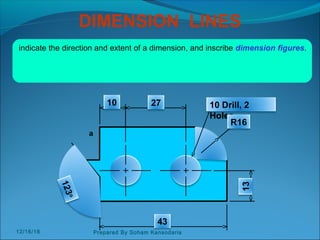
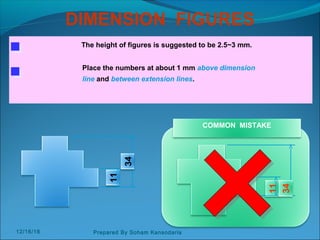
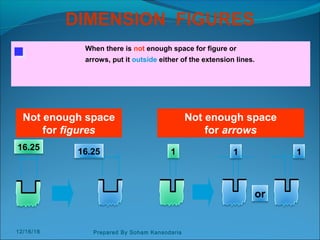
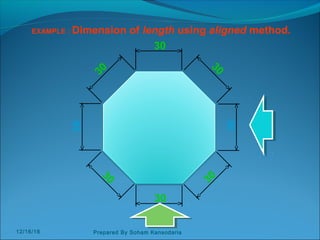
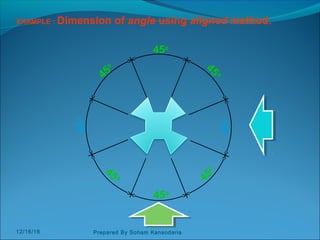
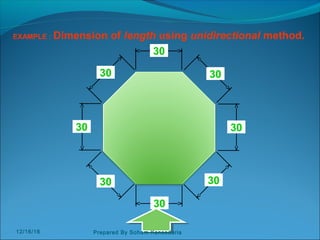
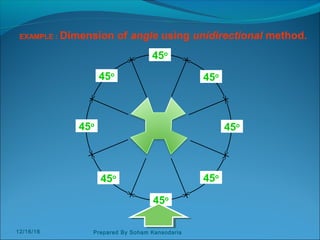
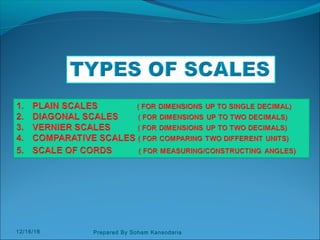
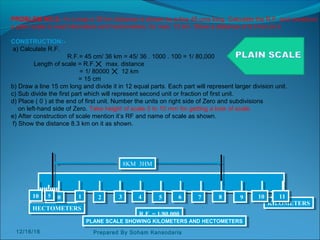
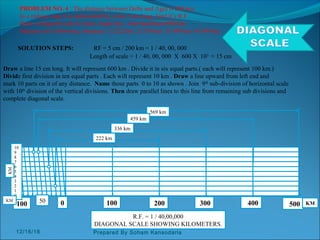
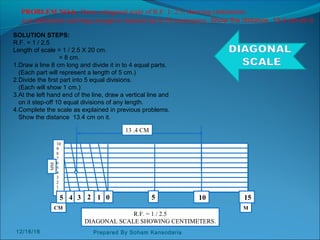
The document discusses various dimensioning and scaling techniques used in engineering graphics. It defines dimensioning as specifying a part's information using figures, symbols and notes. It describes dimension lines, figures and their placement. It also discusses different types of lines used and provides examples of dimensioning lengths and angles using both aligned and unidirectional methods. Furthermore, it explains reducing and enlarging scales using representative factors and provides examples of constructing plain, diagonal and plain scales showing various units of measurement.