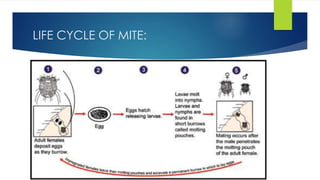
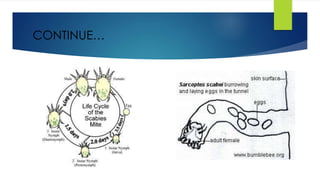
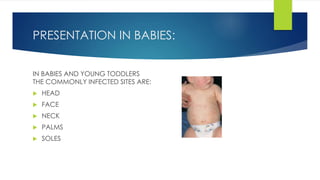
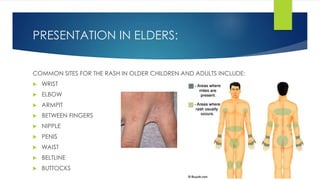
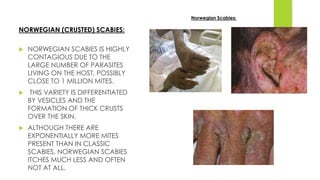
Scabies is caused by the human itch mite Sarcoptes scabiei, which burrows under the skin and lays eggs. It is highly contagious through direct skin-to-skin contact or contact with infested clothing or bedding. Symptoms include intense itching that is usually worst at night. Diagnosis is made by identifying the mites, eggs, or burrows under microscopic examination of skin scrapings. Treatment involves topical scabicides like permethrin or oral medication like ivermectin. Complications can include secondary skin infections if scratching occurs.