Spark and Mesos cluster optimization was discussed. The key points were:
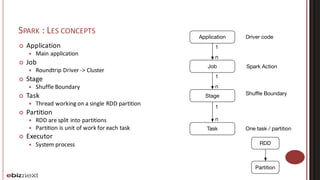
1. Spark concepts like stages, tasks, and partitions were explained to understand application behavior and optimization opportunities around shuffling.
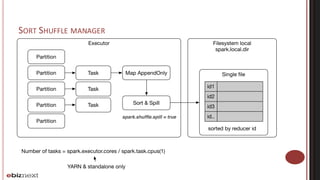
2. Application optimization focused on reducing shuffling through techniques like partitioning, reducing object sizes, and optimizing closures.
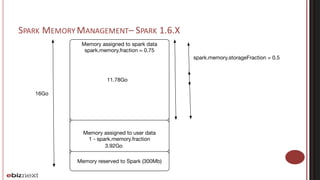
3. Memory tuning in Spark involved configuring storage and shuffling fractions to control memory usage between user data and Spark's internal data.
4. When running Spark on Mesos, coarse-grained and fine-grained allocation modes were described along with solutions like using Mesos roles to control resource allocation and dynamic allocation in coarse-grained mode.

![Grappe
Clic
Nav
AT
DataLake
Avis
Evts.
Supports
Comptes
Spark Job
DataMart
Contribution
Visiteur
Session
Recherche
Bandeau
[LR]
[FD]
[Clic]
Project Context](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sparkmesosclusteroptimization-160429211934/85/Spark-Mesos-Cluster-Optimization-2-320.jpg)













![SHUFFLING OPTIMIZATION 1/2
(k1, v1, w1)
(k2, v2, w2)
(k3, v3, w3)
(k1, v4 w4)
(k1, v5, w5)
(k3,v6,w6)
(k2, v7, w7)
(k2 v8, w8)
(k3,v9,w9)
(k1, v1)
(k2, v2)
(k3,v3)
(k1, v4)
(k1, v5)
(k3,v6)
(k2, v7)
(k2 v8)
(k3,v9)
map map map
(k1, [v1, v4, v5]) (k3, [v3, v6, v9]) (k2, [v2, v7, v8])
groupByKey groupByKey groupByKey
(k1,v1+v4+v5) (k3,v3+v6+v9) (k2, v2+v7+v8])
Shuffling
Bonus : OOM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sparkmesosclusteroptimization-160429211934/85/Spark-Mesos-Cluster-Optimization-17-320.jpg)