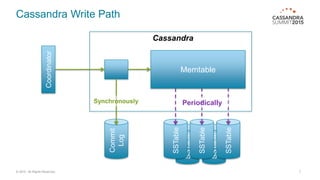
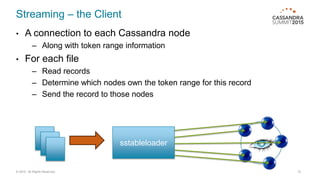
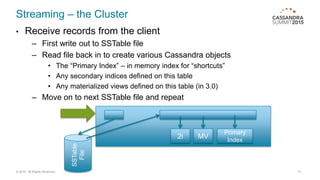
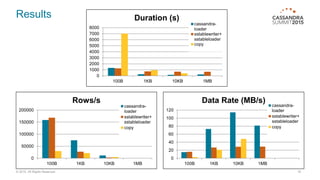
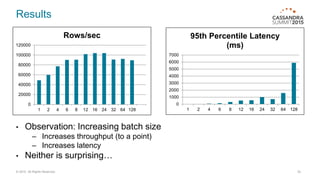
This document discusses bulk loading and unloading data into and from Cassandra. It describes using CQL INSERT statements via Java drivers or CQLSH COPY FROM for loading, as well as using SSTable files via sstableloader or custom code. For unloading, it recommends using parallel CQL SELECT queries by splitting the token range across multiple connections. Testing showed Java asynchronous INSERTs to be the fastest loading method in most cases, while sstableloader requires all nodes be online. Batching INSERTs can improve throughput but increases latency.