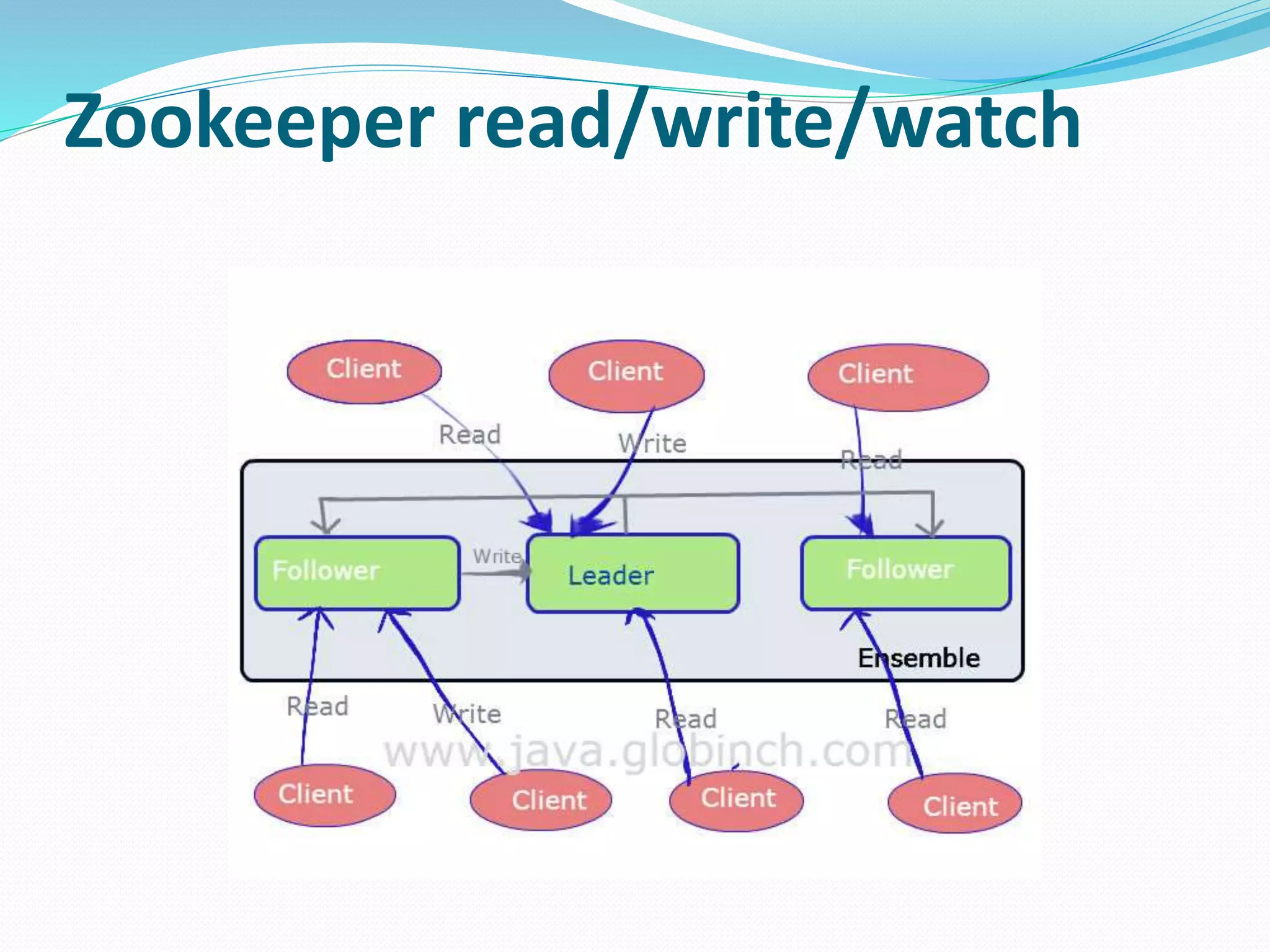
This document provides an overview of Apache Zookeeper, a distributed coordination service. It discusses Zookeeper's data model, use of ZAB protocol for consensus, and common use cases such as naming, configuration management, and leader election. It also provides a brief Java client API example.