:options
error:&localError];
...
40
40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cocoaheads201401coredatamobilecloud-140127214704-phpapp02/75/CocoaHeads-PDX-2014-01-23-CoreData-and-iCloud-Improvements-iOS7-OSX-Mavericks-40-2048.jpg)

![iCloud with Core Data
NSFileManager* fileManager = [NSFileManager defaultManager];
NSURL* persistentStoreUbiquitousContentURL = [fileManager
URLForUbiquityContainerIdentifier:nil];
NSString* ubiquityContainerIdentifierPath =
[[persistentStoreUbiquitousContentURL path]
stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"RoadTripSharedPointOfInterest"
];
persistentStoreUbiquitousContentURL = [NSURL
fileURLWithPath:ubiquityContainerIdentifierPath];
options = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithObjectsAndKeys:[NSString
stringWithFormat:@"%@%@", @"com.neal.coredata.itineraryR02.",
appDelegate.destinationPreference],
NSPersistentStoreUbiquitousContentNameKey,
persistentStoreUbiquitousContentURL,
NSPersistentStoreUbiquitousContentURLKey, [NSNumber
numberWithBool:YES],
NSMigratePersistentStoresAutomaticallyOption, [NSNumber
numberWithBool:YES], NSInferMappingModelAutomaticallyOption,
nil];
...
42
42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cocoaheads201401coredatamobilecloud-140127214704-phpapp02/75/CocoaHeads-PDX-2014-01-23-CoreData-and-iCloud-Improvements-iOS7-OSX-Mavericks-42-2048.jpg)


![iOS7/OSX9 Changes
Asynchronous Setup
• New notifications
these:
•
NSPersistentStoreCoordinatorStoresWillChangeNotification
NSPersistentStoreCoordinatorStoresDidChangeNotification
• encourage you to:
-[NSManagedObjectContext save:]
-[NSManagedObjectContext reset:]
• this:
• encourages you to:
NSPersistentStoreDidImportUbiquitousContentChangesNotification
-[NSManagedObjectContext mergeChangesFromContextDidSaveNotification:]
45
45](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cocoaheads201401coredatamobilecloud-140127214704-phpapp02/75/CocoaHeads-PDX-2014-01-23-CoreData-and-iCloud-Improvements-iOS7-OSX-Mavericks-45-2048.jpg)
![iOS7/OSX9 Changes
Handling Account Changes
notifications:
• Oldthis:
•
• would require you to (and handle all cases of):
NSUbiquityIdentityTokenDidChangeNotification
-[NSManagedObjectContext reset:]
-[NSPersistentStoreCoordinator removePersistentStore:]
-[NSPersistentStoreCoordinator addPersistentStore:]
• New (iOS7/OSX9):
this: (look familiar?)
•
• encourages you to:
NSPersistentStoreCoordinatorStoresWillChangeNotification
-[NSManagedObjectContext save:]
-[NSManagedObjectContext reset:]
• which then: (look familiar?)
• encourages you to:
NSPersistentStoreCoordinatorStoresDidChangeNotification
-[NSManagedObjectContext save:]
46
46](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cocoaheads201401coredatamobilecloud-140127214704-phpapp02/75/CocoaHeads-PDX-2014-01-23-CoreData-and-iCloud-Improvements-iOS7-OSX-Mavericks-46-2048.jpg)