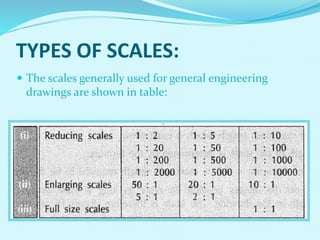
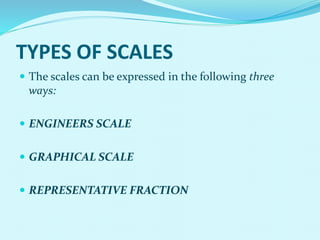
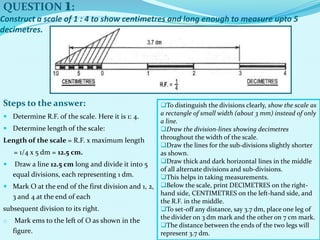
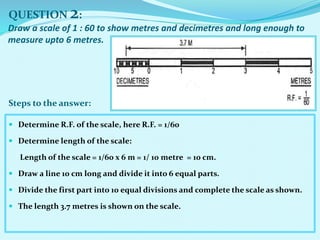
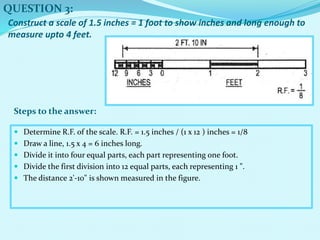
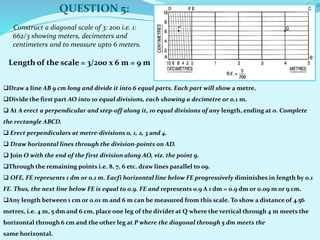
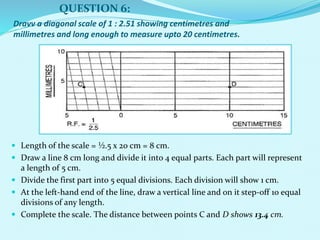
The document discusses scales used in engineering drawings. It defines scale as the ratio of dimensions on a drawing to the actual dimensions of an object. There are three types of scales: engineer's scale, graphical scale, and representative fraction. A representative fraction expresses the ratio of a length on a drawing to the actual length. Steps are provided for constructing various scales, including plain, vernier, diagonal, and comparative scales. Examples show how to construct specific scales measuring different units like meters, centimeters, miles and furlongs.