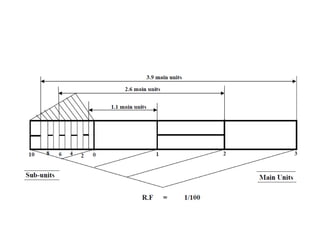
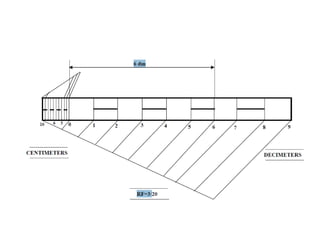
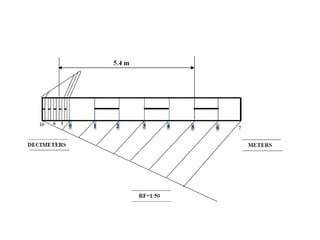
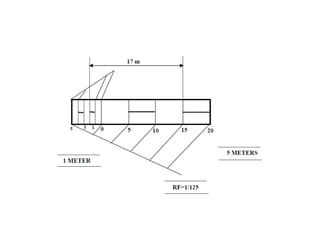
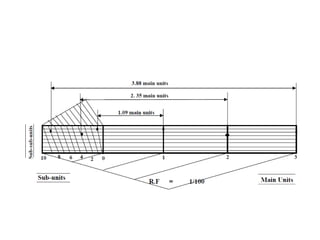
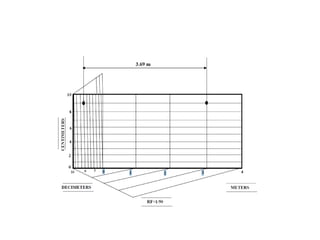
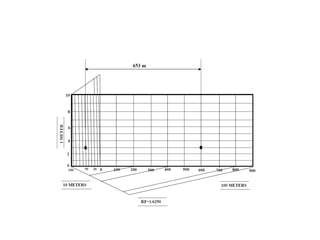
This document provides instructions for constructing different types of scales. It discusses representative fractions, maximum length, length of scale, dividing the scale into parts based on maximum length, and subdividing the first part. It provides examples of plain scales, which show two units, and diagonal scales, which show three units. Specific problems are presented for constructing plain and diagonal scales to measure given lengths.