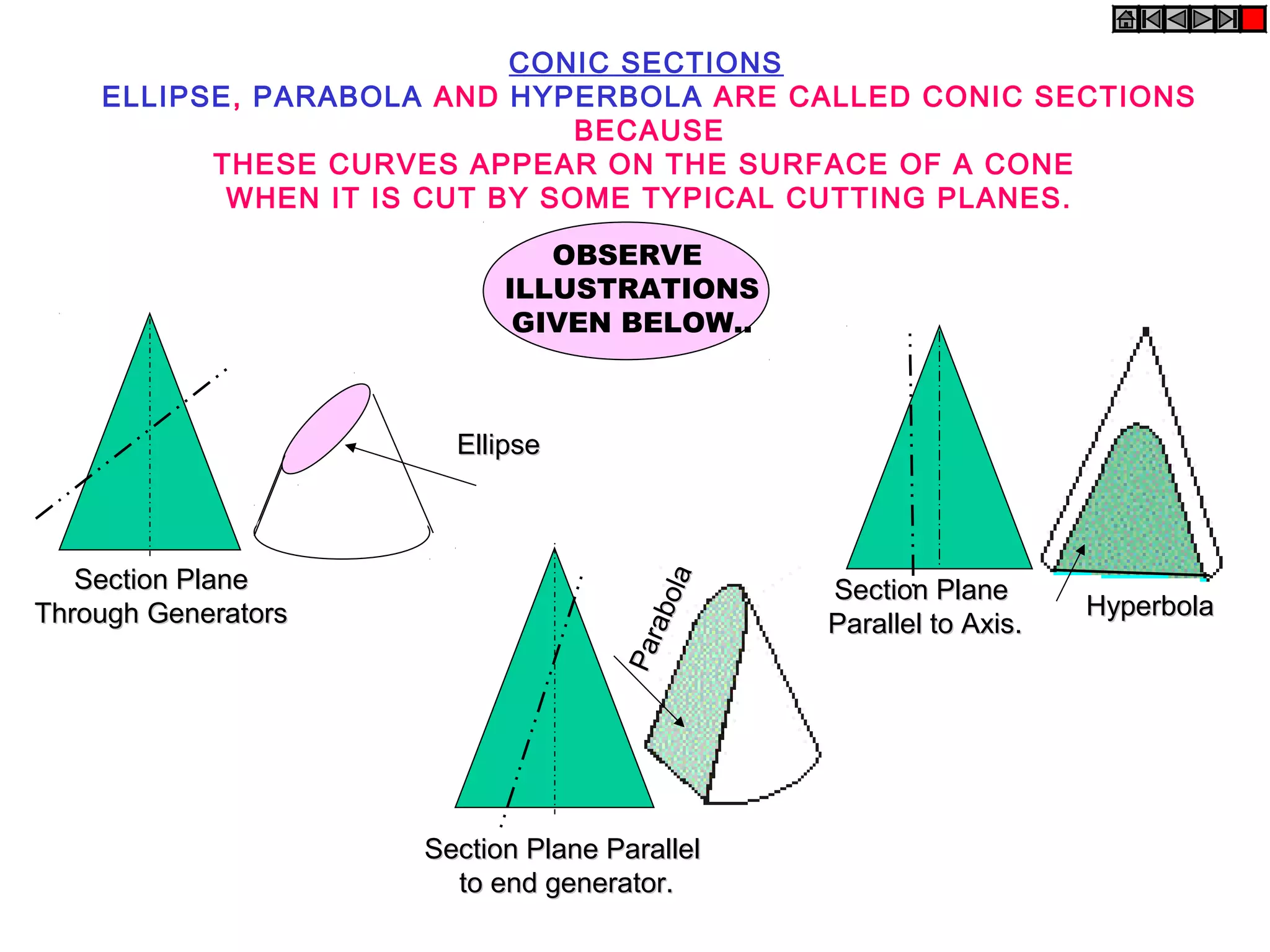
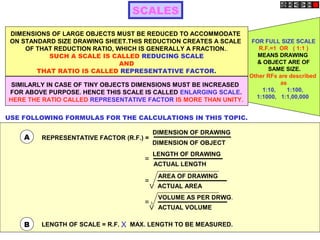
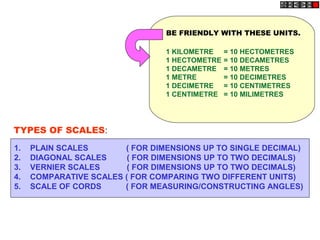
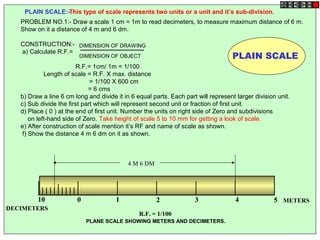
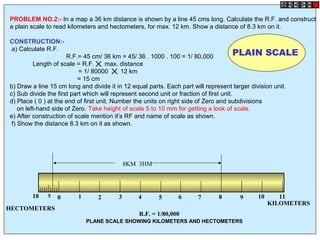
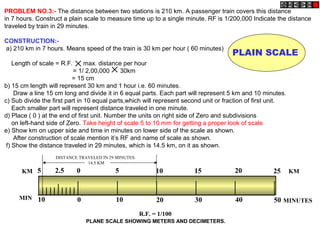
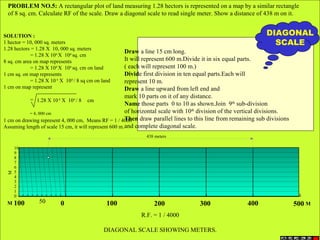
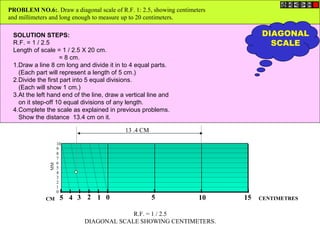
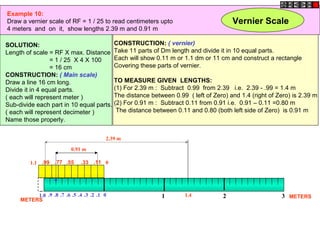
Conic sections such as ellipses, parabolas, and hyperbolas are formed by cutting a cone with planes.
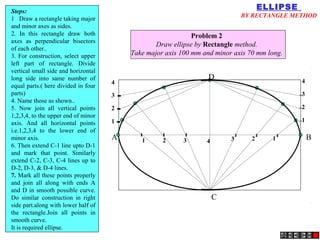
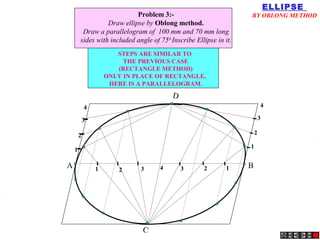
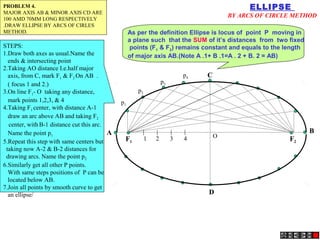
An ellipse is defined as the locus of points where the sum of distances to two fixed foci is a constant equal to the major axis length. A parabola occurs when the cutting plane is parallel to the axis and side of the cone. For a hyperbola, the cutting plane is neither parallel to the axis nor side of the cone.
The ratio of distances from a point on the conic section to the fixed point and fixed line is called the eccentricity. Eccentricity is less than 1 for ellipses, 1 for parabolas, and greater than 1 for